Massively parallel simulation of cardiac electrical
... body in the form of the electrocardiogram (ECG). The QT interval, the time between the ”QRS” complex and the ”T” wave in the ECG, roughly corresponds to the period of time between the upstroke of the AP and repolarization. Heart rhythm disorders, or arrhythmias, refer to a disruption of the normal e ...
... body in the form of the electrocardiogram (ECG). The QT interval, the time between the ”QRS” complex and the ”T” wave in the ECG, roughly corresponds to the period of time between the upstroke of the AP and repolarization. Heart rhythm disorders, or arrhythmias, refer to a disruption of the normal e ...
chapter 14 Cardiac B
... • The cells of the SA node set the heart rate because their rhythm is fastest. • They set the pace. • If the SA node is damaged, the other pacemakers still function, the pace lowers. ...
... • The cells of the SA node set the heart rate because their rhythm is fastest. • They set the pace. • If the SA node is damaged, the other pacemakers still function, the pace lowers. ...
An ECG Primer
... earlier, a 12 lead ECG is a superior diagnostic tool both for dysrhythmia monitoring and for other tasks such as ischemia monitoring. While some cardiac monitor manufacturers include a 10 wire cable to enable real-time 12 lead ECG monitoring, these cables tend to be bulky and restrictive. In an effo ...
... earlier, a 12 lead ECG is a superior diagnostic tool both for dysrhythmia monitoring and for other tasks such as ischemia monitoring. While some cardiac monitor manufacturers include a 10 wire cable to enable real-time 12 lead ECG monitoring, these cables tend to be bulky and restrictive. In an effo ...
ECGprimer
... earlier, a 12 lead ECG is a superior diagnostic tool both for dysrhythmia monitoring and for other tasks such as ischemia monitoring. While some cardiac monitor manufacturers include a 10 wire cable to enable real-time 12 lead ECG monitoring, these cables tend to be bulky and restrictive. In an effo ...
... earlier, a 12 lead ECG is a superior diagnostic tool both for dysrhythmia monitoring and for other tasks such as ischemia monitoring. While some cardiac monitor manufacturers include a 10 wire cable to enable real-time 12 lead ECG monitoring, these cables tend to be bulky and restrictive. In an effo ...
Pregnant Patients with Ebstein`s Anomaly Clinical and
... left ventricular (LV) dysfunction is rare. While pregnant patients with EA are usually acyanotic, those with interatrial shunting can develop shunt reversal and cyanosis in pregnancy. Paradoxical embolism can occur even in totally asymptomatic patients. The presence of arrhythmia or cyanosis in the ...
... left ventricular (LV) dysfunction is rare. While pregnant patients with EA are usually acyanotic, those with interatrial shunting can develop shunt reversal and cyanosis in pregnancy. Paradoxical embolism can occur even in totally asymptomatic patients. The presence of arrhythmia or cyanosis in the ...
10. Behçet`s Disease and the Heart
... Problems with the heart may be caused by thrombosis (blockage due to clotting) of large blood vessels or by vasculitis (inflammation) of smaller blood vessels, such as the arteries providing the blood supply to the heart muscle. Vasculitis can cause inflammation or fibrosis (scarring) of the heart m ...
... Problems with the heart may be caused by thrombosis (blockage due to clotting) of large blood vessels or by vasculitis (inflammation) of smaller blood vessels, such as the arteries providing the blood supply to the heart muscle. Vasculitis can cause inflammation or fibrosis (scarring) of the heart m ...
Chapter 1
... estimation of HR accurate enough for most clinical purposes. First, establish that the QRS complexes are coming along at fairly regular intervals (i.e., the R-R interval is consistent). This is important because in the presence of varying R-R intervals the estimation of rate by the triplet method wi ...
... estimation of HR accurate enough for most clinical purposes. First, establish that the QRS complexes are coming along at fairly regular intervals (i.e., the R-R interval is consistent). This is important because in the presence of varying R-R intervals the estimation of rate by the triplet method wi ...
The Cardiovascular System
... veins Right atrium Right coronary artery (in coronary sulcus) Anterior cardiac vein Right ventricle Right marginal artery Small cardiac vein Inferior vena cava ...
... veins Right atrium Right coronary artery (in coronary sulcus) Anterior cardiac vein Right ventricle Right marginal artery Small cardiac vein Inferior vena cava ...
DCM
... Cells in the heart muscle use lipids as they energy source Impaired cardiac function seems to be the result of increased lipid production in the heart muscle cells ...
... Cells in the heart muscle use lipids as they energy source Impaired cardiac function seems to be the result of increased lipid production in the heart muscle cells ...
as a PDF
... stratification in patients with populationally important cardiovascular diseases. QT interval changes are also a marker of proarrhythmia risk related to treatment with many, not only cardiovascular, drugs. Most often the so-called static correction models are used for QT interval correction (accordi ...
... stratification in patients with populationally important cardiovascular diseases. QT interval changes are also a marker of proarrhythmia risk related to treatment with many, not only cardiovascular, drugs. Most often the so-called static correction models are used for QT interval correction (accordi ...
Inferior and Rt Vent MI ppt
... More commonly occurs with inferior wall MI, occurring in 30-50 % of such cases. ...
... More commonly occurs with inferior wall MI, occurring in 30-50 % of such cases. ...
Day 4 Circulatory System Dissection Guide
... body. Locate the right and left sides of the heart. 3. Each side of the heart has an upper and a lower chamber. Upper chambers are called atria and receive blood, while lower chambers are called ventricles and pump blood out of the heart. Locate the right and left atria and ventricle. 4. Notice that ...
... body. Locate the right and left sides of the heart. 3. Each side of the heart has an upper and a lower chamber. Upper chambers are called atria and receive blood, while lower chambers are called ventricles and pump blood out of the heart. Locate the right and left atria and ventricle. 4. Notice that ...
Cardiovascular emergency crisis: Arrhythmias EKG and Cardiac Arrest
... What an arrhythmia is, and what it does (and doesn’t do) to people About rhythm strips, Holter monitors, and event monitors To determine the heart rate from the EKG The four basic types of arrhythmias To recognize the four common types of sinus arrhythmias What an ectopic rhythm is, and the mechanis ...
... What an arrhythmia is, and what it does (and doesn’t do) to people About rhythm strips, Holter monitors, and event monitors To determine the heart rate from the EKG The four basic types of arrhythmias To recognize the four common types of sinus arrhythmias What an ectopic rhythm is, and the mechanis ...
STUDY GUIDE BSL 111
... 4.) Blood vessels – human vessel model – Identify listed vessels -- fetal pig – blue are veins, pink are arteries remember L vs. R and artery and vein 5.) Case Study – arterial bleeding is generally worse than venous bleeding, blood flow is fastest in aorta and slowest in capillaries, 55-60% of bl ...
... 4.) Blood vessels – human vessel model – Identify listed vessels -- fetal pig – blue are veins, pink are arteries remember L vs. R and artery and vein 5.) Case Study – arterial bleeding is generally worse than venous bleeding, blood flow is fastest in aorta and slowest in capillaries, 55-60% of bl ...
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guiding Pacemaker
... sparing of the epiphyses (Figure 1A).2 Over the last 5 years the patient has been stable through daily oral administration of 5 mg prednisolone. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging was performed to guide placement of the pacemaker electrodes and visualize the overall and local extent of tumor due to ...
... sparing of the epiphyses (Figure 1A).2 Over the last 5 years the patient has been stable through daily oral administration of 5 mg prednisolone. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging was performed to guide placement of the pacemaker electrodes and visualize the overall and local extent of tumor due to ...
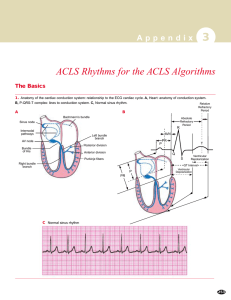
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
... ■ Atrial flutter ➔ impulses take a circular course around the atria, setting up the flutter waves ■ Mechanism of impulse formation: reentry ...
... ■ Atrial flutter ➔ impulses take a circular course around the atria, setting up the flutter waves ■ Mechanism of impulse formation: reentry ...
Innocent Heart Murmurs - Metropolitan Community College
... – Related to valve problems and produce symptoms ...
... – Related to valve problems and produce symptoms ...
Confucius and Mencius Excerpts
... state, hatchets and axes besieged it. Could it remain verdant? Due to the rest it got during the day or night, and the moisture of rain and dew, it was not that there were no sprouts or shoots growing there. But oxen and sheep then came and grazed on them. Hence, it was as if it were barren. People, ...
... state, hatchets and axes besieged it. Could it remain verdant? Due to the rest it got during the day or night, and the moisture of rain and dew, it was not that there were no sprouts or shoots growing there. But oxen and sheep then came and grazed on them. Hence, it was as if it were barren. People, ...
ANTIARRYTHMIC DRUGS
... An AP will travel down the branch 1, into the common distal path (br 3), then travel retrograde through the unidirectional block in branch 2. When the AP exits the block, if it finds the tissue excitable, it will continue by traveling down (reenter) the branch 1. If it finds the tissue unexcitable ( ...
... An AP will travel down the branch 1, into the common distal path (br 3), then travel retrograde through the unidirectional block in branch 2. When the AP exits the block, if it finds the tissue excitable, it will continue by traveling down (reenter) the branch 1. If it finds the tissue unexcitable ( ...
Clinical Concept of Heart Failure
... In an experimental study of short-term hibernation, dobutamine infusion resulted in myocardial infarction (right) when subendocardial blood flow was further reduced from 0.17 mL/min per gram (right). With and Without indicate with and without infarction. Reproduced with kind permission of Professor ...
... In an experimental study of short-term hibernation, dobutamine infusion resulted in myocardial infarction (right) when subendocardial blood flow was further reduced from 0.17 mL/min per gram (right). With and Without indicate with and without infarction. Reproduced with kind permission of Professor ...
The Circulatory System
... • Epicardium- same as the visceral layer of the pericardium • Myocardium- thick contractile cardiac muscle cells. The cells are tightly joined together to form a syncytium which transmits action potentials seamlessly. • Endocardium- thin layer that covers muscular projections called trabeculae. This ...
... • Epicardium- same as the visceral layer of the pericardium • Myocardium- thick contractile cardiac muscle cells. The cells are tightly joined together to form a syncytium which transmits action potentials seamlessly. • Endocardium- thin layer that covers muscular projections called trabeculae. This ...
A CARE STUDY OF A PATIENT WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
... • 1. Chest pain • A. Severe, diffuse, steady sub sternal pain; may be described as crushing, squeezing, or dull • B .Not relived by rest or sublingual vasodilator therapy, but requires opioids • C. May radiate to the arms (usually the left), shoulders, neck, back, and/or jaw • D. Continues for more ...
... • 1. Chest pain • A. Severe, diffuse, steady sub sternal pain; may be described as crushing, squeezing, or dull • B .Not relived by rest or sublingual vasodilator therapy, but requires opioids • C. May radiate to the arms (usually the left), shoulders, neck, back, and/or jaw • D. Continues for more ...
Lecture Notes
... – Recording of overall spread of activity throughout heart during depolarization and repolarization – Not a recording of a single action potential in a single cell at a single point in time – Comparisons in voltage detected by electrodes at two different points on body surface, not the actual potent ...
... – Recording of overall spread of activity throughout heart during depolarization and repolarization – Not a recording of a single action potential in a single cell at a single point in time – Comparisons in voltage detected by electrodes at two different points on body surface, not the actual potent ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.