Anatomy and Physiology
... 3. The integumentary system has many functions. Its main function(s) is(are) to: a. Prevent infection b. Secrete hormones c. Produce white blood cells d. All of the above ...
... 3. The integumentary system has many functions. Its main function(s) is(are) to: a. Prevent infection b. Secrete hormones c. Produce white blood cells d. All of the above ...
Cnidarians etc
... Have a mantle (fold in the body wall that lines the shell) Muscular foot and/or tentacles All except bivlaves have a radula and a well-developed head • Most have an open circulatory system, some have closed circulation • Many respire using gills, slugs use a hole in the side of their head and breath ...
... Have a mantle (fold in the body wall that lines the shell) Muscular foot and/or tentacles All except bivlaves have a radula and a well-developed head • Most have an open circulatory system, some have closed circulation • Many respire using gills, slugs use a hole in the side of their head and breath ...
Chapter 41 Reptiles
... • Lizards, snakes, turtles, tuatarastwo atria & one ventricle- divided by a wall of tissue- septum • Crocodiles- two atria & two separate ventricles • Very little blood (good & bad) mixes in reptile hearts ...
... • Lizards, snakes, turtles, tuatarastwo atria & one ventricle- divided by a wall of tissue- septum • Crocodiles- two atria & two separate ventricles • Very little blood (good & bad) mixes in reptile hearts ...
Evidence of Evolution - Fall River Public Schools
... useful purpose, such as: Human tail bone Human appendix Some snakes have tiny pelvic bones and limb bones Whales have pelvic bones and a four-chamber stomach like a cow Vestigial structures are evidence that the structure was functional in an ancestor ...
... useful purpose, such as: Human tail bone Human appendix Some snakes have tiny pelvic bones and limb bones Whales have pelvic bones and a four-chamber stomach like a cow Vestigial structures are evidence that the structure was functional in an ancestor ...
Human Body Introduction - Living Environment H: 8(A,C)
... Organ systems are living things made of a group of organs that contribute to a specific function within the body. Organs are living things made of tissues that work together to perform a specific, complex function. Tissues are living things made of a group of cells with similar structures and functi ...
... Organ systems are living things made of a group of organs that contribute to a specific function within the body. Organs are living things made of tissues that work together to perform a specific, complex function. Tissues are living things made of a group of cells with similar structures and functi ...
File
... Type II: Scattered among the Type I cells, secrete ingredients for a surfactant to coat the alveoli ...
... Type II: Scattered among the Type I cells, secrete ingredients for a surfactant to coat the alveoli ...
COMPARING INVERTEBRATES
... • The nervous system gathers information from the environment. • The simplest nervous system, found in cnidarians, are nerve nets. ...
... • The nervous system gathers information from the environment. • The simplest nervous system, found in cnidarians, are nerve nets. ...
7th Grade 2nd Semester Test Chapters 14-17, 19
... 24. Amino acids are linked together chemically to form molecules of a. Complex carbohydrate b. Protein c. Simple carbohydrate d. Fat 25. Which of the following is NOT a nutrient? a. Fats b. Vitamins c. Fiber d. Water 26. Waste materials are prepared for elimination from the body in the a. Small int ...
... 24. Amino acids are linked together chemically to form molecules of a. Complex carbohydrate b. Protein c. Simple carbohydrate d. Fat 25. Which of the following is NOT a nutrient? a. Fats b. Vitamins c. Fiber d. Water 26. Waste materials are prepared for elimination from the body in the a. Small int ...
Question Report - Blue Valley Schools
... A true tissues B bilateral symmetry C limited to sexual reproduction D a homeobox-containing family of genes called Hox genes ____ 5 Which example below is NOT a current hypothesis regarding the Cambrian explosion? A Predator-prey relationships led to diversity through natural selection. B Evolution ...
... A true tissues B bilateral symmetry C limited to sexual reproduction D a homeobox-containing family of genes called Hox genes ____ 5 Which example below is NOT a current hypothesis regarding the Cambrian explosion? A Predator-prey relationships led to diversity through natural selection. B Evolution ...
2/13 Human Organ System
... This system consists of the brain and spinal cord, where many bodily functions are controlled, many sensations are processed and signals are sent to different parts of the body. Example: Functions affected by the CNS include muscle control, eyesight, breathing and memory. ...
... This system consists of the brain and spinal cord, where many bodily functions are controlled, many sensations are processed and signals are sent to different parts of the body. Example: Functions affected by the CNS include muscle control, eyesight, breathing and memory. ...
Anatomy of the Skin
... • Epidermis is outermost layer – primarily functional and protective. Subdivided into five layers which migrate upwards and whose purpose is ultimately to form the end layer, or stratum corneum – the outer layer of dead cells that protects us from our environment. Process is called keratinization. ...
... • Epidermis is outermost layer – primarily functional and protective. Subdivided into five layers which migrate upwards and whose purpose is ultimately to form the end layer, or stratum corneum – the outer layer of dead cells that protects us from our environment. Process is called keratinization. ...
exam_review_4_answers_1
... spinal cord), a notochord (a tough rod-like structure that provides support and protection), pharyngeal pouches (which in aquatic chordates develops into gills) and a tail. Some of these structures may exist only during the embryological phase of development and disappear before birth or adulthood. ...
... spinal cord), a notochord (a tough rod-like structure that provides support and protection), pharyngeal pouches (which in aquatic chordates develops into gills) and a tail. Some of these structures may exist only during the embryological phase of development and disappear before birth or adulthood. ...
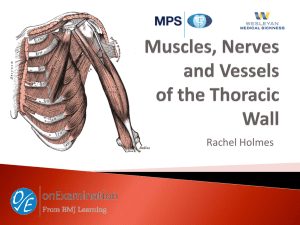
Pectoralis Major - University of Nottingham Surgical Society
... Clinical relevance: Chest drains ...
... Clinical relevance: Chest drains ...
Ch 40 Notes
... In vertebrates, the space between cells is filled with interstitial fluid, which allows for the movement of material into and out of cells A complex body plan helps an animal living in a variable environment to maintain a relatively stable internal environment Most animals are composed of specialize ...
... In vertebrates, the space between cells is filled with interstitial fluid, which allows for the movement of material into and out of cells A complex body plan helps an animal living in a variable environment to maintain a relatively stable internal environment Most animals are composed of specialize ...
The Human Body - St. Aloysius School
... 30. Nerves in the muscles receive messages from the brain. These messages tell the muscles when to pull and when to rest. 31. A muscle is tissue that works with the skeleton to make movement possible. 32. Muscles are either skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, or cardiac muscles. 33. Skeletal muscles a ...
... 30. Nerves in the muscles receive messages from the brain. These messages tell the muscles when to pull and when to rest. 31. A muscle is tissue that works with the skeleton to make movement possible. 32. Muscles are either skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, or cardiac muscles. 33. Skeletal muscles a ...
Name Science The Human Body
... 30. Nerves in the muscles receive messages from the brain. These messages tell the muscles when to pull and when to rest. 31. A muscle is tissue that works with the skeleton to make movement possible. 32. Muscles are either skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, or cardiac muscles. 33. Skeletal muscles a ...
... 30. Nerves in the muscles receive messages from the brain. These messages tell the muscles when to pull and when to rest. 31. A muscle is tissue that works with the skeleton to make movement possible. 32. Muscles are either skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, or cardiac muscles. 33. Skeletal muscles a ...
ANATOMY LECTURE EXAM 1
... 10. Which of the following tissues is voluntary and striated? a. stratified squamous epithelium b. simple squamous epithelium c. cardiac muscle d. dense irregular connective tissue e. skeletal muscle 11. Centers of ossification contain predominately _____. a. chondroblasts b. osteocytes c. osteobla ...
... 10. Which of the following tissues is voluntary and striated? a. stratified squamous epithelium b. simple squamous epithelium c. cardiac muscle d. dense irregular connective tissue e. skeletal muscle 11. Centers of ossification contain predominately _____. a. chondroblasts b. osteocytes c. osteobla ...
Study_Guide_Human_Body_2012_1st_one_answers
... Nervous System - the body system responsible for receiving and sending electrical messages throughout the body. Central Nervous System - the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System - all of the parts of the nervous system except for the brain and spinal cord. Neuron - a nerve cell specializ ...
... Nervous System - the body system responsible for receiving and sending electrical messages throughout the body. Central Nervous System - the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System - all of the parts of the nervous system except for the brain and spinal cord. Neuron - a nerve cell specializ ...
Organ Systems and Life
... channels embedded in the plasma membrane. There are three kinds of muscle tissue, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissues. Skeletal muscles are typically consciously controlled by the central nervous system, whereas cardiac and smooth muscles are controlled subconsciously by the autonomic ner ...
... channels embedded in the plasma membrane. There are three kinds of muscle tissue, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissues. Skeletal muscles are typically consciously controlled by the central nervous system, whereas cardiac and smooth muscles are controlled subconsciously by the autonomic ner ...
Kingdom Animalia
... into halves from the mouth. Example: Anemone Bilateral Symmetry – can be divided lengthwise into 2 mirror images. Example: Humans Cephalization: concentration of sense organs at the front (top) of the body ...
... into halves from the mouth. Example: Anemone Bilateral Symmetry – can be divided lengthwise into 2 mirror images. Example: Humans Cephalization: concentration of sense organs at the front (top) of the body ...
Biology Vocabulary 18, test on Friday, 3/6/15
... toward the head end of an animal with bilateral symmetry body plan that can be divided into mirror images along only one plane through the central axis tendency to concentrate sensory organs and nervous tissue at an animal's anterior end fluid-filled body cavity completely surrounded by mesoderm bac ...
... toward the head end of an animal with bilateral symmetry body plan that can be divided into mirror images along only one plane through the central axis tendency to concentrate sensory organs and nervous tissue at an animal's anterior end fluid-filled body cavity completely surrounded by mesoderm bac ...
7.b. Insect Tracheoles
... Gases are transported from spiracles (openings along the abdomen) by a series of branching hollow tubes (trachea) to the tissues where oxygen is required and where carbon dioxide is produced. The fine tubules that deliver oxygen to the tissues themselves are called tracheoles and often have a film o ...
... Gases are transported from spiracles (openings along the abdomen) by a series of branching hollow tubes (trachea) to the tissues where oxygen is required and where carbon dioxide is produced. The fine tubules that deliver oxygen to the tissues themselves are called tracheoles and often have a film o ...
circulatory system
... Skeletal System • 5 major functions: – Gives shape and support to body – Protects internal organs – Major muscles attach to the bone to help it move – Blood cells are formed in the center of many bones in soft tissue called red marrow – Stores calcium and phosphorous which makes the bones hard ...
... Skeletal System • 5 major functions: – Gives shape and support to body – Protects internal organs – Major muscles attach to the bone to help it move – Blood cells are formed in the center of many bones in soft tissue called red marrow – Stores calcium and phosphorous which makes the bones hard ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.