Redox reaction during glycolysis
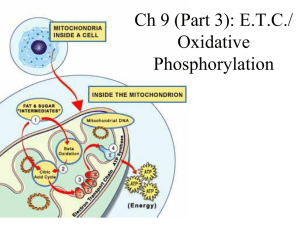
... • NADH+H+ supplies pair of H atoms to the first carrier in the chain, with the NAD+ returning to the matrix. • The hydrogen atoms are split, to release two electrons, which pass from carrier in the chain. • Energy is released as the e- pass from carrier to carrier, and three of these use this energy ...
... • NADH+H+ supplies pair of H atoms to the first carrier in the chain, with the NAD+ returning to the matrix. • The hydrogen atoms are split, to release two electrons, which pass from carrier in the chain. • Energy is released as the e- pass from carrier to carrier, and three of these use this energy ...
8.1 Glycolysis Know the overall reaction: the materials that go in
... Understand how fructose is funneled into glycolysis. Reactions convert the sugars into glycolytic intermediates. 9.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Be able to recognize red-ox reactions Be able to recognize relative oxidation states, which carbons are more oxidized or reduced 9.2 Citric Acid Cycle Co ...
... Understand how fructose is funneled into glycolysis. Reactions convert the sugars into glycolytic intermediates. 9.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Be able to recognize red-ox reactions Be able to recognize relative oxidation states, which carbons are more oxidized or reduced 9.2 Citric Acid Cycle Co ...
Respiratory Substrates
... • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release slightly more energy than equivalent masses of glucose ...
... • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release slightly more energy than equivalent masses of glucose ...
Study Guide
... Stepwise oxidation of glucose = catabolism of glucose Phases of Glycolysis, products of Glycolysis, net yields of energy molecules – location of pathway Role of NAD+, NADH, FAD, FADH2 as electron carriers (redox reactions) Pyruvate oxidation under aerobic conditions, pyruvate fermentation under anae ...
... Stepwise oxidation of glucose = catabolism of glucose Phases of Glycolysis, products of Glycolysis, net yields of energy molecules – location of pathway Role of NAD+, NADH, FAD, FADH2 as electron carriers (redox reactions) Pyruvate oxidation under aerobic conditions, pyruvate fermentation under anae ...
Citric acid Cycle:
... forward or backward? b. How does this reaction proceeds in forward direction? c. Calculate the G for this reaction in forward direction if concentration of oxaloacetate is 1x 10-8 M, malate 0.2 mM, and NAD+/NADH ratio in rat liver mitochondria is 10. ...
... forward or backward? b. How does this reaction proceeds in forward direction? c. Calculate the G for this reaction in forward direction if concentration of oxaloacetate is 1x 10-8 M, malate 0.2 mM, and NAD+/NADH ratio in rat liver mitochondria is 10. ...
cell respiration wilk hl ibdp
... simultaneously hence the step is called Oxidative decarboxylation • Pyruvate + CoA forms Acetyl CoA • CoA comprises of [ adenine + ribose sugar + Pantothenic acid] • CoA is a carrier for Acetyl group into the Krebs cycle. NAD+ ...
... simultaneously hence the step is called Oxidative decarboxylation • Pyruvate + CoA forms Acetyl CoA • CoA comprises of [ adenine + ribose sugar + Pantothenic acid] • CoA is a carrier for Acetyl group into the Krebs cycle. NAD+ ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... The Krebs Cycle (mitochondria matrix) The Electron Transport Chain (inner mitochondrial membrane) ...
... The Krebs Cycle (mitochondria matrix) The Electron Transport Chain (inner mitochondrial membrane) ...
Aerobic Respiration - East Muskingum Schools
... produces 2 ATP. The Kreb's cycle produces 2 ATP, and the electron transport chain produces 34 ATP. That gives a total of ____ATP when ____________ is available to the cell during aerobic respiration. ...
... produces 2 ATP. The Kreb's cycle produces 2 ATP, and the electron transport chain produces 34 ATP. That gives a total of ____ATP when ____________ is available to the cell during aerobic respiration. ...
Name__________________________ 1. Which of these
... 14. Define autotroph and heterotroph, and give an example of each. ...
... 14. Define autotroph and heterotroph, and give an example of each. ...
1. What is substrate level phosphorylation (vs. oxidative
... 12. Beta-oxidation of fatty acids produces an important substrate for the TCA cycle. Name the substrate. ...
... 12. Beta-oxidation of fatty acids produces an important substrate for the TCA cycle. Name the substrate. ...
Unit 3 Study Guide: Energetics
... I. UNIT VOCABULARY (This list is here to help you. You do not have to define any terms but you can if it will help you.) Chapter 8 metabolism catabolism anabolism energy (kinetic vs potential) free energy (ΔG) entropy exergonic / endergonic energy coupling ATP / ADP phosphorylation catalyst activati ...
... I. UNIT VOCABULARY (This list is here to help you. You do not have to define any terms but you can if it will help you.) Chapter 8 metabolism catabolism anabolism energy (kinetic vs potential) free energy (ΔG) entropy exergonic / endergonic energy coupling ATP / ADP phosphorylation catalyst activati ...
Cellular Respiration notes
... Electron Transport Chain • The electron transport chain is a series of chemical reactions ending with hydrogen combining with oxygen to form water. Carbon dioxide is released as a waste product as it is formed in several stages of the Krebs cycle. • Each reaction produces a small amount of energy, ...
... Electron Transport Chain • The electron transport chain is a series of chemical reactions ending with hydrogen combining with oxygen to form water. Carbon dioxide is released as a waste product as it is formed in several stages of the Krebs cycle. • Each reaction produces a small amount of energy, ...
Cellular Respiration
... autotrophs and is required by autotrophs to break down sugars to remove the energy used to form ATP. 2. Write a balanced chemical equation; relate to cellular respiration. Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6 H2O + energy (sunlight) 6O2 + C6H12O6 Cell respiration: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP The product ...
... autotrophs and is required by autotrophs to break down sugars to remove the energy used to form ATP. 2. Write a balanced chemical equation; relate to cellular respiration. Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6 H2O + energy (sunlight) 6O2 + C6H12O6 Cell respiration: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP The product ...
LECTURE 9 – 20th March 2015
... - Reduced electron carriers are produced - Starting material = Acetyl CoA and 4-carbon molecule - Product = 2 ATP, 4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 - The conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA results in CO2 is produced and the first NADH is formed - In the final step, the 4-carbon molecule is fur ...
... - Reduced electron carriers are produced - Starting material = Acetyl CoA and 4-carbon molecule - Product = 2 ATP, 4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 - The conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA results in CO2 is produced and the first NADH is formed - In the final step, the 4-carbon molecule is fur ...
2 ATP - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Broken: (1) P—O bond, (1) H—O bond Formed: (1) P—O bond, (1) H—O bond ...
... Broken: (1) P—O bond, (1) H—O bond Formed: (1) P—O bond, (1) H—O bond ...
Metabolism: Basic concepts
... C. Two reactions share a common intermediate. Could it be that these reactions are coupled? ...
... C. Two reactions share a common intermediate. Could it be that these reactions are coupled? ...
Cell Respiration Notes
... NADH and FADH2 are moved across the ETC e-, H+ and O2 combine to make H 2O ATP synthase pumps H+ across membrane to make ATP ...
... NADH and FADH2 are moved across the ETC e-, H+ and O2 combine to make H 2O ATP synthase pumps H+ across membrane to make ATP ...
Bio 7
... Uses for plants?...Uses for animals? Lipids/fats – single glycerol and three free-fatty acids Uses in animals? Proteins – amino acid chains Used as enzymes and structural components of the cell Fold into unique 3D shape that gives each protein’s its function DNA and RNA Nucleotides (nucleic acids) c ...
... Uses for plants?...Uses for animals? Lipids/fats – single glycerol and three free-fatty acids Uses in animals? Proteins – amino acid chains Used as enzymes and structural components of the cell Fold into unique 3D shape that gives each protein’s its function DNA and RNA Nucleotides (nucleic acids) c ...
Cellular Respiration: the details
... Substrate-level phosphorylation -ADP + Pi = ATP -Formed directly ...
... Substrate-level phosphorylation -ADP + Pi = ATP -Formed directly ...
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme often called the ""molecular unit of currency"" of intracellular energy transfer.ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of photophosphorylation, cellular respiration, and fermentation and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility, and cell division. One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by a wide variety of enzymes, including ATP synthase, from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and various phosphate group donors. Substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration, and photophosphorylation in photosynthesis are three major mechanisms of ATP biosynthesis.Metabolic processes that use ATP as an energy source convert it back into its precursors. ATP is therefore continuously recycled in organisms: the human body, which on average contains only 250 grams (8.8 oz) of ATP, turns over its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day.ATP is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids. It is also used by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and consume ATP. Apart from its roles in signaling and energy metabolism, ATP is also incorporated into nucleic acids by polymerases in the process of transcription. ATP is the neurotransmitter believed to signal the sense of taste.The structure of this molecule consists of a purine base (adenine) attached by the 9' nitrogen atom to the 1' carbon atom of a pentose sugar (ribose). Three phosphate groups are attached at the 5' carbon atom of the pentose sugar. It is the addition and removal of these phosphate groups that inter-convert ATP, ADP and AMP. When ATP is used in DNA synthesis, the ribose sugar is first converted to deoxyribose by ribonucleotide reductase.ATP was discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann, and independently by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow of Harvard Medical School, but its correct structure was not determined until some years later. It was proposed to be the intermediary molecule between energy-yielding and energy-requiring reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. It was first artificially synthesized by Alexander Todd in 1948.