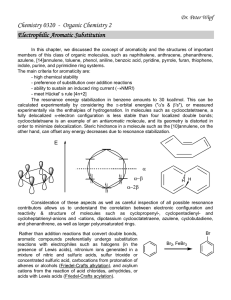
Title
... Brief introduction to sulphonic acid derivatives, reactions and mechanisms (including curly arrows and where appropriate energy diagrams, kinetic aspects) for alkyl halides (SN1, SN2, E1, E2, Grignard), alcohols, amines; formation and hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives and acetals, NMR, react ...
... Brief introduction to sulphonic acid derivatives, reactions and mechanisms (including curly arrows and where appropriate energy diagrams, kinetic aspects) for alkyl halides (SN1, SN2, E1, E2, Grignard), alcohols, amines; formation and hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives and acetals, NMR, react ...
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes 4. Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals 5. Periodic relationships, including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation s ...
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes 4. Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals 5. Periodic relationships, including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation s ...
Organic chemistry - Mr. Amundson`s DCC science
... Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols Primary alcohols become aldehydes and carboxylic acid under oxidation Secondary alcohols become ketones under oxidation. Tertiary alcohols don’t oxidize. ...
... Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols Primary alcohols become aldehydes and carboxylic acid under oxidation Secondary alcohols become ketones under oxidation. Tertiary alcohols don’t oxidize. ...
CM1121 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1
... CM1121 - Organic Chemistry 1 This module is intended for students majoring in Chemistry and Applied Chemistry. It deals primarily with the basic principles to understand the structure and reactivity of organic molecules. Emphasis is on substitution and elimination reactions and chemistry of various ...
... CM1121 - Organic Chemistry 1 This module is intended for students majoring in Chemistry and Applied Chemistry. It deals primarily with the basic principles to understand the structure and reactivity of organic molecules. Emphasis is on substitution and elimination reactions and chemistry of various ...
Organic Chemistry I
... Identify compounds based on 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, IR and mass spectroscopy data Major Topics to be covered 1. The atomic and hybrid orbitals of the carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms and the molecular shapes arising from hybridization. 2. Lewis structures, resonance structures, line structure, formal c ...
... Identify compounds based on 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, IR and mass spectroscopy data Major Topics to be covered 1. The atomic and hybrid orbitals of the carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms and the molecular shapes arising from hybridization. 2. Lewis structures, resonance structures, line structure, formal c ...
Document
... 4. Olestra F. Proteins 5.4 1. Uses 2. Amino Acid structure 3. Different R groups 4. Peptide bond 5. Protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary) 6. Simple vs. compound proteins 7. primary structure determines 3D shape of protein. How? G. Chemical Reactions ...
... 4. Olestra F. Proteins 5.4 1. Uses 2. Amino Acid structure 3. Different R groups 4. Peptide bond 5. Protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary) 6. Simple vs. compound proteins 7. primary structure determines 3D shape of protein. How? G. Chemical Reactions ...
Organic Chemistry Review
... 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about carbs. a. starches and sugars are examples of carbs b. living things use them as their main source of energy c. the monomers of carbs are starch molecules d. plants and some animals use some carbs for strength and rigidity 2. Single sugar mole ...
... 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about carbs. a. starches and sugars are examples of carbs b. living things use them as their main source of energy c. the monomers of carbs are starch molecules d. plants and some animals use some carbs for strength and rigidity 2. Single sugar mole ...
Organic Chemistry
... Have a mixture of 2 or more organics Heat column to change liquids to gases (boil). Collect gases in a tube & cool down to change gas to liquid (condense) ...
... Have a mixture of 2 or more organics Heat column to change liquids to gases (boil). Collect gases in a tube & cool down to change gas to liquid (condense) ...
Chapter 4 Reading Guide File
... Teacher’s Note: Chapter 4 is a quick introduction to organic chemistry. First our authors explain why carbon is ideally suited to make many diverse molecules. The chapter then discusses isomers and ends with functional groups. Students sometimes have trouble with functional groups because they get l ...
... Teacher’s Note: Chapter 4 is a quick introduction to organic chemistry. First our authors explain why carbon is ideally suited to make many diverse molecules. The chapter then discusses isomers and ends with functional groups. Students sometimes have trouble with functional groups because they get l ...
AP Chemistry
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes 4. Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals 5. Periodic relationships including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation st ...
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes 4. Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals 5. Periodic relationships including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation st ...
How to study organic chemistry?
... Bronsted & Lewis theory. Effect of back-bonding , aromaticity, SIR,etc. ...
... Bronsted & Lewis theory. Effect of back-bonding , aromaticity, SIR,etc. ...
AP CHEMISTRY Chang -Chemistry 9
... Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means Atomic number and mass number; isotopes Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals Periodic relationships, including atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidations states ...
... Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means Atomic number and mass number; isotopes Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals Periodic relationships, including atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidations states ...
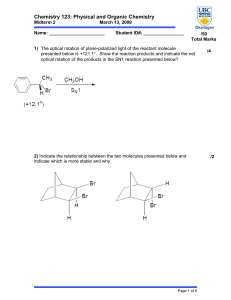
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
... to -10°C. Describe each step of the process and calculate the amount of energy that would need to flow in or out of the system. At each step indicate if the entropy is increasing or decreasing and under what conditions the reaction would be spontaneous. ...
... to -10°C. Describe each step of the process and calculate the amount of energy that would need to flow in or out of the system. At each step indicate if the entropy is increasing or decreasing and under what conditions the reaction would be spontaneous. ...
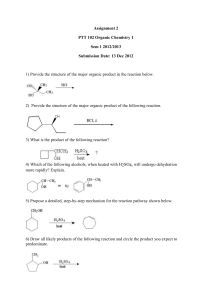
Assignment 2 Group A and B
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
Organic Reactions 1
... Condensation is an organic reaction when two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with the elimination of water or some other simple molecule. Catalysts commonly used in condensation reactions include acids and bases. The combination of two identical molecules is known as self-c ...
... Condensation is an organic reaction when two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with the elimination of water or some other simple molecule. Catalysts commonly used in condensation reactions include acids and bases. The combination of two identical molecules is known as self-c ...
Honors Chemistry Organic Chemistry
... b. carcinogen in burned meat and cigarettes c. organic bases d. hydrogenation e. hydroxyl f. carboxyl g. carbonyl h. containing benzene or benzene-like structures i. from wood distillation / metabolized into formaldehyde j. benzene as a substituent k. reaction in the formation of esters l. phenol ...
... b. carcinogen in burned meat and cigarettes c. organic bases d. hydrogenation e. hydroxyl f. carboxyl g. carbonyl h. containing benzene or benzene-like structures i. from wood distillation / metabolized into formaldehyde j. benzene as a substituent k. reaction in the formation of esters l. phenol ...
Chapter 4: Carbon and the molecular diversity of life
... a. Can vary in length from CH4 and CO2 to C in the thousand b. Can vary in shape form linear to branching to complex folds and twists c. Can form rings d. Can mix single and double bonds e. Isomerism is prevalent i. Compound with the same molecular formula but different shapes and thus different pro ...
... a. Can vary in length from CH4 and CO2 to C in the thousand b. Can vary in shape form linear to branching to complex folds and twists c. Can form rings d. Can mix single and double bonds e. Isomerism is prevalent i. Compound with the same molecular formula but different shapes and thus different pro ...