File - AP Biology with Mrs. Davis
... 1. Testosterone and estrogen (signals) released by sex organs 2. Travel to target cells and bind to nuclear receptors (reception) 3. Hormone-receptor complex move to DNA (transduction) 4. Bind to DNA and affect transcription (response) ...
... 1. Testosterone and estrogen (signals) released by sex organs 2. Travel to target cells and bind to nuclear receptors (reception) 3. Hormone-receptor complex move to DNA (transduction) 4. Bind to DNA and affect transcription (response) ...
Overview
... If pathogens enter the body, the immune system launches an attack. The immune system’s nonspecific response is always the same, regardless of the type of foreign substance that invades the body. The inflammatory response is a nonspecific response that occurs if a foreign invader gets past the five m ...
... If pathogens enter the body, the immune system launches an attack. The immune system’s nonspecific response is always the same, regardless of the type of foreign substance that invades the body. The inflammatory response is a nonspecific response that occurs if a foreign invader gets past the five m ...
2016 department of medicine research day
... Adaptive immune resistance is a mechanism by which tumor cells limit host immune response via upregulation of the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and ligation to the programmed death-1 (PD1) receptor on antigen-specific CD8 T cells. Recent studies of the PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor in nonsmall cell ...
... Adaptive immune resistance is a mechanism by which tumor cells limit host immune response via upregulation of the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and ligation to the programmed death-1 (PD1) receptor on antigen-specific CD8 T cells. Recent studies of the PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor in nonsmall cell ...
4.2 Homework for Chapter 6 - 6th ed
... Critical Thinking Questions (these are similar to the level of questions you can expect on tests) 42. Why are the first and second lines of defense collectively referred to as innate immunity? A) Because they are defenses which are specific to particular disease organisms. B) Because they are locate ...
... Critical Thinking Questions (these are similar to the level of questions you can expect on tests) 42. Why are the first and second lines of defense collectively referred to as innate immunity? A) Because they are defenses which are specific to particular disease organisms. B) Because they are locate ...
Nonspecific Defense Mechanisms
... born with it ready to go); it has made the self/ nonself discrimination on an evolutionary time-scale ...
... born with it ready to go); it has made the self/ nonself discrimination on an evolutionary time-scale ...
Hamel, Misse et al, J Virol 2015
... Cell targets Cell surface receptors Innate and adaptive responses Fetal CNS injury ...
... Cell targets Cell surface receptors Innate and adaptive responses Fetal CNS injury ...
Antibody Structure and Function
... • Binding of antibodies to antigens can facilitate the uptake of the antigens by phagocytic cells (opsonization). • The antibodies bind to antigens by the Fab portion of the antibody, leaving the Fc portion of the antibody free to bind to Fc receptors on the surface of phagocytic cells. • The antibo ...
... • Binding of antibodies to antigens can facilitate the uptake of the antigens by phagocytic cells (opsonization). • The antibodies bind to antigens by the Fab portion of the antibody, leaving the Fc portion of the antibody free to bind to Fc receptors on the surface of phagocytic cells. • The antibo ...
Immune system activation - UCSF Immunology Program
... 1. Exogenous – type 1 IFN treatment (MS, HCV, etc.) 5-30% of patients receiving type 1 IFNs get auto-antibodies (ANA, etc) and ~5% get autoimmune disease (anti-thyroid Ab’s, vitiligo, diabetes). 2. Disease ‘signatures’ of elevated type 1 IFNs ...
... 1. Exogenous – type 1 IFN treatment (MS, HCV, etc.) 5-30% of patients receiving type 1 IFNs get auto-antibodies (ANA, etc) and ~5% get autoimmune disease (anti-thyroid Ab’s, vitiligo, diabetes). 2. Disease ‘signatures’ of elevated type 1 IFNs ...
inflammation response
... recipient as closely as possible so that there is a high number of matching ‘marker’ molecules. This will mean that there are fewer foreign (antigen) molecules on the surface, a situation which may lead to a less ‘violent’ immune response. ...
... recipient as closely as possible so that there is a high number of matching ‘marker’ molecules. This will mean that there are fewer foreign (antigen) molecules on the surface, a situation which may lead to a less ‘violent’ immune response. ...
8.1.1 Second Line of Defence
... recipient as closely as possible so that there is a high number of matching ‘marker’ molecules. This will mean that there are fewer foreign (antigen) molecules on the surface, a situation which may lead to a less ‘violent’ immune response. ...
... recipient as closely as possible so that there is a high number of matching ‘marker’ molecules. This will mean that there are fewer foreign (antigen) molecules on the surface, a situation which may lead to a less ‘violent’ immune response. ...
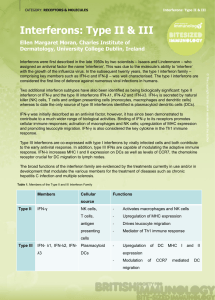
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
... cellular immune responses; activation of macrophages and NK cells; upregulation of MHC expression and promoting leucocyte migration. IFN-γ is also considered the key cytokine in the Th1 immune response. Type III interferons are co-expressed with type I interferons by virally infected cells and both ...
... cellular immune responses; activation of macrophages and NK cells; upregulation of MHC expression and promoting leucocyte migration. IFN-γ is also considered the key cytokine in the Th1 immune response. Type III interferons are co-expressed with type I interferons by virally infected cells and both ...
Grade 8 Cell Unit Review What is an organelle? What is the cell
... that carry air from the trachea into the lungs? ...
... that carry air from the trachea into the lungs? ...
CARBOHYDRATES B: Polysaccharides Learning Goals/Objectives
... b. Gram negative bacteriaThese bacterial can NOT be stained with Gram stain. The wall consists of the same structure as in Gram positive bacteria, but the GlcNAc ( 1->4) MurNAc strands are covalently connected through a direct amide bond between the epsilon amino group of the tetrapeptide Lys on on ...
... b. Gram negative bacteriaThese bacterial can NOT be stained with Gram stain. The wall consists of the same structure as in Gram positive bacteria, but the GlcNAc ( 1->4) MurNAc strands are covalently connected through a direct amide bond between the epsilon amino group of the tetrapeptide Lys on on ...
Multiple sclerosis
... Most people agree that MS is triggered by an external event, and this is certainly the case in animal models that are used to study this condition. However, it is unlikely that acute infection with a single microorganism provides a unique initiation point. And it is important to recognise that anima ...
... Most people agree that MS is triggered by an external event, and this is certainly the case in animal models that are used to study this condition. However, it is unlikely that acute infection with a single microorganism provides a unique initiation point. And it is important to recognise that anima ...
Document
... Most people agree that MS is triggered by an external event, and this is certainly the case in animal models that are used to study this condition. However, it is unlikely that acute infection with a single microorganism provides a unique initiation point. And it is important to recognise that anima ...
... Most people agree that MS is triggered by an external event, and this is certainly the case in animal models that are used to study this condition. However, it is unlikely that acute infection with a single microorganism provides a unique initiation point. And it is important to recognise that anima ...
Bio 347 Ch 12 Cytokines
... 2. cytokines are transient and act over short distances , autocrine (cells that produce them) and paracrine (acting on cells close by) rather than endocrine (acting on cells at a distance) 3. cytokines regulate expression of own receptor or other cytokine receptors 4. many cytokines act by causing a ...
... 2. cytokines are transient and act over short distances , autocrine (cells that produce them) and paracrine (acting on cells close by) rather than endocrine (acting on cells at a distance) 3. cytokines regulate expression of own receptor or other cytokine receptors 4. many cytokines act by causing a ...
Innate Immune Response to Ebolavirus Infection
... (ICEBOV), Bundibugyo ebolavirus (BEBOV), and Reston ebolavirus (REBOV). Mortality rates are approximately 40 to 90%, depending on the virus, with ZEBOV and MARVAngola being the most virulent. There are no FDA-approved vaccines or therapeutics to combat EBOV or MARV infection, and we still lack an un ...
... (ICEBOV), Bundibugyo ebolavirus (BEBOV), and Reston ebolavirus (REBOV). Mortality rates are approximately 40 to 90%, depending on the virus, with ZEBOV and MARVAngola being the most virulent. There are no FDA-approved vaccines or therapeutics to combat EBOV or MARV infection, and we still lack an un ...
05 M301 Host Def NS 2011 - Cal State LA
... antigen-antibody defense Function to attack and destroy invading MOs, stimulate inflammatory response Proteins act in sequence or cascade reactions In sequence of steps, proteins activate one another by cleaving next protein in series Cleaved proteins have new enzymatic or ...
... antigen-antibody defense Function to attack and destroy invading MOs, stimulate inflammatory response Proteins act in sequence or cascade reactions In sequence of steps, proteins activate one another by cleaving next protein in series Cleaved proteins have new enzymatic or ...