Chapter 14
... to organic compounds that gives a significant M + 2 peak – 32S = 95.02% and 34S = 4.21% ...
... to organic compounds that gives a significant M + 2 peak – 32S = 95.02% and 34S = 4.21% ...
File
... give you the ___________________________ of the atom. 3. _________________ move quickly and constantly around the outside of the nucleus in the ____________ __________. 4. The number of __________________ can change which forms _________________ ( + or -). 5. Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS ha ...
... give you the ___________________________ of the atom. 3. _________________ move quickly and constantly around the outside of the nucleus in the ____________ __________. 4. The number of __________________ can change which forms _________________ ( + or -). 5. Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS ha ...
Organic Objectives
... identify the “parent chain” looking at a structural formula give examples of substituted hydrocarbons. draw and name isomers of substituted hydrocarbons. build models using single, double and triple bonds and describe which rotate. demonstrate cis- and trans- isomerism, example: dichloroet ...
... identify the “parent chain” looking at a structural formula give examples of substituted hydrocarbons. draw and name isomers of substituted hydrocarbons. build models using single, double and triple bonds and describe which rotate. demonstrate cis- and trans- isomerism, example: dichloroet ...
Chemistry
... Put a "C" next to the reaction in box 1-1 that is a combination reaction. Put a "D" next to the reaction in Box 1-1 that is a decomposition reaction. Put a "S-R" next to the single replacement reaction in Box 1-1. Put an "O" next to the combustion reaction in Box 1-1. ...
... Put a "C" next to the reaction in box 1-1 that is a combination reaction. Put a "D" next to the reaction in Box 1-1 that is a decomposition reaction. Put a "S-R" next to the single replacement reaction in Box 1-1. Put an "O" next to the combustion reaction in Box 1-1. ...
Thursday, September 4
... Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen Many organic molecules, such as fats, have hydrocarbon components Hydrocarbons can undergo reactions that release a large amount of energy ...
... Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen Many organic molecules, such as fats, have hydrocarbon components Hydrocarbons can undergo reactions that release a large amount of energy ...
Problem Set 3_Chem165_Sp2014
... 9. For carbocations composed of just carbon and hydrogen, the stability is tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl (R3C+ > R2CH+ > RCH2+ > CH3+), as discussed in class. This is the origin of the Markovnikov selectivity observed for electrophilic additions to alkenes. The posted McMurray Chapter 3 is ...
... 9. For carbocations composed of just carbon and hydrogen, the stability is tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl (R3C+ > R2CH+ > RCH2+ > CH3+), as discussed in class. This is the origin of the Markovnikov selectivity observed for electrophilic additions to alkenes. The posted McMurray Chapter 3 is ...
Chem 4471 - Transition Metals and Catalysis
... Please contact the course instructor if you require material in an alternate format or if any other arrangements can make this course more accessible to you. You may also wish to contact Services for Students with Disabilities (SSD) at 661-2111 ext. 82147 if you have questions regarding accommodatio ...
... Please contact the course instructor if you require material in an alternate format or if any other arrangements can make this course more accessible to you. You may also wish to contact Services for Students with Disabilities (SSD) at 661-2111 ext. 82147 if you have questions regarding accommodatio ...
File - docstover.org
... Objective 1: Students will be able to define matter, differentiate between its different states, and understand how it remains constant with a system. Define each: Matter = ...
... Objective 1: Students will be able to define matter, differentiate between its different states, and understand how it remains constant with a system. Define each: Matter = ...
Carbon Chemistry
... water. Water is important because many of our body’s chemical reactions can only occur in solutions containing water. • Blood, sweat, urine… all mostly water! • Salt is also important because of how it can separate into its two ions: Na+ and Cl-. • Sodium ions regular the amount of water in our cell ...
... water. Water is important because many of our body’s chemical reactions can only occur in solutions containing water. • Blood, sweat, urine… all mostly water! • Salt is also important because of how it can separate into its two ions: Na+ and Cl-. • Sodium ions regular the amount of water in our cell ...
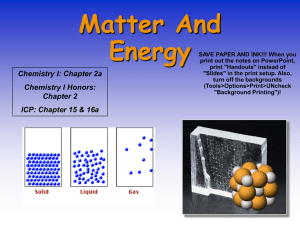
Matter and Energy
... • Extensive properties are dependent upon the amount of substance present. Ex- mass, length • Intensive property is independent of the amount of substance present. Ex- density, temperature ...
... • Extensive properties are dependent upon the amount of substance present. Ex- mass, length • Intensive property is independent of the amount of substance present. Ex- density, temperature ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... Describe the structure and geometry of a water molecule, and explain what properties emerge as a result of this structure. ...
... Describe the structure and geometry of a water molecule, and explain what properties emerge as a result of this structure. ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... changes from 25.000C to 25.225C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 603 J/C. What is the E for this reaction? a) -597 J c) -136 J b) -1660 J d) -149 J 14. Under conditions of constant volume, the heat change that occurs during a chemical reaction is equal to a) H b) E ...
... changes from 25.000C to 25.225C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 603 J/C. What is the E for this reaction? a) -597 J c) -136 J b) -1660 J d) -149 J 14. Under conditions of constant volume, the heat change that occurs during a chemical reaction is equal to a) H b) E ...
CHAPTER 1: ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... 3. non-polar – C and H have almost the same electronegativities and so form non-polar bonds 4. make good non-polar solvents 5. don’t dissolve in polar solvents such as water 1.3: Reactions of Hydrocarbons - all burn to give CO2, H2O and huge amounts of heat energy - less reactive - Alkanes aromati ...
... 3. non-polar – C and H have almost the same electronegativities and so form non-polar bonds 4. make good non-polar solvents 5. don’t dissolve in polar solvents such as water 1.3: Reactions of Hydrocarbons - all burn to give CO2, H2O and huge amounts of heat energy - less reactive - Alkanes aromati ...
TT T p
... which one kind of atom or group of atomsis replaced by anotherkind of atom or group of atoms are called substitutionreactions.Except for combustion and thermal decomposition,reactionsof saturated hydrocarbonsare usually substitution reactions in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced. When a ...
... which one kind of atom or group of atomsis replaced by anotherkind of atom or group of atoms are called substitutionreactions.Except for combustion and thermal decomposition,reactionsof saturated hydrocarbonsare usually substitution reactions in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced. When a ...
Chapter 18 Review 18.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation
... where the agents are separated, the electrons flow through a wire, and there is a salt bridge connecting the two solutions Anode- the electrode where oxidation occurs Cathode- the electrode where reduction occurs Electrolysis- electrical energy is used to produce a chemical change - batteries uses e ...
... where the agents are separated, the electrons flow through a wire, and there is a salt bridge connecting the two solutions Anode- the electrode where oxidation occurs Cathode- the electrode where reduction occurs Electrolysis- electrical energy is used to produce a chemical change - batteries uses e ...
Reaction of potassium atoms with oriented bromotrifluoromethane
... Polarized laser radiation can be used to prepare beams of polarized molecules, which are molecules whose plane of rotation can be oriented with respect to a fixed axis. This technique has been applied, for example, to S r HF and “broadside” attack of the plane-of-rotation of HF is observed3 to yield ...
... Polarized laser radiation can be used to prepare beams of polarized molecules, which are molecules whose plane of rotation can be oriented with respect to a fixed axis. This technique has been applied, for example, to S r HF and “broadside” attack of the plane-of-rotation of HF is observed3 to yield ...
Nature of Molecules and Water
... • Polar molecules have significant amounts of O or N causing it to be polar (electrically charged) and mix readily with water • Nonpolar molecules have little to no O or N causing it to be nonpolar (electrically neutral) and don’t mix readily with water (separate) − Oil and Water don’t mix ...
... • Polar molecules have significant amounts of O or N causing it to be polar (electrically charged) and mix readily with water • Nonpolar molecules have little to no O or N causing it to be nonpolar (electrically neutral) and don’t mix readily with water (separate) − Oil and Water don’t mix ...
Highlights IACChE`s James Y. Oldshue Lecture Tuesday, November
... requires a detailed knowledge on the relationship between the chemical nature of the solvents and the interactions taking place in the gas-liquid-solid catalytic systems. One of the most common types of catalytic reactions carried out in the presence of solvents is the hydrogenation of organic comp ...
... requires a detailed knowledge on the relationship between the chemical nature of the solvents and the interactions taking place in the gas-liquid-solid catalytic systems. One of the most common types of catalytic reactions carried out in the presence of solvents is the hydrogenation of organic comp ...
Catalyst Activity (in your notebook)
... • whole numbers in front of formula • distributes to numbers of atoms in formula • specifies the relative number of moles and molecules involved in the reaction • used to balance the equation ...
... • whole numbers in front of formula • distributes to numbers of atoms in formula • specifies the relative number of moles and molecules involved in the reaction • used to balance the equation ...