CHEM 242 Organic Chemistry II-Bender
... primary grades in lieu of exams. As such, due dates are not negotiable and 10% will be deducted for each class period the assignment is late. ...
... primary grades in lieu of exams. As such, due dates are not negotiable and 10% will be deducted for each class period the assignment is late. ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... 17. State the number of electrons in each shell in this atom in the ground state. Number of electrons in first shell: Number of electrons in second shell: ...
... 17. State the number of electrons in each shell in this atom in the ground state. Number of electrons in first shell: Number of electrons in second shell: ...
Molecules of Life ppt
... – Exceptions: graphite, diamonds, CO2 – Carbon exhibits bonding power of 4 ...
... – Exceptions: graphite, diamonds, CO2 – Carbon exhibits bonding power of 4 ...
Unit 3 Goals - kimscience.com
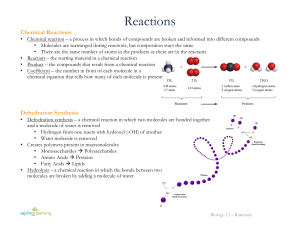
... o explain how a catalyst speeds up a reaction in regards to activation energy. o draw the products of a dehydration synthesis reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, or between an amine and a carboxylic acid, and to explain how this type of reaction can be involved in creation of polymers ...
... o explain how a catalyst speeds up a reaction in regards to activation energy. o draw the products of a dehydration synthesis reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, or between an amine and a carboxylic acid, and to explain how this type of reaction can be involved in creation of polymers ...
Name
... 3. What type of reaction is required to break a polymer and what kind of reaction is required to make a polymer? (2) a. Reaction that breaks polymers ___hydrolysis________________________ b. Reaction that makes polymers ___________dehydration__________ ...
... 3. What type of reaction is required to break a polymer and what kind of reaction is required to make a polymer? (2) a. Reaction that breaks polymers ___hydrolysis________________________ b. Reaction that makes polymers ___________dehydration__________ ...
Nano-transistors Sensitive to Vibrations in a Single Molecule
... A single molecule containing a cobalt atom in a well-defined and deliberately designed bonding configuration is then incorporated into the gap. The electrical characteristics of the transistor can be varied systematically by making chemical changes to the molecule. This work represents two significa ...
... A single molecule containing a cobalt atom in a well-defined and deliberately designed bonding configuration is then incorporated into the gap. The electrical characteristics of the transistor can be varied systematically by making chemical changes to the molecule. This work represents two significa ...
ch02-chemistry
... Questions 2-4 (Matching)-- Match the following terms to their respective statement below. A. Ionic bond B. Covalent bond C. Hydrogen bond 2. _______ Two hydrogen atoms share valence electrons to form a hydrogen molecule 3. _______ A weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom in one mo ...
... Questions 2-4 (Matching)-- Match the following terms to their respective statement below. A. Ionic bond B. Covalent bond C. Hydrogen bond 2. _______ Two hydrogen atoms share valence electrons to form a hydrogen molecule 3. _______ A weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom in one mo ...
Elise Miner Education:
... Sanjeev Mukerjee Physical Chemistry Laboratory Boston, MA Inorganic synthesis September 2012-Present Explored literature-cited and original synthetic pathway possibilities for metal organic frameworks and transition metal catalysts Analyzed and confirmed synthesis of purified intermediates, and ...
... Sanjeev Mukerjee Physical Chemistry Laboratory Boston, MA Inorganic synthesis September 2012-Present Explored literature-cited and original synthetic pathway possibilities for metal organic frameworks and transition metal catalysts Analyzed and confirmed synthesis of purified intermediates, and ...
Chemical Changes in Matter Worksheet
... For each of the following reactions, replace words with formulas and symbols. Be sure to include coefficients and physical states. 1. Two atoms of solid lithium react with two molecules of liquid water to produce two units of aqueous lithium hydroxide and one molecule of hydrogen gas. ...
... For each of the following reactions, replace words with formulas and symbols. Be sure to include coefficients and physical states. 1. Two atoms of solid lithium react with two molecules of liquid water to produce two units of aqueous lithium hydroxide and one molecule of hydrogen gas. ...
10.4b Organic Practice Test Version 2
... a) Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to fewer atoms than the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. b) A hydrogen atom or functional group is replaced with a different atom or functional group. c) Atoms are added to a double or triple carbon–carbon bond. d) Two molecules are combined and ...
... a) Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to fewer atoms than the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. b) A hydrogen atom or functional group is replaced with a different atom or functional group. c) Atoms are added to a double or triple carbon–carbon bond. d) Two molecules are combined and ...
3 · Organic Chemistry 3 · Organic Chemistry C3H8
... B. same parts, two molecules with the same molecular formula but different H 3. polymer structural formulas. E 4. structural formula C. longest string of carbon atoms in a molecule. D 5. bonding capacity D. number of holes in an atom (e.g. O-2, H-1, C-4, etc.) G 6. saturated E. picture of a molecule ...
... B. same parts, two molecules with the same molecular formula but different H 3. polymer structural formulas. E 4. structural formula C. longest string of carbon atoms in a molecule. D 5. bonding capacity D. number of holes in an atom (e.g. O-2, H-1, C-4, etc.) G 6. saturated E. picture of a molecule ...
cell
... Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances – smallest unit of an element is an atom Compound – two or more elements that are chemically combined – smallest unit is called a molecule Water – most chemical reactions in cells would not take place without water Inorganic co ...
... Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances – smallest unit of an element is an atom Compound – two or more elements that are chemically combined – smallest unit is called a molecule Water – most chemical reactions in cells would not take place without water Inorganic co ...
Organic compounds
... • Carbon compounds – Organic compounds- primarily made of carbon • Carbon can from four covalent bonds • As a result, carbon can bon in a number of ways ...
... • Carbon compounds – Organic compounds- primarily made of carbon • Carbon can from four covalent bonds • As a result, carbon can bon in a number of ways ...
Organic Chemistry
... 6. interpret chemical reactions via thermodynamic data 7. use molecular geometries to determine intermolecular forces 8. interpret redox reactions 9. determine if reaction mechanisms fit experimental rate laws 10. use acid-base theory to predict reaction products and extent of reaction Expected Outc ...
... 6. interpret chemical reactions via thermodynamic data 7. use molecular geometries to determine intermolecular forces 8. interpret redox reactions 9. determine if reaction mechanisms fit experimental rate laws 10. use acid-base theory to predict reaction products and extent of reaction Expected Outc ...
Annexure `CD-01` L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 1 4 0 6
... Amino Acids: Classification, structure and stereochemistry of amino acids, Acid-base behavior, isoelectric point and electrophoresis, Preparation and reactions of α- amino acids. Peptides: determination of their primary structures-end group analysis, methods of peptide synthesis. Synthesis of peptid ...
... Amino Acids: Classification, structure and stereochemistry of amino acids, Acid-base behavior, isoelectric point and electrophoresis, Preparation and reactions of α- amino acids. Peptides: determination of their primary structures-end group analysis, methods of peptide synthesis. Synthesis of peptid ...
Collision Theory
... Theories of Chemical Kinetics: Collision Theory • Before atoms/molecules/ions can react, they must first collide • An effective collision between two species puts enough energy to break key bonds • The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy that must be supplied by collisions to trigger a rea ...
... Theories of Chemical Kinetics: Collision Theory • Before atoms/molecules/ions can react, they must first collide • An effective collision between two species puts enough energy to break key bonds • The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy that must be supplied by collisions to trigger a rea ...
hgs molecular model
... Course Philosophy: From a pragmatic point of view, it is important that you attend lectures since all exams in this course will be based on the material covered in lecture. The textbook should be used as a supplement to the lectures. There are many topics covered in lectures that are not in the text ...
... Course Philosophy: From a pragmatic point of view, it is important that you attend lectures since all exams in this course will be based on the material covered in lecture. The textbook should be used as a supplement to the lectures. There are many topics covered in lectures that are not in the text ...