Chapter 17 Immune Response
... • All humans are resistant to certain animal diseases such as canine distemper. • Distemper virus infects the nervous system of dogs. • Humans can’t get the disease because humans do not have the receptor for the virus. ...
... • All humans are resistant to certain animal diseases such as canine distemper. • Distemper virus infects the nervous system of dogs. • Humans can’t get the disease because humans do not have the receptor for the virus. ...
The Body Has Methods of Protecting Itself from Diseases
... Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 2 types of White Blood Cells (1) T cells and (2) B cells ...
... Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 2 types of White Blood Cells (1) T cells and (2) B cells ...
File - Pomp
... • Neutrophils • 60-70% WBCs; engulf and destroy microbes at infected tissue Short lived • Monocytes • 5% WBCs; develop into…. – Macrophages 1)phagocytosis – 2)lysosomal enzymes destroy microbes ...
... • Neutrophils • 60-70% WBCs; engulf and destroy microbes at infected tissue Short lived • Monocytes • 5% WBCs; develop into…. – Macrophages 1)phagocytosis – 2)lysosomal enzymes destroy microbes ...
Immune System Disorders (Hypersensitivities ≈ Allergies)
... • Lymphocytes become involved in attacking the bodies own cells (antigens). • Self-tolerance of lymphocytes is lost: B cells produce antibodies and Tc cells activate their cytotoxicity. ...
... • Lymphocytes become involved in attacking the bodies own cells (antigens). • Self-tolerance of lymphocytes is lost: B cells produce antibodies and Tc cells activate their cytotoxicity. ...
Document
... 1. Vertebrates only 2. Specificity - recognition modules - BCR, Ab and TCR - gene rearrangement is the source of diversity - clonal selection 3. Small lymphocytes - types and sub-types - functions ...
... 1. Vertebrates only 2. Specificity - recognition modules - BCR, Ab and TCR - gene rearrangement is the source of diversity - clonal selection 3. Small lymphocytes - types and sub-types - functions ...
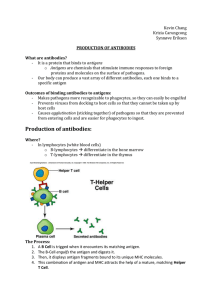
BLOCK F – Krizia,Kevin,Synnove – Production of Antibodies
... 5. Cytokines secreted by the Helper T cell help the B cell to multiply and mature into antibody producing plasma cells. 6. Antibodies then lock onto matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound ant ...
... 5. Cytokines secreted by the Helper T cell help the B cell to multiply and mature into antibody producing plasma cells. 6. Antibodies then lock onto matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound ant ...
Human Immune System - West Linn High School
... Bind to foreign antigens Each antibody is specific for a particular antigen Body can make 10B different antibodies!!! ...
... Bind to foreign antigens Each antibody is specific for a particular antigen Body can make 10B different antibodies!!! ...
Immune Response
... Skin/cells are damaged, pathogens enter Cells recognize invaders and release chemicals called histamines These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
... Skin/cells are damaged, pathogens enter Cells recognize invaders and release chemicals called histamines These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
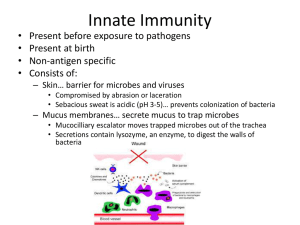
Innate Immunity - Santa Susana High School
... • Natural Killer Cells – Patrol the body looking for infected cells. • They attack and cause cell death through apoptosis • Evaded in some viral infections and cancer ...
... • Natural Killer Cells – Patrol the body looking for infected cells. • They attack and cause cell death through apoptosis • Evaded in some viral infections and cancer ...
Overview of Adaptive Immunity 01/24/06
... Antibody dependent Antibody functions Enhanced elimination Neutralization C fixation/lysis ...
... Antibody dependent Antibody functions Enhanced elimination Neutralization C fixation/lysis ...
The Immune System - Clark Pleasant Community School Corp
... off only one particular pathogen • Lymphocytes specialize and become T cells and B cells • T cells activate B cells ...
... off only one particular pathogen • Lymphocytes specialize and become T cells and B cells • T cells activate B cells ...
Immunity Ch. 11.1-6
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... b.) Binds CO2 c.) Binds O2 d.) Binds H+ e.) All of the above are true 4. Which blood cell type is required for adaptive immune response? a.) Neutrophils b.) Lymphocytes c.) Macrophages d.) Natural killer cells e.) All of the above 5. A lymphocyte a.) Expresses several different antigen receptors b.) ...
... b.) Binds CO2 c.) Binds O2 d.) Binds H+ e.) All of the above are true 4. Which blood cell type is required for adaptive immune response? a.) Neutrophils b.) Lymphocytes c.) Macrophages d.) Natural killer cells e.) All of the above 5. A lymphocyte a.) Expresses several different antigen receptors b.) ...
2-immune system
... Overview of the two arms of the immune system: innate immunity & adaptive immunity. ...
... Overview of the two arms of the immune system: innate immunity & adaptive immunity. ...
ppt 3.2.4 immunity revision Revision powerpoint on
... immune system and stimulates an immune response. For example – proteins that are part of the cell membrane or cell wall of invading cells such as microorganisms. The presence of an antigen triggers the production of an antibody. ...
... immune system and stimulates an immune response. For example – proteins that are part of the cell membrane or cell wall of invading cells such as microorganisms. The presence of an antigen triggers the production of an antibody. ...
For more information
... Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is a rheumatic autoimmune disease, with focal lymphocyte infiltration and inflammation in exocrine glands, resulting in destruction of glandular tissue. B cells have an important role in the humoral part of the adaptive immune response where they carry out several functions; ...
... Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is a rheumatic autoimmune disease, with focal lymphocyte infiltration and inflammation in exocrine glands, resulting in destruction of glandular tissue. B cells have an important role in the humoral part of the adaptive immune response where they carry out several functions; ...
How does my immune system react when I puncture my skin on
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
Acquired immunity
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
Adaptive or acquired immune system
... 5. Alternate complement pathway – cascade of serum proteins that are activated by bacterial cell wall components 2. Adaptive or acquired immune system: Found only in vertebrates (fish, amphibians, birds and mammals), Must be induced to be active against infections or tumors. Antigen-specific – a ...
... 5. Alternate complement pathway – cascade of serum proteins that are activated by bacterial cell wall components 2. Adaptive or acquired immune system: Found only in vertebrates (fish, amphibians, birds and mammals), Must be induced to be active against infections or tumors. Antigen-specific – a ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.