Introduction to Cross Sectional Anatomy ABDOMEN
... Introduction to Cross Sectional Anatomy Chris Kowtko, MSRS, R.T. (R)(M) 20th WCEC Student-Educator – Radiographer Seminar ...
... Introduction to Cross Sectional Anatomy Chris Kowtko, MSRS, R.T. (R)(M) 20th WCEC Student-Educator – Radiographer Seminar ...
27-As of Mid& hindgut
... spleen. Portocaval shunts for the treatment of the portal hypertension may involve the anstomosis of the portal vein, because it lies within the lesser omentum and to the anterior wall of the inferior vena cava behind the entrance into the lesser sac. The splenic vein may be anastomosed to the left ...
... spleen. Portocaval shunts for the treatment of the portal hypertension may involve the anstomosis of the portal vein, because it lies within the lesser omentum and to the anterior wall of the inferior vena cava behind the entrance into the lesser sac. The splenic vein may be anastomosed to the left ...
Review Digestion Test PREAP 2014 Key
... 11. _I__ Long, winding organ where final digestion occurs and food is in a form that can be absorbed into the blood 12. List the organs where mechanical digestion occurs. Mouth and stomach 13. List the organs where chemical digestion occurs. Mouth, Stomach, Small Intestine 14. What breaks down fats ...
... 11. _I__ Long, winding organ where final digestion occurs and food is in a form that can be absorbed into the blood 12. List the organs where mechanical digestion occurs. Mouth and stomach 13. List the organs where chemical digestion occurs. Mouth, Stomach, Small Intestine 14. What breaks down fats ...
Endocrine Power PointPresentation1
... If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and glucose secreted in urine (glycosuria) Since glucose not available for cellular oxidation, body starts to burn up protein and fat If too much insulin is given, blood sugar may go too low (hypogycemia insulin shock) If blood sugar gets too ...
... If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and glucose secreted in urine (glycosuria) Since glucose not available for cellular oxidation, body starts to burn up protein and fat If too much insulin is given, blood sugar may go too low (hypogycemia insulin shock) If blood sugar gets too ...
Explain the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion.
... What is the function of bile? ...
... What is the function of bile? ...
endocrine system - Natural science Tree
... hormones: TSH, ACTH, prolactin, growth hormone, FSH and LH. ...
... hormones: TSH, ACTH, prolactin, growth hormone, FSH and LH. ...
1 - Biology Mad
... endopeptidases break protein from inside / into smaller polypeptides / peptides; pepsin in stomach / gastric juice; trypsin from pancreas / acting in small intestine; exopeptidases break off single amino acids / dipeptides from end; dipeptidases in epithelial cells / on cell surface membrane / brush ...
... endopeptidases break protein from inside / into smaller polypeptides / peptides; pepsin in stomach / gastric juice; trypsin from pancreas / acting in small intestine; exopeptidases break off single amino acids / dipeptides from end; dipeptidases in epithelial cells / on cell surface membrane / brush ...
The human Digestive system
... Storage of glucose as glycogen Removal of old red blood cells from blood and store the iron they contain Break down of alcohol and other toxic substance (toxins) in a process called Detoxification Break down of excess amino acids to urea excreted in urine (Deamination) Regulation of the le ...
... Storage of glucose as glycogen Removal of old red blood cells from blood and store the iron they contain Break down of alcohol and other toxic substance (toxins) in a process called Detoxification Break down of excess amino acids to urea excreted in urine (Deamination) Regulation of the le ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... – The stomach wall has three layers of muscles that churns the food, mixing it with gastric juices. – Gastric glands in the lining of the stomach secretes pepsinogen, HCl, and mucus. • Pepsinogen is converted to pepsin ...
... – The stomach wall has three layers of muscles that churns the food, mixing it with gastric juices. – Gastric glands in the lining of the stomach secretes pepsinogen, HCl, and mucus. • Pepsinogen is converted to pepsin ...
Digestion
... We used to think these were caused by stress, spicy foods, and alcohol. Now we know that most peptic ulcers are caused by a particular bacterial infection in the stomach and upper intestine, by certain medications, or by smoking. ...
... We used to think these were caused by stress, spicy foods, and alcohol. Now we know that most peptic ulcers are caused by a particular bacterial infection in the stomach and upper intestine, by certain medications, or by smoking. ...
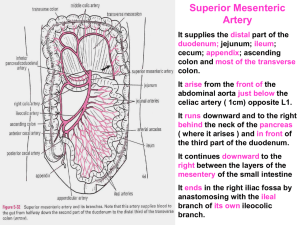
Abdomen 4 AvS 20060319b
... parts (regions) and duct system of the pancreas • Identify and list the general and peritoneal relations of the four parts of the duodenum • Identify and briefly discuss the relations of the pancreas to the spleen, duodenum, stomach and transverse colon and peritoneum • Identify the root of the tran ...
... parts (regions) and duct system of the pancreas • Identify and list the general and peritoneal relations of the four parts of the duodenum • Identify and briefly discuss the relations of the pancreas to the spleen, duodenum, stomach and transverse colon and peritoneum • Identify the root of the tran ...
Digestion and Excretion Chapter Test B Matching 1.
... 3. muscle contractions in organs of the digestive ...
... 3. muscle contractions in organs of the digestive ...
The Endocrine System
... The Endocrine System • Alpha () cells release glucagon, essential for controlling blood glucose levels. • When blood glucose levels fall, cells the amount of glucagon in the blood . ...
... The Endocrine System • Alpha () cells release glucagon, essential for controlling blood glucose levels. • When blood glucose levels fall, cells the amount of glucagon in the blood . ...
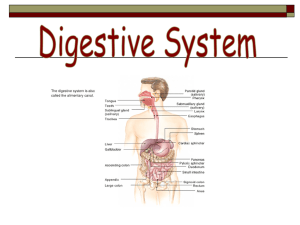
Digestive System
... • Secretes 1L of pancreatic fluid into small intestine daily • Pancreatic fluid contains enzymes to digest carbohydrates, lipids, proteins ...
... • Secretes 1L of pancreatic fluid into small intestine daily • Pancreatic fluid contains enzymes to digest carbohydrates, lipids, proteins ...
The Digestive Tract of the Cod Eleutheroembryo ("Yolk
... No mouth is present just after hatching, but it is perforated one day after hatching, and the eleutheroembryo was found to drink to maintain its osmotic state. The mouth is fully open at two days, and movements of the lower jaw, which contains well developed cartilages, have been reported. There is ...
... No mouth is present just after hatching, but it is perforated one day after hatching, and the eleutheroembryo was found to drink to maintain its osmotic state. The mouth is fully open at two days, and movements of the lower jaw, which contains well developed cartilages, have been reported. There is ...
lecture1 - University of Agriculture, Abeokuta
... flattening of the tube or the folding of its lining, the lumen is considerably reduced. The oesophagus forms a connecting channel between the pharynx and the next region, the stomach. The Stomach: In this region the tube is dialated to form a receptacle in which the food can accumulate during feedin ...
... flattening of the tube or the folding of its lining, the lumen is considerably reduced. The oesophagus forms a connecting channel between the pharynx and the next region, the stomach. The Stomach: In this region the tube is dialated to form a receptacle in which the food can accumulate during feedin ...
Digestion- Check your Understanding 1. What are the four stages of
... of the ______________ so that the food does not go down the wrong tube. The food enters the digestive tube, called the ______________________. 7. The esophagus is made up of smooth muscle. It relaxes and contracts in a special motion called _______________________ which pushes the food down into the ...
... of the ______________ so that the food does not go down the wrong tube. The food enters the digestive tube, called the ______________________. 7. The esophagus is made up of smooth muscle. It relaxes and contracts in a special motion called _______________________ which pushes the food down into the ...
bf971d386b8c4c3
... 2. SUBLINGUAL: (below tongue) and 3. SUBMANDIBULAR: both in lower jaw produce saliva Functions of Salivary 1. Lubrication : to facilitate mastication of food and make it slides easily through the 2.Saliva coats the oral cavity and esophagus 3.Solubilises dry food: in order to be tasted, the molecule ...
... 2. SUBLINGUAL: (below tongue) and 3. SUBMANDIBULAR: both in lower jaw produce saliva Functions of Salivary 1. Lubrication : to facilitate mastication of food and make it slides easily through the 2.Saliva coats the oral cavity and esophagus 3.Solubilises dry food: in order to be tasted, the molecule ...
Digetsive System glossary
... The last part of the small intestine before the large intestine begins. ...
... The last part of the small intestine before the large intestine begins. ...
Digestion
... - bile from liver and gall bladder - trypsin (a protease), lipase, amylase and biocarbonate from the pancreas • Duodenum is ~25 cm of 6 m of small intestine (most digestion compete by the end of duodenum) ...
... - bile from liver and gall bladder - trypsin (a protease), lipase, amylase and biocarbonate from the pancreas • Duodenum is ~25 cm of 6 m of small intestine (most digestion compete by the end of duodenum) ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.