1) In the reaction H2O + CH3COOH H3O+ + CH3COO
... is spontaneous. Is the standard potential for this reaction greater than zero, less than zero, equal to zero or impossible to determine? ...
... is spontaneous. Is the standard potential for this reaction greater than zero, less than zero, equal to zero or impossible to determine? ...
Export To Word
... Body of Knowledge: Physical Science Standard: Matter A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, react ...
... Body of Knowledge: Physical Science Standard: Matter A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, react ...
elements of chemistry unit
... Of all the elements on the periodic table, carbon forms the strongest bonds, and bonds to the most kinds of atoms. Also, multiple carbon atoms link together with single, double, and triple bonds. The number of carbon-based compounds is many times greater than the sum of all other compounds. ORGANIC ...
... Of all the elements on the periodic table, carbon forms the strongest bonds, and bonds to the most kinds of atoms. Also, multiple carbon atoms link together with single, double, and triple bonds. The number of carbon-based compounds is many times greater than the sum of all other compounds. ORGANIC ...
are physical changes - Chemistry Information Site
... - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved changes * Total mass remains constant from (1) to (2), even though the mass of the GAS decreases and the mass of the SOLID ...
... - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved changes * Total mass remains constant from (1) to (2), even though the mass of the GAS decreases and the mass of the SOLID ...
Physical vs
... How can I determine if a change in matter is a physical or chemical change? If it is a chemical change, how do I determine if it’s an endothermic or exothermic reaction? Background: Physical change does not make any substance in the matter into a different substance. It only alters the form or app ...
... How can I determine if a change in matter is a physical or chemical change? If it is a chemical change, how do I determine if it’s an endothermic or exothermic reaction? Background: Physical change does not make any substance in the matter into a different substance. It only alters the form or app ...
Thermodynamic Properties of Hydrated and Ammoniated Electrons
... Publication coats borne completely by The Journal of Physical Chemistry ...
... Publication coats borne completely by The Journal of Physical Chemistry ...
Lipids Lesson Plan
... B2.3: construct and draw three-dimensional molecular models of important biochemical compounds (lipids) B3.2: describe the structure of important biochemical compounds (lipids) and explain their function within cells B3.3: identify common functional groups within biological molecules and explain how ...
... B2.3: construct and draw three-dimensional molecular models of important biochemical compounds (lipids) B3.2: describe the structure of important biochemical compounds (lipids) and explain their function within cells B3.3: identify common functional groups within biological molecules and explain how ...
- gst boces
... *<7 acidic (H+ > OH-), farther from neutral = more acidic *>7 basic (OH- . H+), farther from neutral = more basic *each move a 10x change in H+ concentration (1 is 10x stronger than 2, 1 is 100x stronger than 3) 145. All organic compounds contain C, carbon *and (usually) H, hydrogen 146. Carbon ALWA ...
... *<7 acidic (H+ > OH-), farther from neutral = more acidic *>7 basic (OH- . H+), farther from neutral = more basic *each move a 10x change in H+ concentration (1 is 10x stronger than 2, 1 is 100x stronger than 3) 145. All organic compounds contain C, carbon *and (usually) H, hydrogen 146. Carbon ALWA ...
Review for second exam:
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
Regents Chemistry Review Questions
... 23. Draw the Lewis dot structure for magnesium bromide. 24. In an experiment, a student determined the normal boiling points of four unknown liquids. The collected data were organized into the table below. A – 9 ºC B – 31 ºC C – 80 ºC D – 100 ºC Which liquid has the weakest attractive forces between ...
... 23. Draw the Lewis dot structure for magnesium bromide. 24. In an experiment, a student determined the normal boiling points of four unknown liquids. The collected data were organized into the table below. A – 9 ºC B – 31 ºC C – 80 ºC D – 100 ºC Which liquid has the weakest attractive forces between ...
Organic Chemistry Midterm Review Go over the Activities and
... 12. Used curved arrows to show the flow of electron in the reaction: HCO3− + OH− → ...
... 12. Used curved arrows to show the flow of electron in the reaction: HCO3− + OH− → ...
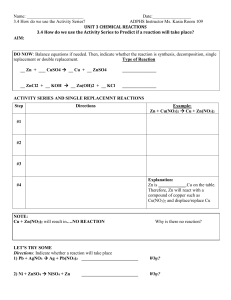
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
슬라이드 1
... In 1956, Longuet and Orgel propose the complex compound. In 1959, Criegee isolated the complex. ...
... In 1956, Longuet and Orgel propose the complex compound. In 1959, Criegee isolated the complex. ...
Bond
... including its role in nature, depends primarily on its molecular structure, or shape. Molecular shape contributes toward determining a compound’s boiling point, freezing point, viscosity, solubility, types of reactions it can participate in, and a host of other physical and chemical properties. The ...
... including its role in nature, depends primarily on its molecular structure, or shape. Molecular shape contributes toward determining a compound’s boiling point, freezing point, viscosity, solubility, types of reactions it can participate in, and a host of other physical and chemical properties. The ...
Chemistry 300 - Sacramento City College
... solids, and quantitative relationships of variables affecting behavior of gases. -identify the properties of acids and bases (and their conjugates) with the ability to convert back and forth between acid concentration and pH. -demonstrate a basic understanding of nuclear chemistry and its applicatio ...
... solids, and quantitative relationships of variables affecting behavior of gases. -identify the properties of acids and bases (and their conjugates) with the ability to convert back and forth between acid concentration and pH. -demonstrate a basic understanding of nuclear chemistry and its applicatio ...
Compound Name
... Balance chemical equations by adding coefficients and not by changing compound subscripts; ...
... Balance chemical equations by adding coefficients and not by changing compound subscripts; ...
Exam only.
... the enthalpy of reaction is the difference between product and reactant enthalpies. the Gibbs free energy is a function of both enthalpy and entropy. ...
... the enthalpy of reaction is the difference between product and reactant enthalpies. the Gibbs free energy is a function of both enthalpy and entropy. ...
Natural Products Chemistry. The Isolation of Trimyristin from Nutmeg
... from natural sources. Methods such as infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and x-ray methods are used to identify the structures of the compounds. Laboratory synthesis of the compounds from simpler compounds provides confirmation of the structure as well as a labo ...
... from natural sources. Methods such as infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and x-ray methods are used to identify the structures of the compounds. Laboratory synthesis of the compounds from simpler compounds provides confirmation of the structure as well as a labo ...
Chemistry I Review - BarbaraElam-Rice
... 33) How are intermolecular forces different from chemical bonds? Which is stronger? 34) If the electronegativity difference between atoms is greater than 1.7, what type of bond will form? If the difference is less than 1.7, what type of bond will form? 35) What type of molecule has an electronegativ ...
... 33) How are intermolecular forces different from chemical bonds? Which is stronger? 34) If the electronegativity difference between atoms is greater than 1.7, what type of bond will form? If the difference is less than 1.7, what type of bond will form? 35) What type of molecule has an electronegativ ...