EKG Interpretation - Fire Training Tracker
... Normal PR interval should not exceed 0.2 seconds or one large bolded square on the EKG paper QRS complex- represents electrical depolarization of the ventricle Normal duration of the QRS complex is from 0.08-0.10 seconds (2 to 3 small boxes on the EKG paper ...
... Normal PR interval should not exceed 0.2 seconds or one large bolded square on the EKG paper QRS complex- represents electrical depolarization of the ventricle Normal duration of the QRS complex is from 0.08-0.10 seconds (2 to 3 small boxes on the EKG paper ...
Important questions of physiology.
... 24. Define and explain the Frank-Starling mechanism of heart function regulation? 25. Why SA node is called as the normal pacemaker of heart? What is meant by ectopic pacemaker? What is the clinical importance of override suppressive mechanism of SA node on all other parts of cardiac conduction syst ...
... 24. Define and explain the Frank-Starling mechanism of heart function regulation? 25. Why SA node is called as the normal pacemaker of heart? What is meant by ectopic pacemaker? What is the clinical importance of override suppressive mechanism of SA node on all other parts of cardiac conduction syst ...
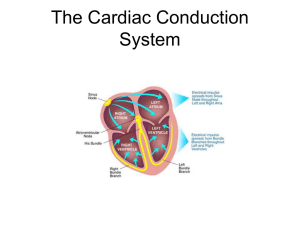
The Cardiac Conduction System
... • S-A node- “Pacemaker” -bundle of cardiac muscle tissue -sends impulses that cause the atria to contract -Passes impulses to the A-V node/A-V bundle Did you know the heart can beat outside of the body because of the S-A node? Click on the heart to watch. ...
... • S-A node- “Pacemaker” -bundle of cardiac muscle tissue -sends impulses that cause the atria to contract -Passes impulses to the A-V node/A-V bundle Did you know the heart can beat outside of the body because of the S-A node? Click on the heart to watch. ...
RT 30 Final Exam Review - Respiratory Therapy Files
... •Fluid accumulation surrounding the heart, may lead to a life threatening condition called cardiac tamponade ...
... •Fluid accumulation surrounding the heart, may lead to a life threatening condition called cardiac tamponade ...
CMC Sept. 2010 CE - Advocatehealth.com
... Rate: 40-60 bpm (if not driven by the rate above) Bundle of His: Has the ability to self-initiate electrical activity Rate: 40-60 bpm Purkinje Fibers: Network of fibers that carry electrical impulses directly to ventricular muscle. Rate: 20-40 bpm (if not driven by the rate above) ...
... Rate: 40-60 bpm (if not driven by the rate above) Bundle of His: Has the ability to self-initiate electrical activity Rate: 40-60 bpm Purkinje Fibers: Network of fibers that carry electrical impulses directly to ventricular muscle. Rate: 20-40 bpm (if not driven by the rate above) ...
File
... o Heart relaxes and fills with blood to be ejected during the nest systolic contraction ...
... o Heart relaxes and fills with blood to be ejected during the nest systolic contraction ...
Wenckebach - Florida Heart CPR
... (Mobitz Type I) As the sinus node initiates impulses each one is delayed in the AV NODE a little longer than the preceding one until one is eventually blocked completely. Those impulses that are conducted travel normally through the ventricles. REGULARITY Irregular in a pattern of grouped beating. R ...
... (Mobitz Type I) As the sinus node initiates impulses each one is delayed in the AV NODE a little longer than the preceding one until one is eventually blocked completely. Those impulses that are conducted travel normally through the ventricles. REGULARITY Irregular in a pattern of grouped beating. R ...
天津医科大学授课教案
... Emphasis,Difficult Points and Requirements on Student 1 To master Sinus Tachycardia, Sinus Bradycardia, Sinus Pause or Sinus Arrest ,Sinoatrial Exit and Block Sick Sinus Syndrome(SSS) 2 To master Premature Atrial Complexes ,Atrial Flutter ,Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Tachycardias 3 To master AV J ...
... Emphasis,Difficult Points and Requirements on Student 1 To master Sinus Tachycardia, Sinus Bradycardia, Sinus Pause or Sinus Arrest ,Sinoatrial Exit and Block Sick Sinus Syndrome(SSS) 2 To master Premature Atrial Complexes ,Atrial Flutter ,Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Tachycardias 3 To master AV J ...
Boredom at its HEART by Dhravid - Fitz
... electrocardiogram and is shown in Figure 3. The ECG is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart in the form of a wave with spikes and dips. These waves are then broken up into different sections. The sections in a typical pattern is shown in Figure 4. To read an EKG for an ...
... electrocardiogram and is shown in Figure 3. The ECG is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart in the form of a wave with spikes and dips. These waves are then broken up into different sections. The sections in a typical pattern is shown in Figure 4. To read an EKG for an ...
Slide 1 - Access Emergency Medicine
... A: Undersensing. The fifth beat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). The next beat is a ventricular paced beat. Note that the paced beat occurs soon after the PVC, indicating a failure to sense the preceding complex. B: The first and second beats are paced and the third and fourth beats sho ...
... A: Undersensing. The fifth beat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). The next beat is a ventricular paced beat. Note that the paced beat occurs soon after the PVC, indicating a failure to sense the preceding complex. B: The first and second beats are paced and the third and fourth beats sho ...
Comparison on Time Basis of Atrial Fibrillation with Normal Sinus
... per 1,000 in females, and 8 per 1,000 in males, and with an incidence of 0.2 new cases per 1,000 patient years in females and 0.9 new cases per 1,000 patient years in males [2]. Age, sex and the occurrence of some other similar maladies are directly related to the raised incidence, including high bl ...
... per 1,000 in females, and 8 per 1,000 in males, and with an incidence of 0.2 new cases per 1,000 patient years in females and 0.9 new cases per 1,000 patient years in males [2]. Age, sex and the occurrence of some other similar maladies are directly related to the raised incidence, including high bl ...
Setting the Heart`s Tempo
... Diagnosing Heart Conditions Doctors can use electrocardiographs, which map electrical fields within the heart, to make tracings to diagnose certain heart problems. Electrodes placed on the body surface are connected to a recording device. The electrical impulses are displayed on a graph called an el ...
... Diagnosing Heart Conditions Doctors can use electrocardiographs, which map electrical fields within the heart, to make tracings to diagnose certain heart problems. Electrodes placed on the body surface are connected to a recording device. The electrical impulses are displayed on a graph called an el ...
ECG signs of Cardiac hypertrophy and enlargement of heart chambers
... The right and left atrial waveforms summate to form the P wave. The first 1/3 of the P wave corresponds to right atrial activation, the final 1/3 corresponds to left atrial activation; the middle 1/3 is a combination of the two. In most leads (e.g. lead II), the right and left atrial waveforms move ...
... The right and left atrial waveforms summate to form the P wave. The first 1/3 of the P wave corresponds to right atrial activation, the final 1/3 corresponds to left atrial activation; the middle 1/3 is a combination of the two. In most leads (e.g. lead II), the right and left atrial waveforms move ...
Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... The heart lies slightly to the left of the midline. The heart sits at an oblique angle to the longitudinal axis of the ...
... The heart lies slightly to the left of the midline. The heart sits at an oblique angle to the longitudinal axis of the ...
Surgery in Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
... Surgery in Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome The Wolff-Parkinson-White (W-P-W) syndrome, first described in 1930,1 consists of a characteristic electrocardiographic abnormality in people who are prone to paroxysmal tachycardia. The electrocardiogram shows a short PR interval with a widened QRS complex, ...
... Surgery in Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome The Wolff-Parkinson-White (W-P-W) syndrome, first described in 1930,1 consists of a characteristic electrocardiographic abnormality in people who are prone to paroxysmal tachycardia. The electrocardiogram shows a short PR interval with a widened QRS complex, ...
Introduction to the Heart
... • The coronary arteries that nourish the myocardium arise from the _____________. • The ____________ are receiving chambers; the _________ are discharging chambers. • The muscular walls of the heart is called the _____________. • The myocardium of the ______ ventricle is much thicker than that of th ...
... • The coronary arteries that nourish the myocardium arise from the _____________. • The ____________ are receiving chambers; the _________ are discharging chambers. • The muscular walls of the heart is called the _____________. • The myocardium of the ______ ventricle is much thicker than that of th ...
Analysis and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram A Self
... The measurement of important electrocardiographic intervals usually includes the PR interval, the QRS interval and the QT interval. At a standard paper speed of 25 mm/second, the width of each small square (1mm) represents 0.04 seconds. One large square (5mm) represents 0.2 seconds. ...
... The measurement of important electrocardiographic intervals usually includes the PR interval, the QRS interval and the QT interval. At a standard paper speed of 25 mm/second, the width of each small square (1mm) represents 0.04 seconds. One large square (5mm) represents 0.2 seconds. ...
Click here for the printable version of this module.
... The measurement of important electrocardiographic intervals usually includes the PR interval, the QRS interval and the QT interval. At a standard paper speed of 25 mm/second, the width of each small square (1mm) represents 0.04 seconds. One large square (5mm) represents 0.2 seconds. ...
... The measurement of important electrocardiographic intervals usually includes the PR interval, the QRS interval and the QT interval. At a standard paper speed of 25 mm/second, the width of each small square (1mm) represents 0.04 seconds. One large square (5mm) represents 0.2 seconds. ...
Cardiac anatomy and physiology
... RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN P & QRS (HOW DO WE KNOW THIS…. WIDE QRS) PR – NO PATTERN QRS – WIDE ...
... RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN P & QRS (HOW DO WE KNOW THIS…. WIDE QRS) PR – NO PATTERN QRS – WIDE ...
Definitions
... • Asymptomatic bradycardia in the elderly (resting heart rate in mid 40s) do not need intervention Syncope without preceding palpitation, or occurring less then once a week, investigation with a 24hr ECG is rarely helpful Investigation of symptoms - Cardiomemo or 24 hour tape? ...
... • Asymptomatic bradycardia in the elderly (resting heart rate in mid 40s) do not need intervention Syncope without preceding palpitation, or occurring less then once a week, investigation with a 24hr ECG is rarely helpful Investigation of symptoms - Cardiomemo or 24 hour tape? ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.