* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
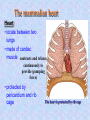
Download The heart is protected by rib cage
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
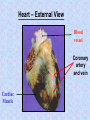
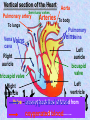
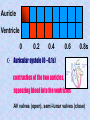
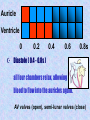
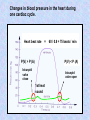
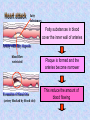
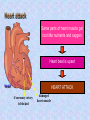
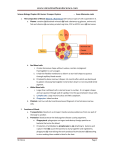
The mammalian heart Heart • locate between two lungs • made of cardiac muscle contracts and relaxes continuously to provide (pumping force) • protected by pericardium and rib cage The heart is protected by rib cage Heart – External View Blood vessel Coronary artery and vein Cardiac Muscle Vertical section of the Heart Semi-lunar valves Pulmonary artery Arteries To lungs Aorta To body Pulmonary Veinsveins Vena Veins cava Left auricle bicuspid valve Right auricle tricuspid valve septum Left Right ventricle ventricle Valve – deoxygenated prevent back flow of blood from blood ……………… toblood …………….. oxygenated Oxygenated blood Higher oxygen concentration Full of Oxygen Lower carbon dioxide concentration Deoxygenated blood Lower oxygen concentration Full of carbon dioxide Higher carbon dioxide concentration The cardiac cycle (the sequence of events that takes place in one heart beat) The heart beats as the cardiac muscles in its wall contracts (systole) and relaxes (diastole). Auricle Ventricle 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8s Auricle Ventricle 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8s Auricular systole (0 –0.1s) contraction of the two auricles, squeezing blood into the ventricles AV valves (open), semi-lunar valves (close) Auricle Ventricle 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8s Ventricular systole (0.1 –0.4s) contraction of the two ventricles, forcing blood out of the ventricles into the arteries AV valves (close), semi-lunar valves (open) Auricle Ventricle 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8s Diastole ( 0.4 - 0.8s ) all four chambers relax, allowing blood to flow into the auricles again. AV valves (open), semi-lunar valves (close) Changes in blood pressure in the heart during one cardiac cycle. Heart beat rate = P(V) > P (A) 60 / 0.8 = 75 beats / min P(V) < P (A) bicuspid valve close bicuspid valve open 1st heat sound Heart attack fatty substances Fatty substances in blood cover the inner wall of arteries Normal artery Artery with fatty deposits blood flow restricted Formation of blood clot (artery blocked by blood clot) Plaque is formed and the arteries become narrower This reduce the amount of blood flowing Heart attack Same parts of heart muscle get too little nutrients and oxygen Heart beat is upset heart HEART ATTACK if coronary artery is blocked damaged heart muscle