Chapters 9 and 10
... Indicate the total number of sigma (σ) bonds and the total number of pi (π) bonds in the molecule ...
... Indicate the total number of sigma (σ) bonds and the total number of pi (π) bonds in the molecule ...
CHEMISTRY MCQ
... 39) peroxyacetylene is an irritant to human beings and it effects a) ears b) eyes c) nose d) stomach 40) which enzyme is involved in fermentation of glucose? a) zymase b) invertase c) urease d) diastase 41) relative acidic strength of alcohol , phenol , water and carboxylic acids is a) carboxylic ac ...
... 39) peroxyacetylene is an irritant to human beings and it effects a) ears b) eyes c) nose d) stomach 40) which enzyme is involved in fermentation of glucose? a) zymase b) invertase c) urease d) diastase 41) relative acidic strength of alcohol , phenol , water and carboxylic acids is a) carboxylic ac ...
Ch. 3 Biochemistry Review PowerPoint
... How many available bonding sites does a carbon atom have? ...
... How many available bonding sites does a carbon atom have? ...
Chapters 1-4 Numbers and Measurements in Chemistry Units SI
... together in polymers. • Polymer backbone - The long chain of bonded atoms formed when monomers link together to form polymers. ...
... together in polymers. • Polymer backbone - The long chain of bonded atoms formed when monomers link together to form polymers. ...
Exp`t 88 - Chemistry Courses
... microclamp. Using a glass Pasteur pipet, cautiously add 3 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid, one drop at a time, letting the sulfuric acid run down the inside wall of the flask neck. Add 4 boiling chips and gently swirl the liquids so that they are thoroughly mixed. Now slowly add 1.3 mL of isopro ...
... microclamp. Using a glass Pasteur pipet, cautiously add 3 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid, one drop at a time, letting the sulfuric acid run down the inside wall of the flask neck. Add 4 boiling chips and gently swirl the liquids so that they are thoroughly mixed. Now slowly add 1.3 mL of isopro ...
Slide 1
... • In these polymers, two different functional groups are required and for each new bond between the monomer units (shown coloured below), a small molecule (often water) is produced. • Each monomer must also have two functional groups. • This can involve two different functional groups on the same mo ...
... • In these polymers, two different functional groups are required and for each new bond between the monomer units (shown coloured below), a small molecule (often water) is produced. • Each monomer must also have two functional groups. • This can involve two different functional groups on the same mo ...
Slide 1 In this lesson, we will give you a general
... Let us look at the definition of organic molecules. Organic Molecules are the compounds containing carbon atoms. We do not include Carbon dioxide and diamonds under this category. Early Thoughts were that only living things could synthesize organic compounds. But, in 1800, an organic compound was sy ...
... Let us look at the definition of organic molecules. Organic Molecules are the compounds containing carbon atoms. We do not include Carbon dioxide and diamonds under this category. Early Thoughts were that only living things could synthesize organic compounds. But, in 1800, an organic compound was sy ...
Hydrocarbon - TeacherWeb
... 7. Branched-chain alkanes must be named differently than straight-chain alkanes. 8. Parent chain: the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms 9. All side branches are called substituent groups because they appear to substitute for a hydrogen atom in the parent chain. 10. Copy the five steps for nam ...
... 7. Branched-chain alkanes must be named differently than straight-chain alkanes. 8. Parent chain: the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms 9. All side branches are called substituent groups because they appear to substitute for a hydrogen atom in the parent chain. 10. Copy the five steps for nam ...
Periodic Table, Bonding, Reactions, and Moles
... similar to the bonding in barium chloride, BaCl2. 9. Identify the type of bonding between the atoms in an oxygen molecule. ...
... similar to the bonding in barium chloride, BaCl2. 9. Identify the type of bonding between the atoms in an oxygen molecule. ...
WM4 Instrumental analysis
... which electromagnetic radiation is transmitted through a sample of substance. Frequency ranges absorbed give clues about functional groups which are present. IR spectrum of salicylic acid gives evidence of C=O and –OH groups. ...
... which electromagnetic radiation is transmitted through a sample of substance. Frequency ranges absorbed give clues about functional groups which are present. IR spectrum of salicylic acid gives evidence of C=O and –OH groups. ...
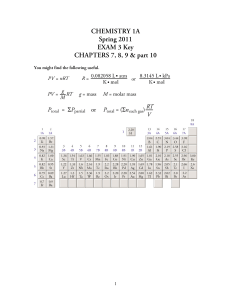
Exam 3 Key
... a. What is the hybridization for the left oxygen atom? sp3 b. What is the hybridization for the right oxygen atom? sp2 c. What is the hybridization for the top oxygen atom? sp2 d. What is the hybridization for the nitrogen atom? sp2 e. Write a description of the bonding, stating whether each bond is ...
... a. What is the hybridization for the left oxygen atom? sp3 b. What is the hybridization for the right oxygen atom? sp2 c. What is the hybridization for the top oxygen atom? sp2 d. What is the hybridization for the nitrogen atom? sp2 e. Write a description of the bonding, stating whether each bond is ...
Chemistry 116: General Chemistry
... 7. A closed system of three gases is governed by the reversible reaction shown. Kp = 4 10-7 at the current temperature of the mixture, PNO2 = 4.1 10-2 atm, PNO = 8.9 10-4 atm, and PO2 = 8.5 10-3 atm. In order to reach equilibrium, how must the system adjust? ...
... 7. A closed system of three gases is governed by the reversible reaction shown. Kp = 4 10-7 at the current temperature of the mixture, PNO2 = 4.1 10-2 atm, PNO = 8.9 10-4 atm, and PO2 = 8.5 10-3 atm. In order to reach equilibrium, how must the system adjust? ...
Formula Mass (weight)
... • What important law is adhered to by this reaction (and all the reactions we will study in CHEM 111) ...
... • What important law is adhered to by this reaction (and all the reactions we will study in CHEM 111) ...
Chemistry EOC Review Spring 2013
... 19. How are the noble gases different from other families? Unit 3 Matter & Atomic Structure (Chapter 2 & 4) (Lots of good questions may come from this section): 20. List the characteristics of the four states of matter. ...
... 19. How are the noble gases different from other families? Unit 3 Matter & Atomic Structure (Chapter 2 & 4) (Lots of good questions may come from this section): 20. List the characteristics of the four states of matter. ...
Spring Benchmark Exam
... until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settled to the bottom of the flask. Which statement best describes what happened? A As the solution cooled, evapor ...
... until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settled to the bottom of the flask. Which statement best describes what happened? A As the solution cooled, evapor ...
Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry….
... If the Daddy gives a push every 3 seconds, the kid will go higher and energy will be absorbed. Every 2 seconds and the motion will get stalled and “interfered” with. Every 1.5 seconds and the energy will get absorbed but not as efficiently. The Daddy will get tired. This general principal applies in ...
... If the Daddy gives a push every 3 seconds, the kid will go higher and energy will be absorbed. Every 2 seconds and the motion will get stalled and “interfered” with. Every 1.5 seconds and the energy will get absorbed but not as efficiently. The Daddy will get tired. This general principal applies in ...
Reaction Rate Reading Packet
... Surface area can also be important if a reaction occurs between two liquids that do not mix. In this case, the reaction occurs only at the boundary where the two liquids meet. It is also important to note that not all reactions depend on surface area. If both reactants are gases or liquids that mix ...
... Surface area can also be important if a reaction occurs between two liquids that do not mix. In this case, the reaction occurs only at the boundary where the two liquids meet. It is also important to note that not all reactions depend on surface area. If both reactants are gases or liquids that mix ...
CHEM 400 - El Camino College
... Distinguish between heat at constant volume (qv = ΔE) and heat at constant pressure (qp = ΔH). Concept of enthalpy. Why do chemists prefer to use enthalpy rather that internal energy? Know how calorimetry can be used to determine specific heats of substances and heats of reactions. What are the adva ...
... Distinguish between heat at constant volume (qv = ΔE) and heat at constant pressure (qp = ΔH). Concept of enthalpy. Why do chemists prefer to use enthalpy rather that internal energy? Know how calorimetry can be used to determine specific heats of substances and heats of reactions. What are the adva ...