Comparing Invertebrates
... Movement and support Most animals use muscles to move Muscles move organisms by contraction Usually work with skeletal system – Hydrostatic-muscles surround a fluid filled opening, when muscles contract animal changes shape – Exoskeleton-hard body covering made of chitin, arthropods,muscles bend and ...
... Movement and support Most animals use muscles to move Muscles move organisms by contraction Usually work with skeletal system – Hydrostatic-muscles surround a fluid filled opening, when muscles contract animal changes shape – Exoskeleton-hard body covering made of chitin, arthropods,muscles bend and ...
BIOL241StudyGuide LabPracticalsBIOL241
... of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint (ppt) slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to learn the material for these and additional time available during open labs. Thi ...
... of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint (ppt) slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to learn the material for these and additional time available during open labs. Thi ...
File - Mr Schmitt
... be by kidney-like organs called green glands in organisms such as crayfish ...
... be by kidney-like organs called green glands in organisms such as crayfish ...
The Animal Kingdom
... small growth forms on the parent organism and then breaks off to form a new sponge. ...
... small growth forms on the parent organism and then breaks off to form a new sponge. ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... Aims and scope of human anatomy Anatomy – knowledge of the structure of living things Gr. ἀνατομία anatomia = to cut apart; from ἀνατέμνειν ana: separate, apart from, and temnein, to cut up, cut open ...
... Aims and scope of human anatomy Anatomy – knowledge of the structure of living things Gr. ἀνατομία anatomia = to cut apart; from ἀνατέμνειν ana: separate, apart from, and temnein, to cut up, cut open ...
Organ Systems: Urinary, Respiratory, Circulatory - Jocha
... oral cavity has two but one functions: ingestion and digestion. Explain how the saliva helps the oral cavity to do its work a) What is the approximate pH of the stomach? What is released by the stomach cells in order to change the pH in this way? b) Explain why the cells of the stomach are not affec ...
... oral cavity has two but one functions: ingestion and digestion. Explain how the saliva helps the oral cavity to do its work a) What is the approximate pH of the stomach? What is released by the stomach cells in order to change the pH in this way? b) Explain why the cells of the stomach are not affec ...
click here for printable human body systems vocab.
... muscle controlled without thinking about it (pumping heart) tissues that connect bones, hold organs in place tissues that cause motion in the body when contracted muscular and skeletal systems Exercise that involves working your muscles against free weights or your body's own weight (walking, runnin ...
... muscle controlled without thinking about it (pumping heart) tissues that connect bones, hold organs in place tissues that cause motion in the body when contracted muscular and skeletal systems Exercise that involves working your muscles against free weights or your body's own weight (walking, runnin ...
Human Body Systems
... • It protects, provides form and structure. • Humans, like all vertebrates, have an endoskeleton (internal framework) made up of bone and cartilage and the muscles attach to the bone. • Made up of 206 separate different shapes and sizes of bone, which make up 18% of a person’s body weight. • Joints ...
... • It protects, provides form and structure. • Humans, like all vertebrates, have an endoskeleton (internal framework) made up of bone and cartilage and the muscles attach to the bone. • Made up of 206 separate different shapes and sizes of bone, which make up 18% of a person’s body weight. • Joints ...
25 PowerPoint – Invertebrates
... Have a soft body with a tough, leathery outer skin Five rows of tube feet run lengthwise on the top surface of the body Have a fringe of tentacles (modified tube feet) surrounding the mouth to sweep in food & water Tentacles have sticky ends to collect plankton Show bilateral symmetry Can eject part ...
... Have a soft body with a tough, leathery outer skin Five rows of tube feet run lengthwise on the top surface of the body Have a fringe of tentacles (modified tube feet) surrounding the mouth to sweep in food & water Tentacles have sticky ends to collect plankton Show bilateral symmetry Can eject part ...
General Biology 101 - Linn
... deposits. This structure may be an adaptation for defense, and it also limits water loss. Must be periodically shed/molted though to grow. - Jointed appendages: cuticle is thinnest at the joints. Arthropod means “jointed foot.” - Fused and modified segments: In most modern arthropods groups of segme ...
... deposits. This structure may be an adaptation for defense, and it also limits water loss. Must be periodically shed/molted though to grow. - Jointed appendages: cuticle is thinnest at the joints. Arthropod means “jointed foot.” - Fused and modified segments: In most modern arthropods groups of segme ...
Copy of Final Exam Review A&P 2013
... 17. Thick filaments of myofibrils are made up of the protein ___________ while thin filaments are made up of the protein _____________. 18. The __________ has a zone of overlap between thin and thick filaments, while the _____________ only contains thick filaments. The zone with only thin filaments ...
... 17. Thick filaments of myofibrils are made up of the protein ___________ while thin filaments are made up of the protein _____________. 18. The __________ has a zone of overlap between thin and thick filaments, while the _____________ only contains thick filaments. The zone with only thin filaments ...
HISTOLOGY
... surfaces and cavities of the body. • These cells are close together with very little intercellular material. • Can be arranged in one layer (simple) or more than one layer (stratified) • Functions include: protection, absorption, and secretion • Some possess specialized structures, such as cilia and ...
... surfaces and cavities of the body. • These cells are close together with very little intercellular material. • Can be arranged in one layer (simple) or more than one layer (stratified) • Functions include: protection, absorption, and secretion • Some possess specialized structures, such as cilia and ...
Human Body Systems PPT
... • Skin and mucous membranes • Inflammatory response • Temperature • White blood cells • Specific immune responses • To bacteria and viruses ...
... • Skin and mucous membranes • Inflammatory response • Temperature • White blood cells • Specific immune responses • To bacteria and viruses ...
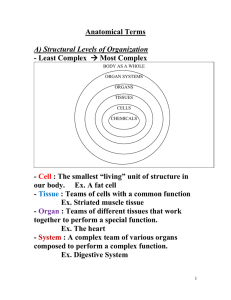
Anatomical Terms - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... - Anterior : Front/In front of (ventral) ex. The nose is on the anterior side of the head - Posterior : Back/In back of (dorsal) ex. The shoulder blades are on the posterior side of the torso. - Medial : Towards the midline of the body ex. The big toe is on the medial side of the foot. - Lateral : ...
... - Anterior : Front/In front of (ventral) ex. The nose is on the anterior side of the head - Posterior : Back/In back of (dorsal) ex. The shoulder blades are on the posterior side of the torso. - Medial : Towards the midline of the body ex. The big toe is on the medial side of the foot. - Lateral : ...
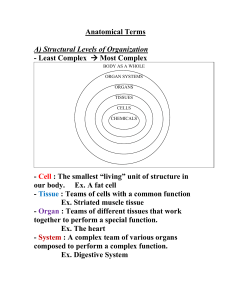
Anatomical Terms - Mr. Lesiuk
... - Anterior : Front/In front of (ventral) ex. The nose is on the anterior side of the head - Posterior : Back/In back of (dorsal) ex. The shoulder blades are on the posterior side of the torso. - Medial : Towards the midline of the body ex. The big toe is on the medial side of the foot. - Lateral : ...
... - Anterior : Front/In front of (ventral) ex. The nose is on the anterior side of the head - Posterior : Back/In back of (dorsal) ex. The shoulder blades are on the posterior side of the torso. - Medial : Towards the midline of the body ex. The big toe is on the medial side of the foot. - Lateral : ...
anatomical terms and terminoogy
... Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism. Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human organism. Anatomy is derived from the Greek word anatome which means "cutting up". Its Latin equivalent is dissectio. Anatomy has a wider scope than mere cutting up. It is the foundatio ...
... Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism. Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human organism. Anatomy is derived from the Greek word anatome which means "cutting up". Its Latin equivalent is dissectio. Anatomy has a wider scope than mere cutting up. It is the foundatio ...
the human body systems
... 1. w/respiratory – deliver O2 from lungs to cells and drop off CO2 from cells to lungs 2. w/digestive – absorb and deliver digested nutrients to cells 3. w/excretory – kidneys filter cellular waste out of blood for removal 4. w/lymphatic – both transport things to and from cells 5. w/immune – transp ...
... 1. w/respiratory – deliver O2 from lungs to cells and drop off CO2 from cells to lungs 2. w/digestive – absorb and deliver digested nutrients to cells 3. w/excretory – kidneys filter cellular waste out of blood for removal 4. w/lymphatic – both transport things to and from cells 5. w/immune – transp ...
the human body systems
... 1. w/respiratory – deliver O2 from lungs to cells and drop off CO2 from cells to lungs 2. w/digestive – absorb and deliver digested nutrients to cells 3. w/excretory – kidneys filter cellular waste out of blood for removal 4. w/lymphatic – both transport things to and from cells 5. w/immune – transp ...
... 1. w/respiratory – deliver O2 from lungs to cells and drop off CO2 from cells to lungs 2. w/digestive – absorb and deliver digested nutrients to cells 3. w/excretory – kidneys filter cellular waste out of blood for removal 4. w/lymphatic – both transport things to and from cells 5. w/immune – transp ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.