Salivary Amylase
... Gastric juices – controlled by hormone called Gastrin – food in mouth Pepsinogen –contact with acid Pepsin Proteins –pepsin polypeptides Mucin – forms a layer of mucus After 3-4 hours - chyme DUODENUM Pancreas o Starch –amylase Maltose o Lipids –Lipase Fatty acids and glycerol o Tryp ...
... Gastric juices – controlled by hormone called Gastrin – food in mouth Pepsinogen –contact with acid Pepsin Proteins –pepsin polypeptides Mucin – forms a layer of mucus After 3-4 hours - chyme DUODENUM Pancreas o Starch –amylase Maltose o Lipids –Lipase Fatty acids and glycerol o Tryp ...
Digestive-2404digestivesystem12-04-06-1-
... Intestinal crypts – simple tubular glands Lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue Epithelium changes at anal canal ...
... Intestinal crypts – simple tubular glands Lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue Epithelium changes at anal canal ...
Presentation - Online Veterinary Anatomy Museum
... Look at slide 153. Note that the glands lie within the capsule of the thyroid. Q 9. What is the main cell type present in this gland? ...
... Look at slide 153. Note that the glands lie within the capsule of the thyroid. Q 9. What is the main cell type present in this gland? ...
Digestive System - El Camino College
... • I. Liver- considered the largest gland, it performs over 500 functions that influence several systems beside the digestive system. In regards to the digestive system it produces bile. A substance that emulsifies fat and makes it accessible to fat digesting enzymes. The liver is involved in balanc ...
... • I. Liver- considered the largest gland, it performs over 500 functions that influence several systems beside the digestive system. In regards to the digestive system it produces bile. A substance that emulsifies fat and makes it accessible to fat digesting enzymes. The liver is involved in balanc ...
Digestion - Net Start Class
... • Enzymes continue the chemical reactions on the food – chemical digestion • The nutrients are broken down small enough to pass through the lining of the small intestine, and into the blood (diffusion). • Digests proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. • Peristalsis = mechanical digestion ...
... • Enzymes continue the chemical reactions on the food – chemical digestion • The nutrients are broken down small enough to pass through the lining of the small intestine, and into the blood (diffusion). • Digests proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. • Peristalsis = mechanical digestion ...
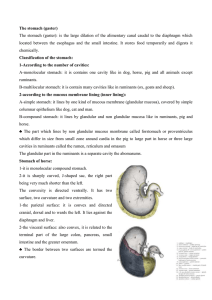
The stomach (gaster)
... cranial, dorsal and to wards the left. It lies against the diaphragm and liver. 2-the visceral surface: also convex, it is related to the terminal part of the large colon, pancreas, small intestine and the greater omentum. ♣ The border between two surfaces are termed the curvature. ...
... cranial, dorsal and to wards the left. It lies against the diaphragm and liver. 2-the visceral surface: also convex, it is related to the terminal part of the large colon, pancreas, small intestine and the greater omentum. ♣ The border between two surfaces are termed the curvature. ...
Digestive System
... • Mixture of exocrine and endocrine tissue • Elongated gland located behind and below the stomach • Endocrine function – Islets of Langerhans • Found throughout pancreas • Secrete insulin and glucagon ...
... • Mixture of exocrine and endocrine tissue • Elongated gland located behind and below the stomach • Endocrine function – Islets of Langerhans • Found throughout pancreas • Secrete insulin and glucagon ...
The Endocrine System - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... Glucagon: promotes movement of glucose into the blood by breaking down glycogen stored in liver cells ...
... Glucagon: promotes movement of glucose into the blood by breaking down glycogen stored in liver cells ...
The Digestive System - Valhalla High School
... Near the point where the small intestine and large intestine meet, there is a small fingerlike projection called the appendix. In modern humans, the appendix serves no purpose. It is believed that in our evolutionary past the appendix did aid in digestion. Organs, such as the appendix are called ves ...
... Near the point where the small intestine and large intestine meet, there is a small fingerlike projection called the appendix. In modern humans, the appendix serves no purpose. It is believed that in our evolutionary past the appendix did aid in digestion. Organs, such as the appendix are called ves ...
And through a series of chemical reactions, break down these
... 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be ...
... 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be ...
Section IX – Digestive System
... Section IX – Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source of energy through absorption of nutrients and to eliminate solid waste products. The GI tract ...
... Section IX – Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source of energy through absorption of nutrients and to eliminate solid waste products. The GI tract ...
Digestive System
... • Ingestion occurs when food enters the mouth. • It is mechanically broken down by teeth. Question: Is this a form of digestion? ...
... • Ingestion occurs when food enters the mouth. • It is mechanically broken down by teeth. Question: Is this a form of digestion? ...
Chapter 14 PowerPoint
... highly folded (circular folds). These folds have villi on them which are made up of cells with microvilli. All of which make more surface area for absorption. ...
... highly folded (circular folds). These folds have villi on them which are made up of cells with microvilli. All of which make more surface area for absorption. ...
File - Sanders School
... (split into 3 sections) that breaks down food using enzymes released by the pancreas and bile from the liver. Peristalsis is also at work here, moving food through and mixing it with digestive secretions from the pancreas and liver. The first part is largely responsible for the continuous breakingdo ...
... (split into 3 sections) that breaks down food using enzymes released by the pancreas and bile from the liver. Peristalsis is also at work here, moving food through and mixing it with digestive secretions from the pancreas and liver. The first part is largely responsible for the continuous breakingdo ...
Adrenal glands
... Pancreas Parathyroid gland Pineal gland (draw this in) Pituitary Testes Thymus gland (draw this in) Thyroid gland ...
... Pancreas Parathyroid gland Pineal gland (draw this in) Pituitary Testes Thymus gland (draw this in) Thyroid gland ...
The Digestive System - Valhalla High School
... Near the point where the small intestine and large intestine meet, there is a small fingerlike projection called the appendix. In modern humans, the appendix serves no purpose. It is believed that in our evolutionary past the appendix did aid in digestion. Organs, such as the appendix are called ves ...
... Near the point where the small intestine and large intestine meet, there is a small fingerlike projection called the appendix. In modern humans, the appendix serves no purpose. It is believed that in our evolutionary past the appendix did aid in digestion. Organs, such as the appendix are called ves ...
Digestive System - Sheweat Kubrom`s Technology System Portfolio
... The jejunum is the next portion of the small intestine, and it has a lining which is specialized in the absorption of carbohydrates and proteins. The proteins have been broken down in the stomach by enzymes called pepsin and acid into amino acids. The carbohydrates are broken down in the duodenum by ...
... The jejunum is the next portion of the small intestine, and it has a lining which is specialized in the absorption of carbohydrates and proteins. The proteins have been broken down in the stomach by enzymes called pepsin and acid into amino acids. The carbohydrates are broken down in the duodenum by ...
Objectives for Chapter 9
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
Digestion
... The digestive system is, in essence, a long tube that starts at the mouth and ends at the anus. This tube connects with the various organs and passages that play important roles in digestion. One of the most important things to know about the digestive system is the manner in which it propels food. ...
... The digestive system is, in essence, a long tube that starts at the mouth and ends at the anus. This tube connects with the various organs and passages that play important roles in digestion. One of the most important things to know about the digestive system is the manner in which it propels food. ...
1.Fecal pH test
... ampular of vater, before entering the duodenum through the sphincter of oddi. 2. Islets of Langerhans -These are endocrine cells that secrete insulin and glucagon. -Insulin and glucagon are important for CHO metabolism. ...
... ampular of vater, before entering the duodenum through the sphincter of oddi. 2. Islets of Langerhans -These are endocrine cells that secrete insulin and glucagon. -Insulin and glucagon are important for CHO metabolism. ...
Specialised parts of the digestive system
... – salivary glands (moisten food and contain enzymes) Oesophagus – peristalsis Stomach – physical and chemical digestion Liver bile Pancreas enzymes Small intestine(first part) enzymes Small intestine (second part) absorption Large intestine absorbs water ...
... – salivary glands (moisten food and contain enzymes) Oesophagus – peristalsis Stomach – physical and chemical digestion Liver bile Pancreas enzymes Small intestine(first part) enzymes Small intestine (second part) absorption Large intestine absorbs water ...
Document
... Pass post. to the stomach & sup. to pancreas Enters the ?? ligament to reach the hilum of the spleen Branches: pancreatic arteries (retroperitoneally) short gastric arteries (#5-6, to the fundus) left gastro-epiploic a. (greater curvature on lf.) (synonym: gastro-omental) ...
... Pass post. to the stomach & sup. to pancreas Enters the ?? ligament to reach the hilum of the spleen Branches: pancreatic arteries (retroperitoneally) short gastric arteries (#5-6, to the fundus) left gastro-epiploic a. (greater curvature on lf.) (synonym: gastro-omental) ...
15.2 General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal
... 1. ____________________(esophageal opening, cardiac sphincter) 2. Fundic (temporary storage area, lies slightly above the cardiac region) 3. Body (central area of the stomach) 5. ___________________(pyloric sphincter, controls emptying of the stomach into the sm. intestine) Stomach Lining: _________ ...
... 1. ____________________(esophageal opening, cardiac sphincter) 2. Fundic (temporary storage area, lies slightly above the cardiac region) 3. Body (central area of the stomach) 5. ___________________(pyloric sphincter, controls emptying of the stomach into the sm. intestine) Stomach Lining: _________ ...
Introduction to Cross Sectional Anatomy ABDOMEN
... Introduction to Cross Sectional Anatomy Chris Kowtko, MSRS, R.T. (R)(M) 20th WCEC Student-Educator – Radiographer Seminar ...
... Introduction to Cross Sectional Anatomy Chris Kowtko, MSRS, R.T. (R)(M) 20th WCEC Student-Educator – Radiographer Seminar ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.