* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
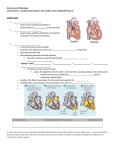
Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes – Cardiovascular System: The Cardiac Cycle and Blood Pressure” Cardiac Cycle SYSTOLE o Heart muscle contracts and blood is ejected from the atria to the ventricles DIASTOLE o Heart relaxes and fills with blood to be ejected during the nest systolic contraction Sinoatrial Node (SA NODE) o Commonly known as the SA Node o Located in the right atrium and is the Pacemaker of the heart o Specialized muscle cells o Automatically generate electrical impulses Electrical impulses are generated through polarization and depolarization o “speedy” route: SA NODE AV NODE bundle of His Purkinje fibers Commonly known as the AV node passes the signal from the SA node to the ventricles, causing a delay in the cardiac cycle. o Permits the atria to complete the SYSTOLIC CONTRACTION before ventricular systole begins o Bundle of His fibers travel down the interventricular septum the APEX o Purkinje fibers carry impulses from the bundle of His into the VENTRICULAR MYOCARDIUM o o Resting Heart Rate Active Heart Rate To check your pulse at your wrist, place two fingers between the bone and the tendon over your radial artery — which is located on the thumb side of your wrist. When you feel your pulse, count the number of beats in 15 seconds. Multiply this number by 4 to calculate your beats a minute. Normal Heart Rates (Resting Heart Rates) Canine: o 70-120 Adult Dog o 160 to 200 beats per minute at birth (puppy) o 70-180 Toy Breed Feline: o 120–140 in a comfortable setting o 120 - >220 in a veterinary clinical setting Equine: 28-40 Elephant: 25-35 Guinea Pig: 200-300 Human: 60-100 Auscultation Auscultation is LISTENING o Auscultated through the chest wall with a stethoscope o Canine/feline hearts lie between the 3rd and 7th ribs o Equines/ruminants heart lies between 2nd and 6th ribs Cardiac Rhythm is typically described as lub/dub o LUB is called S1 Associated with the simultaneous closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves at the beginning of ventricular systole Mitral valve better heard on the right side of the chest Tricuspid valve better heard on the right side of the chest o DUB is called S2 Associated with the closure of the semilunar valves at the beginning of the ventricular diastole Aortic valve best listened to on the left Pulmonary valve best heard on the left also Cardiac Output Cardiac output is the AMOUNT OF BLOOD THAT LEAVES THE HEART PER MINUTE o STROKE VOLUME Amount of blood ejected with each cardiac contraction (one beat) o HEART RATE How often the heart contracts Cardiac Output Equation: CO (Cardiac Output) = SV (Stroke Volume) x HR (Heart rate) *SV = EDV-ESV EDV= End diastolic volume – amount of blood in the ventricle right before ventricular contraction ESV = End systolic volume – amount of blood in the ventricle right after ventricular contraction COMPLETE Practice Questions 1-4 to calculate Cardiac Output 1. HR = 108 beats/min SV= ________mL CO= __________mL/min EDV = ______ ESV = ______ 2. HR = 140 beats/min SV= ________mL CO= __________mL/min 3. HR = 100 beats/min SV= ________mL CO= __________mL/min 4. HR = 70 beats/min SV= ________mL CO= __________mL/min *Starling’s Law Video https://youtu.be/cco0Vd3eIqE?list=PLdK9Q57ovliyKx7wKv-fwIdu5T9ubZbEd Affecters of Cardiac Output Exercise o O2 demand increases o Heart begins to contract more forcefully, this is called CONTRACTILITY Shock o BLOOD PRESSURE drops rapidly o Decreased preload VENTRICLES do not fill completely o HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK occurs because of blood loss o ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK occurs due to small blood vessels in organs and tissues dilating at the same time Other affecters o Autonomic nervous system (fight or flight) Increases CO due to epinephrine o Anesthesia can stimulate parasympathetic nervous system Decreases CO due to acetylcholine Blood Pressure The pressure of the blood in the circulatory system, often measured for diagnosis since it is closely related to the force and rate of the heartbeat and the diameter and elasticity of the arterial walls. Ideal Blood Pressure (BP) = 120/80 mm Hg Recorded as two numbers: SYSTOLIC o Measures pressure in the arteries during contraction DIASTOLIC o Measures pressure in arteries between heartbeats Veterinarian also use the _________________________________ MAP calculation: MAP = SBP + 2 (DBP) 3 Example: To calculate a mean arterial pressure, double the diastolic blood pressure and add the sum to the systolic blood pressure. Then divide by 3. For example, if a patient’s blood pressure is 83 mm Hg/50 mm Hg, his MAP would be 61 mm Hg. Here are the steps for this calculation: MAP = SBP + 2 (DBP) 3 MAP = 83 +2 (50) 3 MAP = 83 +100 3 MAP = 183 3 MAP = 61 mm HG Complete Questions 1-4 to find MAP 1. BP = 110 mmHg vvvvvv70 MAP=_______ 2. BP = 96 mmHg vvvvv 40 MAP=_______ 3. BP = 83 mmHg vvvvvv44 MAP=_______ 4. BP = 120 mmHg vvvvvv80 MAP=_______ ECG BASICS ECG is short for ELECTROCARDIOGRAM o ECG is a graph of the HEART’S ELECTRICAL CURRENT Monitoring RATE, RHYTHM and CONDUCTION o Most commonly used to identify arrhythmias in veterinary medicine Normal ECG consists of multiple waveforms called COMPLEXES o Each complete cardiac cycle consists of P, QRS and T Waves COMPLEXES: P WAVE: ATRIAL DEPOLARIZATION (CONTRACTION) QRS Complex: VENTRICULAR DEPOLARIZTION (CONTRACTION) T Wave: RECOVERY WAVE (VENTRICULAR REPOLARIZATION)