Peripheral Vascular Disease
... *All primary SCD prevention ICD recommendations apply only to patients who are receiving optimal medical therapy and have reasonable expectation of survival with good functional capacity for more than 1 year. ...
... *All primary SCD prevention ICD recommendations apply only to patients who are receiving optimal medical therapy and have reasonable expectation of survival with good functional capacity for more than 1 year. ...
Arrhythmias: Presentation and Associated Disease
... •The state of the patient will depend on the heart rate and underlying heart disease not the arrhythmia per se •The age of the patient, and associated disease can guide the provisional differential diagnosis before seeing the ECG •Examine for signs of AV dissociation ...
... •The state of the patient will depend on the heart rate and underlying heart disease not the arrhythmia per se •The age of the patient, and associated disease can guide the provisional differential diagnosis before seeing the ECG •Examine for signs of AV dissociation ...
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
... same time, the muscle cells themselves are unorganized or in disarray. This disease occurs in some fashion in approximately 1 out of 500 individuals. In many instances it is unrecognized and without any symptoms. It may, however, cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain and fainting. I ...
... same time, the muscle cells themselves are unorganized or in disarray. This disease occurs in some fashion in approximately 1 out of 500 individuals. In many instances it is unrecognized and without any symptoms. It may, however, cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain and fainting. I ...
study notes for test
... Diastolic blood pressure (the lower number) — indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats. Normal BP – 120/80 Hypertension: >140/90 Hypotension: <90/60 ...
... Diastolic blood pressure (the lower number) — indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats. Normal BP – 120/80 Hypertension: >140/90 Hypotension: <90/60 ...
PVC project
... A PVC is a depolarization that arises in either ventricle before the next expected sinus beat, i.e., prematurely. It may result from the firing of an automatic focus or reentry. Since PVCs originate in the ventricle, the normal sequence of ventricular depolarization is altered, i.e., instead of the ...
... A PVC is a depolarization that arises in either ventricle before the next expected sinus beat, i.e., prematurely. It may result from the firing of an automatic focus or reentry. Since PVCs originate in the ventricle, the normal sequence of ventricular depolarization is altered, i.e., instead of the ...
What is atrial fibrillation? Why has my cat got atrial fibrillation? How
... What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is one type of disturbance of the normal heart rhythm (dysrhythmia). To understand this disease we first need to know how the normal heart functions: In the normal heart electrical activity is initiated from a natural pacemaker in the heart and follow ...
... What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is one type of disturbance of the normal heart rhythm (dysrhythmia). To understand this disease we first need to know how the normal heart functions: In the normal heart electrical activity is initiated from a natural pacemaker in the heart and follow ...
Cardiology - Congestive Heart Failure
... nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other drugs which can lead to fluid retention such as rosglitazone (Avandia™). 6. Importance of age, gender and ethnicity on the prevalence and prognosis of CHF 7. Physiological basis and scientific evidence supporting each type of treatment, intervention, or ...
... nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other drugs which can lead to fluid retention such as rosglitazone (Avandia™). 6. Importance of age, gender and ethnicity on the prevalence and prognosis of CHF 7. Physiological basis and scientific evidence supporting each type of treatment, intervention, or ...
Basics of Pacing - St. Joseph Mercy Health System
... • Lead(s) • Systems can have up to three leads depending on implant indication ...
... • Lead(s) • Systems can have up to three leads depending on implant indication ...
The Cardiovascular System
... heart more elastic fibres those further away have more muscle fibre C. Tunica Externa – Contains collagen fibres for strength ...
... heart more elastic fibres those further away have more muscle fibre C. Tunica Externa – Contains collagen fibres for strength ...
Cardiac Arrest due to Recurrent Ventricular Fibrillation Triggered by
... A 51-year-old male patient was referred for a sudden out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Upon arrival, he was conscious and had no chest pain complaints. There was no abnormality in initial electrocardiographic and echocardiographic examinations. However, episodes of recurrent ventricular fibrillation ( ...
... A 51-year-old male patient was referred for a sudden out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Upon arrival, he was conscious and had no chest pain complaints. There was no abnormality in initial electrocardiographic and echocardiographic examinations. However, episodes of recurrent ventricular fibrillation ( ...
EKG Technician - Mrs. Covington`s Class Website
... Trace the flow of blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulatory systems. Describe the electrophysiology of the heart and relate the events of cardiac conduction to the electrocardiogram. Outline the process of electrocardiography. Explain the purpose of measuring the standard 12 lead electroc ...
... Trace the flow of blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulatory systems. Describe the electrophysiology of the heart and relate the events of cardiac conduction to the electrocardiogram. Outline the process of electrocardiography. Explain the purpose of measuring the standard 12 lead electroc ...
639 Arrhythmias - SA & Atrial
... • Treatment: DC cardioversion & O2 if patient is unstable • drugs: (rate control) b & Ca++ channel blockers, digitalis, to d AV Conduction • amiodarone to d AV conduction + prolong myocardial AP (u refractoriness of myocardium) •The danger of thromboembolic events are enhanced due to d flow in left ...
... • Treatment: DC cardioversion & O2 if patient is unstable • drugs: (rate control) b & Ca++ channel blockers, digitalis, to d AV Conduction • amiodarone to d AV conduction + prolong myocardial AP (u refractoriness of myocardium) •The danger of thromboembolic events are enhanced due to d flow in left ...
Adenosine Report
... Protocol: 1 Day Adenosine rest/stress Tc99m Myoview History: This is a 70 year old man with a history of coronary artery disease. He had coronary artery bypass surgery in 1996. Clinical Indications: Assessment of chest pain Procedure: The patient was given 32.6 mg Adenosine intravenously over 6 minu ...
... Protocol: 1 Day Adenosine rest/stress Tc99m Myoview History: This is a 70 year old man with a history of coronary artery disease. He had coronary artery bypass surgery in 1996. Clinical Indications: Assessment of chest pain Procedure: The patient was given 32.6 mg Adenosine intravenously over 6 minu ...
Spontaneously terminating ventricular fibrillation and
... family history of ischaemic heart disease, two of his uncles having died from ischaemic heart disease. There was no history of sudden death in the family. The patient smoked 80–90 g of tobacco per week. On examination he was well and had no fever. His pulse was 66 beats/min and regular, ...
... family history of ischaemic heart disease, two of his uncles having died from ischaemic heart disease. There was no history of sudden death in the family. The patient smoked 80–90 g of tobacco per week. On examination he was well and had no fever. His pulse was 66 beats/min and regular, ...
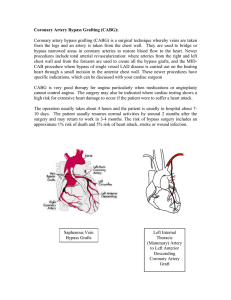
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
... from the legs and an artery is taken from the chest wall. They are used to bridge or bypass narrowed areas in coronary arteries to restore blood flow to the heart. Newer procedures include total arterial revascularization: where arteries from the right and left chest wall and from the forearm are us ...
... from the legs and an artery is taken from the chest wall. They are used to bridge or bypass narrowed areas in coronary arteries to restore blood flow to the heart. Newer procedures include total arterial revascularization: where arteries from the right and left chest wall and from the forearm are us ...
VALITUDE™ X4 CRT-P System Overview Brochure
... (S-ICD) is contraindicated because it may cause inappropriate therapy or inhibition of appropriate S-ICD therapy; • Single-chamber atrial pacing is contraindicated in patients with impaired AV nodal conduction; • Atrial tracking modes are contraindicated in patients with chronic refractory atrial ta ...
... (S-ICD) is contraindicated because it may cause inappropriate therapy or inhibition of appropriate S-ICD therapy; • Single-chamber atrial pacing is contraindicated in patients with impaired AV nodal conduction; • Atrial tracking modes are contraindicated in patients with chronic refractory atrial ta ...
AED Study Guide
... CPR is performed in conjunction with the use of an automated external defibrillator (AED). An AED is a device that analyzes the heart’s electrical rhythm and, if necessary, prompts you to deliver a shock to a person experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. Defibrillation is a process of delivering an ele ...
... CPR is performed in conjunction with the use of an automated external defibrillator (AED). An AED is a device that analyzes the heart’s electrical rhythm and, if necessary, prompts you to deliver a shock to a person experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. Defibrillation is a process of delivering an ele ...
Escape-capture bigeminy caused by blocked - Heart
... the atrioventricular nodal pacemaker (Schamroth and Dubb, I965) is the PP interval encompassing the blocked atrial extrasystole, i.e. the sum of preand post-extrasystolic PP intervals; PP' + P'P which equals I.I2S. This is slightly longer than the atrioventricular nodal escape rhythm and thereby per ...
... the atrioventricular nodal pacemaker (Schamroth and Dubb, I965) is the PP interval encompassing the blocked atrial extrasystole, i.e. the sum of preand post-extrasystolic PP intervals; PP' + P'P which equals I.I2S. This is slightly longer than the atrioventricular nodal escape rhythm and thereby per ...
(IFRAME) Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs
... valves. The murmur's location and intensity helps determine its significance. Heart rhythm is also assessed during auscultation, and if there ...
... valves. The murmur's location and intensity helps determine its significance. Heart rhythm is also assessed during auscultation, and if there ...
4B Worksheet
... sulcus, supplies ______________blood to the ________________artery and the anterior ________________artery which is located in the _________________groove or sulcus. 4) The Atria are separated by the ______________septum where you will find remnants of an internal depression referred to as the _____ ...
... sulcus, supplies ______________blood to the ________________artery and the anterior ________________artery which is located in the _________________groove or sulcus. 4) The Atria are separated by the ______________septum where you will find remnants of an internal depression referred to as the _____ ...
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Originating From Right
... Introduction: Brugada Syndrome is a cardiac ion channel disorder that affects the sodium current. This syndrome is characterized by cove-shaped ST elevation in ECG leads V1 to V3 in the absence of structural heart disease. Case Presentation: A 36-year-old man diagnosed with Brugada Syndrome was reff ...
... Introduction: Brugada Syndrome is a cardiac ion channel disorder that affects the sodium current. This syndrome is characterized by cove-shaped ST elevation in ECG leads V1 to V3 in the absence of structural heart disease. Case Presentation: A 36-year-old man diagnosed with Brugada Syndrome was reff ...
Decreased cardiac output due to the heart pump failing
... Use angle of Louis as arbitrary reference point, and compare it with highest level of venous pulsation Hold a vertical ruler on sternal angle Align a straight edge on ruler like a T-square, and adjust level of horizontal straight edge to level of pulsation Read level of intersection on verti ...
... Use angle of Louis as arbitrary reference point, and compare it with highest level of venous pulsation Hold a vertical ruler on sternal angle Align a straight edge on ruler like a T-square, and adjust level of horizontal straight edge to level of pulsation Read level of intersection on verti ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.