Immunity/Immunology
... and so are found in _________________ and tissue fluid. There are possibly 10 million types of B cell, each having a different_________________ that responds to a specific antigen. An antigen invading the blood or tissue fluid will have a _________________ B cell with an antibody on its surface that ...
... and so are found in _________________ and tissue fluid. There are possibly 10 million types of B cell, each having a different_________________ that responds to a specific antigen. An antigen invading the blood or tissue fluid will have a _________________ B cell with an antibody on its surface that ...
B Cells - School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences
... of normal cells. If caused by any specific pathogen (controversial) then it could be that just a tiny amount needs to go unattacked for a short time, and the problem starts. Leukaemia: a cancer of the bone marrow – it (and its treatment) throw an enormous spanner into the heart of B-cell production. ...
... of normal cells. If caused by any specific pathogen (controversial) then it could be that just a tiny amount needs to go unattacked for a short time, and the problem starts. Leukaemia: a cancer of the bone marrow – it (and its treatment) throw an enormous spanner into the heart of B-cell production. ...
“The Immune System”
... How does your body know there is an invader? • All pathogens have “distinct” marker proteins that are antigens. • Antigens -anything that causes an immune response. • Your body must recognize antigens as FOREIGN (NON-SELF) in order to create an immune response. ...
... How does your body know there is an invader? • All pathogens have “distinct” marker proteins that are antigens. • Antigens -anything that causes an immune response. • Your body must recognize antigens as FOREIGN (NON-SELF) in order to create an immune response. ...
Name: Date: Period: ___ Immune System Immune System Guided
... surrounding and engulfing them. B cells and T cells fight pathogens in other ways. Complement proteins might attract phagocytes to an infected area. Antibodies are proteins made by B cells that cause pathogens to become inactive. Interferons are proteins that prevent viruses from reproducing. Peop ...
... surrounding and engulfing them. B cells and T cells fight pathogens in other ways. Complement proteins might attract phagocytes to an infected area. Antibodies are proteins made by B cells that cause pathogens to become inactive. Interferons are proteins that prevent viruses from reproducing. Peop ...
White Blood Cells: An Overview of the Body`s Defense Army Human
... Basophils. When these are triggered to leave the blood and enter tissues, they become mast cells and release heparin and histamine (among other chemicals) as an inflammatory response to an allergic trigger. Histamine causes dilation of blood vessels to bring more help to the site of a threat, and he ...
... Basophils. When these are triggered to leave the blood and enter tissues, they become mast cells and release heparin and histamine (among other chemicals) as an inflammatory response to an allergic trigger. Histamine causes dilation of blood vessels to bring more help to the site of a threat, and he ...
Document
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
APUnit9sheet2017
... 3 – Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life 4 – Biologic systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties Chapter 43 – Immune System 1. Compare and contrast specific (innate) and nonspecific (acquired) defense mechani ...
... 3 – Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life 4 – Biologic systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties Chapter 43 – Immune System 1. Compare and contrast specific (innate) and nonspecific (acquired) defense mechani ...
(2) Viral and bacterial superantigens
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
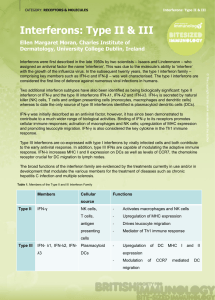
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
NAME___________________________________TA__________
... In some cases, where the match is not perfect, the immune cells of the marrow can mount a response against the body of the recipient. In anything less than an extremely close match, the immune cells of the bone marrow will launch an attack on the recipient’s body, causing graft-versus-host disease. ...
... In some cases, where the match is not perfect, the immune cells of the marrow can mount a response against the body of the recipient. In anything less than an extremely close match, the immune cells of the bone marrow will launch an attack on the recipient’s body, causing graft-versus-host disease. ...
Microbiology 204: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Microbiology
... Immune system and chronic inflammation • Sterile inflammation (tissue injury but no infectious agent present): innate recognition of tissue damage • Chronic inflammation: if antigen persists, antigenreactive T cells can drive continued inflammation, which can cause tissue damage (autoimmune disea ...
... Immune system and chronic inflammation • Sterile inflammation (tissue injury but no infectious agent present): innate recognition of tissue damage • Chronic inflammation: if antigen persists, antigenreactive T cells can drive continued inflammation, which can cause tissue damage (autoimmune disea ...
IMMUNITY MEDIATED BY B LYMPHOCYTES AND ANTIBODIES
... THE INNATE IMMUNE SYSTEM * First line of defense against pathogens * Components ...
... THE INNATE IMMUNE SYSTEM * First line of defense against pathogens * Components ...
The humoral immune response defends against pathogens that are
... These antibodies circulate in the blood stream and lymphatic system, binding with the antigen whenever it is encountered. The binding can fight infection in several ways. Antibodies can bind to viruses or bacteria, which interferes with the chemical interactions required for them to infect or bind t ...
... These antibodies circulate in the blood stream and lymphatic system, binding with the antigen whenever it is encountered. The binding can fight infection in several ways. Antibodies can bind to viruses or bacteria, which interferes with the chemical interactions required for them to infect or bind t ...
TOLERANCE
... Tolerance or immunity can also be influenced by the tissue microenvironment Immuno-suppressive mediators are secreted by the foetus and ...
... Tolerance or immunity can also be influenced by the tissue microenvironment Immuno-suppressive mediators are secreted by the foetus and ...
Southern Methodist University
... enhances the release of glutamate. The Ca2+ mediated effects of glutamate receptor activation leads to neuronal degeneration. Viral: Activated T cells could cross the BBB following by a microbe much like a component of the myelin sheath. ...
... enhances the release of glutamate. The Ca2+ mediated effects of glutamate receptor activation leads to neuronal degeneration. Viral: Activated T cells could cross the BBB following by a microbe much like a component of the myelin sheath. ...
Lymphatic System
... particular T cell programmed to react with the antigen becomes activated – Macrophages phagocytize the antigen – Macrophages present it to the T cell ...
... particular T cell programmed to react with the antigen becomes activated – Macrophages phagocytize the antigen – Macrophages present it to the T cell ...
Natural Defenses for Healthy Animals
... of the innate immune system has been shown to provide a rapid, potent and broad protective response to infectious agents. Scientists at Bayer are exploring the potential of immunostimulants to help veterinarians and producers around the world better mitigate infectious diseases in livestock. Daniel ...
... of the innate immune system has been shown to provide a rapid, potent and broad protective response to infectious agents. Scientists at Bayer are exploring the potential of immunostimulants to help veterinarians and producers around the world better mitigate infectious diseases in livestock. Daniel ...
Overview
... that cause a particular disease is called immunity. You were born with some immunities that were passed on to you from your mother. These immunities lasted for a few months, after which you began to produce antibodies on your own. ...
... that cause a particular disease is called immunity. You were born with some immunities that were passed on to you from your mother. These immunities lasted for a few months, after which you began to produce antibodies on your own. ...
Mary Beth Murphy Ms. Huntemann AP Biology Chapter 31
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)- Contracted by bodily fluid transmission, kills off Tcells until the immune system is useless, killing the host Humoral Immune System- Made up of B-cells and Antibodies Immunity- Ability to be resistant to a pathogen Immunoglobulins- the classes of antibodies Immun ...
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)- Contracted by bodily fluid transmission, kills off Tcells until the immune system is useless, killing the host Humoral Immune System- Made up of B-cells and Antibodies Immunity- Ability to be resistant to a pathogen Immunoglobulins- the classes of antibodies Immun ...
Ch06-Diseases of Immunity
... Major Histocompatibility Complex • A genetic “LOCUS” on Chromosome 6, which codes for cell surface compatibility • Also called HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigens) in humans and H-2 in mice • It’s major job is to make sure all self cell antigens are recognized and “tolerated”, because the general rule of ...
... Major Histocompatibility Complex • A genetic “LOCUS” on Chromosome 6, which codes for cell surface compatibility • Also called HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigens) in humans and H-2 in mice • It’s major job is to make sure all self cell antigens are recognized and “tolerated”, because the general rule of ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.