17-6 Electric Dipoles
... positive electrode called an anode exist as two plates in an evacuated tube. • When the negative electrode is heated it gives off electrons, originally called cathode rays. (See pg. 519) • An oscilloscope is a device for representing an electric signal on a screen, using a CRT. ...
... positive electrode called an anode exist as two plates in an evacuated tube. • When the negative electrode is heated it gives off electrons, originally called cathode rays. (See pg. 519) • An oscilloscope is a device for representing an electric signal on a screen, using a CRT. ...
ABCD- Airway, Breathing, Circulation, and Defibrillation
... Defibrillation- shocking the heart to stop fibrillation Emergency Medical Services (EMS)- A rapid response system that responds to emergencies by providing emergency care and transport Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)- An entry-level EMS worker trained to provide basic emergency care and transport ...
... Defibrillation- shocking the heart to stop fibrillation Emergency Medical Services (EMS)- A rapid response system that responds to emergencies by providing emergency care and transport Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)- An entry-level EMS worker trained to provide basic emergency care and transport ...
Electrocardiography: Atrial Fibrillation - e
... Etiology The conditions most likely to produce atrial fibrillation are rheumatic heart disease, ischemic heart disease, hypertension, heart failure, thyrotoxicosis, valvular disease, cardiac surgery, advancing age, and left atrial enlargement. ECG findings In AF, atrial activity is completely disorg ...
... Etiology The conditions most likely to produce atrial fibrillation are rheumatic heart disease, ischemic heart disease, hypertension, heart failure, thyrotoxicosis, valvular disease, cardiac surgery, advancing age, and left atrial enlargement. ECG findings In AF, atrial activity is completely disorg ...
Electrical Properties of the Heart
... two electrodes. Standard surface electrodes (right and left arm, right and left leg, and the six precordial electrodes) measure the electrical potential at a site. Leads may unipolar or bipolar. Bipolar leads, which include I, II and III measure the difference between two surface electrodes, and dra ...
... two electrodes. Standard surface electrodes (right and left arm, right and left leg, and the six precordial electrodes) measure the electrical potential at a site. Leads may unipolar or bipolar. Bipolar leads, which include I, II and III measure the difference between two surface electrodes, and dra ...
PDF - US Pharmacist
... by electrical impulses transmitted to the atria, the smaller upper chambers of the heart, and then to the ventricles, the larger, lower chambers of the heart. These electrical impulses result in a heartbeat, which allows the ventricles to pump blood throughout the body. Any time the normal electrica ...
... by electrical impulses transmitted to the atria, the smaller upper chambers of the heart, and then to the ventricles, the larger, lower chambers of the heart. These electrical impulses result in a heartbeat, which allows the ventricles to pump blood throughout the body. Any time the normal electrica ...
Evaluation of the Patient Suspected of Having Underlying Arrhythmias
... Premature atrial contractions Benign in absence of underlying heart disease Early p wave, sometimes with different morphology than a sinus p wave Can be either: ...
... Premature atrial contractions Benign in absence of underlying heart disease Early p wave, sometimes with different morphology than a sinus p wave Can be either: ...
Comparative Study Of FIR Digital Filter for Noise
... Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnosis tool that reported the electrical activity of heart recorded by skin electrode. The morphology and heart rate reflects the cardiac health of human heart beat[1]. It is a non-invasive technique that means this signal is measured on the surface of human body, whi ...
... Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnosis tool that reported the electrical activity of heart recorded by skin electrode. The morphology and heart rate reflects the cardiac health of human heart beat[1]. It is a non-invasive technique that means this signal is measured on the surface of human body, whi ...
VERAPAMIL (CALAN)
... Blocks the entry of calcium into the cell Slows conduction through the AV node Negative chronotrope (slows heart rate) Negative inotrope (decreased force of cardiac contraction) To control the rate in hemodynamically stable atrial fibrillation or INDICATIONS atrial flutter with rapid ventric ...
... Blocks the entry of calcium into the cell Slows conduction through the AV node Negative chronotrope (slows heart rate) Negative inotrope (decreased force of cardiac contraction) To control the rate in hemodynamically stable atrial fibrillation or INDICATIONS atrial flutter with rapid ventric ...
All I need is a cast…
... 1. Describe to him the Buckle Fracture study in detail and keep him in the splint 2. Cast him and avoid the hassle 3. 1 or 2 + have a discussion about what “friends” are 4. 3 + ECG ...
... 1. Describe to him the Buckle Fracture study in detail and keep him in the splint 2. Cast him and avoid the hassle 3. 1 or 2 + have a discussion about what “friends” are 4. 3 + ECG ...
Heart Activity
... HR: 30 bpm Diagnosis: Sinus rhythm with PVC, area of ventricles are irritable and sending reverse conduction signals, both the SA node and the ventricles are sending a signal ...
... HR: 30 bpm Diagnosis: Sinus rhythm with PVC, area of ventricles are irritable and sending reverse conduction signals, both the SA node and the ventricles are sending a signal ...
Preoperative Evaluation and Risk Assessment in the Cardiac
... Abnormal but usually benign • Concerns: very frequent, history of ischemia ...
... Abnormal but usually benign • Concerns: very frequent, history of ischemia ...
ECG Made EASIER
... An ECG is the primary monitor for diagnosis of cardiac conduction abnormalities and rhythm disturbances. An ECG is a tracing created with electrodes on the skin that amplify cardiac electrical potentials. The normal ECG tracing is a complex composed of three waveforms: P wave (atrial depolarizatio ...
... An ECG is the primary monitor for diagnosis of cardiac conduction abnormalities and rhythm disturbances. An ECG is a tracing created with electrodes on the skin that amplify cardiac electrical potentials. The normal ECG tracing is a complex composed of three waveforms: P wave (atrial depolarizatio ...
The Normal ECG and its (Normal) Variants
... and horizontal leads. The right atrium vector points inferiorly, anteriorly, and slightly to the right, whereas the left atrial vector points posteriorly, to the left, and slightly downwards (Figures 3.1a and 3.1b). The p vector in sinus rhythm is a fusion of the right atrial vector and the left atr ...
... and horizontal leads. The right atrium vector points inferiorly, anteriorly, and slightly to the right, whereas the left atrial vector points posteriorly, to the left, and slightly downwards (Figures 3.1a and 3.1b). The p vector in sinus rhythm is a fusion of the right atrial vector and the left atr ...
Paced ECG Morphology–Reveals More than What It Conceals
... patients with paced rhythms. The GUSTO-1 trial has provided useful information in this regard. In this trial, 32 patients had ventricular paced rhythm. The only ECG criterion with a high specificity and statistical significance for the diagnosis of an acute myocardial infarction was ST segment eleva ...
... patients with paced rhythms. The GUSTO-1 trial has provided useful information in this regard. In this trial, 32 patients had ventricular paced rhythm. The only ECG criterion with a high specificity and statistical significance for the diagnosis of an acute myocardial infarction was ST segment eleva ...
Dia 1 - EPCCS
... What is heart failure ? a complex clinical syndrome • (left) ventricular dysfunction with origin in heart : HFREF • (left) ventricular dysfunction in response to endothelial dysfunction (DM, etc) and pressure overload (HT): HFPEF ...
... What is heart failure ? a complex clinical syndrome • (left) ventricular dysfunction with origin in heart : HFREF • (left) ventricular dysfunction in response to endothelial dysfunction (DM, etc) and pressure overload (HT): HFPEF ...
module h - Macomb
... • Describe the pharmacologic action of nitrate therapy. • List the cardiac glycosides and describe when they are indicated in the clinical setting. • Name two anticoagulants and an antidote for each. • Name the three thrombolytics used to treat myocardial infarctions, strokes and pulmonary embolism. ...
... • Describe the pharmacologic action of nitrate therapy. • List the cardiac glycosides and describe when they are indicated in the clinical setting. • Name two anticoagulants and an antidote for each. • Name the three thrombolytics used to treat myocardial infarctions, strokes and pulmonary embolism. ...
Ventricular tachycardia in abnormal heart
... • Documented VT/VF on c/c OMT, have reasonable expectation of survival- ICD to prevent SCD – class 1,level of evidence B • Severe disease LV inv,FH of SCD,undiagnosed syncope, on c/c OMT-class iia, level of evidence C • Amiodarone or sotalol effective , when ICD not feasible – class iia, level of ev ...
... • Documented VT/VF on c/c OMT, have reasonable expectation of survival- ICD to prevent SCD – class 1,level of evidence B • Severe disease LV inv,FH of SCD,undiagnosed syncope, on c/c OMT-class iia, level of evidence C • Amiodarone or sotalol effective , when ICD not feasible – class iia, level of ev ...
Slide ()
... A. Jugular venous pulse wave tracing (top) with heart sounds (bottom). The A wave represents right atrial presystolic contraction and occurs just after the electrocardiographic P wave and just before the first heart sound (I). In this example, the A wave is accentuated and larger than normal due to ...
... A. Jugular venous pulse wave tracing (top) with heart sounds (bottom). The A wave represents right atrial presystolic contraction and occurs just after the electrocardiographic P wave and just before the first heart sound (I). In this example, the A wave is accentuated and larger than normal due to ...
SRAdoc®/SRA24® Report The SRAdoc®/SRA24® report is
... There is a risk of AF (without proven fibrillation episodes). Further studies with long-term ECG (SRA24®) are recommended. Significant signs of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation There is a high risk on existing AF (without proven fibrillation episodes). Further studies with longterm ECG (SRA24®) are ...
... There is a risk of AF (without proven fibrillation episodes). Further studies with long-term ECG (SRA24®) are recommended. Significant signs of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation There is a high risk on existing AF (without proven fibrillation episodes). Further studies with longterm ECG (SRA24®) are ...
SEMESTER 5 – WEEK 4 PHARMACOLOGY ANTIARRHYTHMIC
... – Combination of the two Results in rate and/or timing of contraction of heart muscle that is insufficient to maintain normal cardiac output (CO) To understand how antiarrhythmic drugs work, need to understand electrophysiology of normal contraction of heart Normal heartbeat and atrial arrhythmia Ve ...
... – Combination of the two Results in rate and/or timing of contraction of heart muscle that is insufficient to maintain normal cardiac output (CO) To understand how antiarrhythmic drugs work, need to understand electrophysiology of normal contraction of heart Normal heartbeat and atrial arrhythmia Ve ...
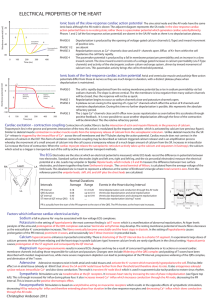
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.