CR 10: Myocarditis mimicking an acute coronary syndrome
... acute coronary syndrome was considered. • The patient received anti-ischemic treatment. ...
... acute coronary syndrome was considered. • The patient received anti-ischemic treatment. ...
Chapter 19: Blood Vessels
... 1. The stethoscope should be plugged in to channel 1 2. The ECG leads need to be plugged into channel 2 ...
... 1. The stethoscope should be plugged in to channel 1 2. The ECG leads need to be plugged into channel 2 ...
Electricity Wthin The Body
... *Across the surface or membrane of every neuron is an electrical potential (voltage) difference due to the presence of more "negative ions" on the inside of the membrane than the outside, 60 to 90 mv it's polarized. * This potential difference is called Resting Potential of the neuron. When the neur ...
... *Across the surface or membrane of every neuron is an electrical potential (voltage) difference due to the presence of more "negative ions" on the inside of the membrane than the outside, 60 to 90 mv it's polarized. * This potential difference is called Resting Potential of the neuron. When the neur ...
equine - Voorjaarsdagen
... The two most important physiological and pathological arrhythmias to differentiate are second degree atrioventricular block (2°AVB) and atrial fibrillation (AF). 2°Atrioventricular Block is the most common physiological dysrhythmia in horses appearing at rest when vagal tone is high. It is completel ...
... The two most important physiological and pathological arrhythmias to differentiate are second degree atrioventricular block (2°AVB) and atrial fibrillation (AF). 2°Atrioventricular Block is the most common physiological dysrhythmia in horses appearing at rest when vagal tone is high. It is completel ...
syllabus apk 6128 ekg interpretation fall semester, 2012
... Dean of Students Office will provide documentation to the student who must then provide this documentation to the instructor when requesting accommodation.” DISABILITY RESOURCE CENTER NOTE: “For optimal consideration, you must see the Professor within the first three (3) days of class.” ACADEMIC HON ...
... Dean of Students Office will provide documentation to the student who must then provide this documentation to the instructor when requesting accommodation.” DISABILITY RESOURCE CENTER NOTE: “For optimal consideration, you must see the Professor within the first three (3) days of class.” ACADEMIC HON ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... Specialized Excitatory and Conductive System a. Sinus (Sinoatrial node)-located in the wall of the right atrium and has almost no contractile muscle filaments b. Automatic rhythmicity-cardiac fibers with the ability of self-excitation ...
... Specialized Excitatory and Conductive System a. Sinus (Sinoatrial node)-located in the wall of the right atrium and has almost no contractile muscle filaments b. Automatic rhythmicity-cardiac fibers with the ability of self-excitation ...
Review Sheet
... 1. The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is about the size of a _________________________. 2. The heart is surrounded by a thin layer of tissue called the ______________________________ or heart sac. ...
... 1. The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is about the size of a _________________________. 2. The heart is surrounded by a thin layer of tissue called the ______________________________ or heart sac. ...
This is the new PowerPoint template
... Following CRT implant, approximately 20-25% of heart failure patients do not appear to improve. A key unmet need is a means to determine acute response to CRT pacing during implant and follow-up procedures. Such feedback may improve LV lead placement and programming, thus improving patient outcomes. ...
... Following CRT implant, approximately 20-25% of heart failure patients do not appear to improve. A key unmet need is a means to determine acute response to CRT pacing during implant and follow-up procedures. Such feedback may improve LV lead placement and programming, thus improving patient outcomes. ...
Postoperative rate induced left bundle branch block after craniotomy
... ischemia which cannot be detected n routine coronary angiography. Observational studies have shown greater possibilities of death and major cardiovascular events in patients developing LBBB during exercise or induced by rate. However, patients with normal coronaries presenting with exercise induced ...
... ischemia which cannot be detected n routine coronary angiography. Observational studies have shown greater possibilities of death and major cardiovascular events in patients developing LBBB during exercise or induced by rate. However, patients with normal coronaries presenting with exercise induced ...
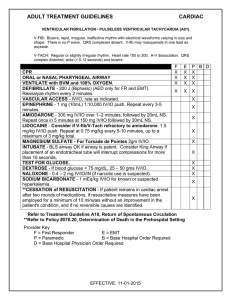
ventricular fibrillation - pulseless ventricular tachycardia (a01)
... placement of an endotracheal tube will interrupt compressions for more than 10 seconds. TEST FOR GLUCOSE. DEXTROSE - If blood glucose < 75 mg/dL, 25 – 50 gms IV/IO. NALOXONE - 0.4 – 2 mg IV/IO/IN (if narcotic use is suspected). SODIUM BICARBONATE - 1 mEq/kg IV/IO for known or suspected hyperkalemia. ...
... placement of an endotracheal tube will interrupt compressions for more than 10 seconds. TEST FOR GLUCOSE. DEXTROSE - If blood glucose < 75 mg/dL, 25 – 50 gms IV/IO. NALOXONE - 0.4 – 2 mg IV/IO/IN (if narcotic use is suspected). SODIUM BICARBONATE - 1 mEq/kg IV/IO for known or suspected hyperkalemia. ...
Cardiovascular System 1
... sympathetic - faster depolarization → ↑ heart rate parasympathetic - slower depolarization → ↓ heart rate 2. Myocardial Action Potential in Contractile Cells (0) initial AP depolarization - similar to other APs (voltage-gated Na+ channels) (1) slight repolarization (2) plateau phase (100-200 ms) - d ...
... sympathetic - faster depolarization → ↑ heart rate parasympathetic - slower depolarization → ↓ heart rate 2. Myocardial Action Potential in Contractile Cells (0) initial AP depolarization - similar to other APs (voltage-gated Na+ channels) (1) slight repolarization (2) plateau phase (100-200 ms) - d ...
Cardiac A&P
... • Pressure in ventricles is greater than pressure in great vessels (pulmonary artery and aorta) so… • Milliseconds later, the semilunar valves (pulmonic and aortic) open, and the ventricles contract. • Blood is forced thru the great vessels. • When pressure is low in ventricles, semilunar valves sna ...
... • Pressure in ventricles is greater than pressure in great vessels (pulmonary artery and aorta) so… • Milliseconds later, the semilunar valves (pulmonic and aortic) open, and the ventricles contract. • Blood is forced thru the great vessels. • When pressure is low in ventricles, semilunar valves sna ...
Cardiac Cycle and Intrinsic Beat - Mr. Lesiuk
... - The SA Node (also called the pacemaker) initiates the heartbeat and sends out an excitation impulses every 0.85 seconds. The impulse causes both Atria to contract. - When the impulse reaches the AV Node, an impulse is sent from the AV Node, down the "Bundles of His" and onto the Purkinje Fibers ca ...
... - The SA Node (also called the pacemaker) initiates the heartbeat and sends out an excitation impulses every 0.85 seconds. The impulse causes both Atria to contract. - When the impulse reaches the AV Node, an impulse is sent from the AV Node, down the "Bundles of His" and onto the Purkinje Fibers ca ...
Heart and Circulatory System?Arrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeat)
... that originate in the upper chambers of the heart, the atria, are referred to as "supraventricular" arrhythmias. The atria are the heart's pacemakers and also act as primers for the pump chambers, the ventricles. The most common atrial arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation, which is a rapid, irregular r ...
... that originate in the upper chambers of the heart, the atria, are referred to as "supraventricular" arrhythmias. The atria are the heart's pacemakers and also act as primers for the pump chambers, the ventricles. The most common atrial arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation, which is a rapid, irregular r ...
Disturbances of Rate and Rhythm
... are gradual. Rate infrequently exceeds 160/min but may reach 180/min in young persons. ...
... are gradual. Rate infrequently exceeds 160/min but may reach 180/min in young persons. ...
PDF
... higher officials/patients to keep track of their heart beat rate by self-opinion or for remote diagnosis of chronic heart disease patients before sudden flicker. This watch works by ceaseless monitoring over a person’s heart beat rate if any deflection is found it generates an alert. It is mainly us ...
... higher officials/patients to keep track of their heart beat rate by self-opinion or for remote diagnosis of chronic heart disease patients before sudden flicker. This watch works by ceaseless monitoring over a person’s heart beat rate if any deflection is found it generates an alert. It is mainly us ...
Pericarditis
... Pericarditis Causes Infections - Viruses (especially Coxsackie) - TB (often rapid effusion, look for calcification) - Other bacteria - Parasites Malignant pericarditis Uraemia Myocardial infarction Dressler's syndrome (10 days post MI) Trauma Radiotherapy Connective tissue disease ...
... Pericarditis Causes Infections - Viruses (especially Coxsackie) - TB (often rapid effusion, look for calcification) - Other bacteria - Parasites Malignant pericarditis Uraemia Myocardial infarction Dressler's syndrome (10 days post MI) Trauma Radiotherapy Connective tissue disease ...
There are three basic parts to an EKG: 5 things to
... There are two types: type 1 aka Wenckebach or Mobitz I and type 2 or Mobitz II Wenckebach (Mobitz I): the PR interval increases more and more with each beat until there’s a P wave without a QRS (aka the PR interval gets longer and longer and then there’s a drop). This usually occurs in a pattern. Tx ...
... There are two types: type 1 aka Wenckebach or Mobitz I and type 2 or Mobitz II Wenckebach (Mobitz I): the PR interval increases more and more with each beat until there’s a P wave without a QRS (aka the PR interval gets longer and longer and then there’s a drop). This usually occurs in a pattern. Tx ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... Division of Cardiology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx NY, USA ; ...
... Division of Cardiology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx NY, USA ; ...
Electrocardiogram
... seen with patients post Inferior MI, Digitalis toxicity, or postoperative Mobitz II more serious that Mobitz I less common than Mobitz I characterized by nonconducted sinus impulses despite constant PR intervals usually the QRS are widened because of a BBB, the dropped beat represents a fo ...
... seen with patients post Inferior MI, Digitalis toxicity, or postoperative Mobitz II more serious that Mobitz I less common than Mobitz I characterized by nonconducted sinus impulses despite constant PR intervals usually the QRS are widened because of a BBB, the dropped beat represents a fo ...
ECG Measurement and Analysis
... ~ and angle with respect to the x-axis, (α). The easiest is VI = H cos(α) vector amplitude (H) ~ and α in terms of two of the limb leads. Then use two of these expressions to solve for |H| Note that because of the redundancy in the system, you will only need two of the limb leads to determine the he ...
... ~ and angle with respect to the x-axis, (α). The easiest is VI = H cos(α) vector amplitude (H) ~ and α in terms of two of the limb leads. Then use two of these expressions to solve for |H| Note that because of the redundancy in the system, you will only need two of the limb leads to determine the he ...
Holter ECG - AMEDTEC Medizintechnik Aue GmbH
... AMEDTEC ECGpro Holter makes no compromises in the presentation of the ECG curves. From every graph and table you have direct access to the synchronous ECG. The whole ECG is shown in the typical speeds up to 50mm/s. Ventricular and supraventricular events as well as paced beats are color-highlighted. ...
... AMEDTEC ECGpro Holter makes no compromises in the presentation of the ECG curves. From every graph and table you have direct access to the synchronous ECG. The whole ECG is shown in the typical speeds up to 50mm/s. Ventricular and supraventricular events as well as paced beats are color-highlighted. ...
ECG basics
... across the chest and provide a view of the heart’s horizontal plane (see Precordial views, page 16): 䡵 The precordial lead V1 electrode is placed on the right side of the sternum at the fourth intercostal rib space. 䡵 Lead V2 is placed to the left of the sternum at the ...
... across the chest and provide a view of the heart’s horizontal plane (see Precordial views, page 16): 䡵 The precordial lead V1 electrode is placed on the right side of the sternum at the fourth intercostal rib space. 䡵 Lead V2 is placed to the left of the sternum at the ...
INTERPRETATION OF AN ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG / EKG
... There is an isoelectric line. The P wave is the wave of the atrial depolarization (be careful, it’s the depolarization of the right and the left atria!) The PR interval is the delay between the sinoatrial node and the atrioventricular node. The QRS complex corresponds to the depolarization of the i ...
... There is an isoelectric line. The P wave is the wave of the atrial depolarization (be careful, it’s the depolarization of the right and the left atria!) The PR interval is the delay between the sinoatrial node and the atrioventricular node. The QRS complex corresponds to the depolarization of the i ...
Document
... A.S.D If the hole is substantially large the patient will need to undergo open heart surgery. Many can lead a healthy life with this condition. They need medical attention. And arrhythmias may develop over time. ...
... A.S.D If the hole is substantially large the patient will need to undergo open heart surgery. Many can lead a healthy life with this condition. They need medical attention. And arrhythmias may develop over time. ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.