File
... 2. Veins carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 3. Define myocardium. 4. What is the normal blood pressure? 5. Where are the atria located? 6. Arteries carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 7. Define edema. 8. List the symptoms of a heart attack. 9. What is the function ...
... 2. Veins carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 3. Define myocardium. 4. What is the normal blood pressure? 5. Where are the atria located? 6. Arteries carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 7. Define edema. 8. List the symptoms of a heart attack. 9. What is the function ...
Risk factors for heart disease
... sensation., burning sensation like indigestion it may radiate to the left jaw or arm, SOB, anxiety, light-headedness ...
... sensation., burning sensation like indigestion it may radiate to the left jaw or arm, SOB, anxiety, light-headedness ...
SELF-ORGANIZING PIECEWISE AGGREGATE APPROXIMATION
... are clustered using the k-means clustering algorithm for the results presented here. However, the authors note that SOPAA can be paired with a variety of other clustering or classification algorithms. The basic k-means algorithm fixes the position of n class centroids and calculates the distance of ...
... are clustered using the k-means clustering algorithm for the results presented here. However, the authors note that SOPAA can be paired with a variety of other clustering or classification algorithms. The basic k-means algorithm fixes the position of n class centroids and calculates the distance of ...
heart trivia
... 6. How big is an average heart of a grown-up? 7. How many times does an average human heart beat? 8. Why is laughter healthy for the body? TASK 4. Work in pairs. One person looks at the infographic, the other one only looks at the questions in Task 3. The person who looks at the questions reads them ...
... 6. How big is an average heart of a grown-up? 7. How many times does an average human heart beat? 8. Why is laughter healthy for the body? TASK 4. Work in pairs. One person looks at the infographic, the other one only looks at the questions in Task 3. The person who looks at the questions reads them ...
cardiovascular terms - AAEC Veterinary Science
... 7. necrosis = dead tissue as a result of ischemia a. infarct = area of necrosis 8. electrocardiogram = record of electrical activity of the heart 9. arrhythmia = abnormal rhythm of the heart 10. systole = contraction of the ventricles (largest chambers of heart) 11. diastole = relaxation of the vent ...
... 7. necrosis = dead tissue as a result of ischemia a. infarct = area of necrosis 8. electrocardiogram = record of electrical activity of the heart 9. arrhythmia = abnormal rhythm of the heart 10. systole = contraction of the ventricles (largest chambers of heart) 11. diastole = relaxation of the vent ...
Human Body Systems - Athens Academy ~Homepage
... • Heart is divided into 4 chambers… – Top two chambers = atria (left and right) – Bottom two chambers = ventricles (left and right) ...
... • Heart is divided into 4 chambers… – Top two chambers = atria (left and right) – Bottom two chambers = ventricles (left and right) ...
Advances in Electronic Sensoring Through High
... Chronis, D. I. Tseles (2007)]. According to patients’ needs, such system has not to be only affordable and user friendly, but also “invisible”, autonomous in terms of power consumption and able to assist individuals in their own health management. ΙΙ. Progress Beyond the State of The Art The creatio ...
... Chronis, D. I. Tseles (2007)]. According to patients’ needs, such system has not to be only affordable and user friendly, but also “invisible”, autonomous in terms of power consumption and able to assist individuals in their own health management. ΙΙ. Progress Beyond the State of The Art The creatio ...
Elina Barnabas
... almost all of the body’s 75 trillion cells. Only the corneas receive no blood supply. The human heart is a very special organ. It is the only organ with a specialised type of muscle fibers; the Cardiac Muscle. In addition to this, it has specialised cells responsible for generating electrical impuls ...
... almost all of the body’s 75 trillion cells. Only the corneas receive no blood supply. The human heart is a very special organ. It is the only organ with a specialised type of muscle fibers; the Cardiac Muscle. In addition to this, it has specialised cells responsible for generating electrical impuls ...
Get Educated to Prevent Sudden Cardiac Death
... of cardiac arrest—and if you begin chest compressions replaced by a distinctive rapid wavy line, characteristic in such individuals, they are more likely to continue of ventricular fibrillation (Figure below). to gasp—a sign that you are doing a good job! Do not stop chest compressions when someone ...
... of cardiac arrest—and if you begin chest compressions replaced by a distinctive rapid wavy line, characteristic in such individuals, they are more likely to continue of ventricular fibrillation (Figure below). to gasp—a sign that you are doing a good job! Do not stop chest compressions when someone ...
CT Anatomy of the Heart
... • The tricuspid valve is contained within the anterior atrioventricular ring between the RA and RV. • Right Ventricle: resides immediately posterior to the sternum. The right ventricular surface of the interventricular septum is irregular. The septomarginal trabeculation has papillary muscles extend ...
... • The tricuspid valve is contained within the anterior atrioventricular ring between the RA and RV. • Right Ventricle: resides immediately posterior to the sternum. The right ventricular surface of the interventricular septum is irregular. The septomarginal trabeculation has papillary muscles extend ...
Advances in Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology
... Leads I, aVF, and frontal plane vectorcardiogram shown at baseline, during ventricular pacing, 1 hour after interruption of ventricular pacing for 7, 21, and 3 days after cessation of ventricular pacing. Leads I and aVF are shown (top). At baseline (left column), the T waves during sinus rhythm are ...
... Leads I, aVF, and frontal plane vectorcardiogram shown at baseline, during ventricular pacing, 1 hour after interruption of ventricular pacing for 7, 21, and 3 days after cessation of ventricular pacing. Leads I and aVF are shown (top). At baseline (left column), the T waves during sinus rhythm are ...
The Cardiovascular System - Mediapolis Community School
... from the right atrium to the right ventricle. • The pulmonary valve allows blood to leave the right ventricle and prevents backflow into the ventricular chamber. • The mitral valve permits blood to move from the left atrium to the left ventricle. • The aortic valve allows blood to move from the left ...
... from the right atrium to the right ventricle. • The pulmonary valve allows blood to leave the right ventricle and prevents backflow into the ventricular chamber. • The mitral valve permits blood to move from the left atrium to the left ventricle. • The aortic valve allows blood to move from the left ...
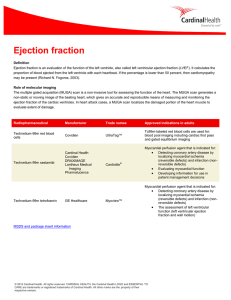
Nuclear Medicine: Ejection Fraction
... Ejection fraction is an evaluation of the function of the left ventricle, also called left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). It calculates the proportion of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat. If the percentage is lower than 50 percent, then cardiomyopathy may be present ( ...
... Ejection fraction is an evaluation of the function of the left ventricle, also called left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). It calculates the proportion of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat. If the percentage is lower than 50 percent, then cardiomyopathy may be present ( ...
ITU Event Information for ITU Website
... stimulation to multi-organs of the human body will unavoidably elicit Acute Trauma or Sickness (ATS) of the cardiovascular, respiratory, central nervous, gastrointestinal and motor (bone and muscle etc.) systems, which in serious cases, will endanger the competitor’s life. 1.2 Because of the unpredi ...
... stimulation to multi-organs of the human body will unavoidably elicit Acute Trauma or Sickness (ATS) of the cardiovascular, respiratory, central nervous, gastrointestinal and motor (bone and muscle etc.) systems, which in serious cases, will endanger the competitor’s life. 1.2 Because of the unpredi ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... doctors to see the cardiac actions of a particular person. It provides a graphic depiction of the electrical forces generated by the heart and then by analysing this graph doctors can tell about any abnormality present in heart. In the paper we focus on the QRS complex detection in electrocardiogram ...
... doctors to see the cardiac actions of a particular person. It provides a graphic depiction of the electrical forces generated by the heart and then by analysing this graph doctors can tell about any abnormality present in heart. In the paper we focus on the QRS complex detection in electrocardiogram ...
Cardiomyopathy
... ventricular arrhythmias, systemic embolization and progressive heart failure. Biventricular pacing may be helpful in patients with a QRS interval > 130 msecs to improve symptoms. In patients with dilated cardiomyopathy associated with a prior myocardial infarction and a left ventricular ejection fra ...
... ventricular arrhythmias, systemic embolization and progressive heart failure. Biventricular pacing may be helpful in patients with a QRS interval > 130 msecs to improve symptoms. In patients with dilated cardiomyopathy associated with a prior myocardial infarction and a left ventricular ejection fra ...
Topic 2.2 Cardiovascular System Student Outline
... 2.2.4: Describe the intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of heart rate and the sequence of excitation of the heart muscle. o The heart has it’s own pacemaker, but heart rate is also influence by the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system and by adrenaline. (It should ...
... 2.2.4: Describe the intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of heart rate and the sequence of excitation of the heart muscle. o The heart has it’s own pacemaker, but heart rate is also influence by the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system and by adrenaline. (It should ...
Polar S810 as an Alternative Resource to the Use of the
... Background: The 4-second exercise test (T4s) evaluates the cardiac vagal tone during the initial heart rate (HR) transient at sudden dynamic exercise, through the identification of the cardiac vagal index (CVI) obtained from the electrocardiogram (ECG). Objective: To evaluate the use of the Polar S8 ...
... Background: The 4-second exercise test (T4s) evaluates the cardiac vagal tone during the initial heart rate (HR) transient at sudden dynamic exercise, through the identification of the cardiac vagal index (CVI) obtained from the electrocardiogram (ECG). Objective: To evaluate the use of the Polar S8 ...
First Aid Power Point 2
... • Call: Once you check to see if the victim is safe call 911 • Care: Care for the victim if ok by the person. If the victim can’t speak then provide care for the individual. ...
... • Call: Once you check to see if the victim is safe call 911 • Care: Care for the victim if ok by the person. If the victim can’t speak then provide care for the individual. ...
Review guide for test 2 – Chapters 21, 22 and 23
... Heart histology – 3 layers of the heart wall and their composition ...
... Heart histology – 3 layers of the heart wall and their composition ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.