Terms related to the position . median sagittal plane . is a vertical
... denote levels relative high or low with reference to the upper & lower ends of the body. internal & external are used to describe the relative distance of the structure from the center of the organ or cavity . ipsilateral referred the same side of the body ,controlateral referred the opposite side o ...
... denote levels relative high or low with reference to the upper & lower ends of the body. internal & external are used to describe the relative distance of the structure from the center of the organ or cavity . ipsilateral referred the same side of the body ,controlateral referred the opposite side o ...
Body Systems - emseducation.info
... supplies nutrients to the other two layers. It also cushions the body and protects it from the cold. ...
... supplies nutrients to the other two layers. It also cushions the body and protects it from the cold. ...
Name Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide
... and nerves c. Muscles that immobilize a bone or a muscle’s origin so that only the desired ...
... and nerves c. Muscles that immobilize a bone or a muscle’s origin so that only the desired ...
Anatomy Man - Get a Clue with Mrs. Perdue
... Friday, you will need to bring all materials to class. I will supply glue, tape, and scissors. You and your group will have the whole class time to complete your anatomy man in class. On Tuesday, your group will present your project. On the back is a list of terms that must be labeled on your anatom ...
... Friday, you will need to bring all materials to class. I will supply glue, tape, and scissors. You and your group will have the whole class time to complete your anatomy man in class. On Tuesday, your group will present your project. On the back is a list of terms that must be labeled on your anatom ...
Chapter 11 Structure and
... within their bodies, reproduce, and move about to meet their needs. How are animals classified? Animals are classified according to how they are related, which is based on their evolutionary history. 1. Anatomy is the structure of an organism. Physiology is the study of functions in organisms. 2. a. ...
... within their bodies, reproduce, and move about to meet their needs. How are animals classified? Animals are classified according to how they are related, which is based on their evolutionary history. 1. Anatomy is the structure of an organism. Physiology is the study of functions in organisms. 2. a. ...
Body Systems Powerpoint
... Purpose: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body– each muscle is an organ– over 600 muscles– attaches to bone Amazing Medical Stories - Season 3, Episode 3 Functions: 1. Contract and relax to cause movement 2. Stabilize bod ...
... Purpose: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body– each muscle is an organ– over 600 muscles– attaches to bone Amazing Medical Stories - Season 3, Episode 3 Functions: 1. Contract and relax to cause movement 2. Stabilize bod ...
Introduction to Anatomy - Mt. Olive School District
... Introduction to Anatomy The Human Organism ...
... Introduction to Anatomy The Human Organism ...
A) Animal Tissue
... a grouping of cells having a similar set of limited functions. (The second level of organization) ...
... a grouping of cells having a similar set of limited functions. (The second level of organization) ...
human-anatomy-and-body-systems-student
... -- radius and ulna (lower arm) -- cranium (skull) -- sternum (breastbone) -- clavicle (shoulder blade) -- fibula and tibia (calf) -- vertebrae (back) -- scalpula (shoulder) -- pelvic bone -- coccyx (tail bone) -- phalanges (fingers/toes) ...
... -- radius and ulna (lower arm) -- cranium (skull) -- sternum (breastbone) -- clavicle (shoulder blade) -- fibula and tibia (calf) -- vertebrae (back) -- scalpula (shoulder) -- pelvic bone -- coccyx (tail bone) -- phalanges (fingers/toes) ...
Organization of Life Study Guide Skeletal System pg.444
... through the eyes, nose, mouth, or wound. What is the body's first line of defense against ...
... through the eyes, nose, mouth, or wound. What is the body's first line of defense against ...
4 - Bulldogbiology.com
... to bone o Skeletal muscle tissue- main tissue of muscles attached to bones Functions in maintaining posture and in moving the body and its assorted parts Contracts rapidly Voluntary contractions ...
... to bone o Skeletal muscle tissue- main tissue of muscles attached to bones Functions in maintaining posture and in moving the body and its assorted parts Contracts rapidly Voluntary contractions ...
Kingdom Animalia
... Notochord- stiff rod that provide support in lower chordates – Cells along the dorsal surface of the mesoderm germ layer form the notochord. – In higher chordates, the vertebrea are formed from nearby cells in the mesoderm ...
... Notochord- stiff rod that provide support in lower chordates – Cells along the dorsal surface of the mesoderm germ layer form the notochord. – In higher chordates, the vertebrea are formed from nearby cells in the mesoderm ...
Characteristics to Classify Animals
... Although all animals are multi-cellular, they do not all possess tissues, organs, or organ systems Members of some phyla possess bodies in which cells are only poorly organized into tissues Members of other phyla have highly complex bodies in which cells, tissues, and organs and organized into ...
... Although all animals are multi-cellular, they do not all possess tissues, organs, or organ systems Members of some phyla possess bodies in which cells are only poorly organized into tissues Members of other phyla have highly complex bodies in which cells, tissues, and organs and organized into ...
Lecture PowerPoint
... Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are groups of similar cells that function together. T ...
... Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are groups of similar cells that function together. T ...
Unit B Glossary
... oxygen-enriched blood to body tissues. Atrium (plural: atria) -One of the two upper chambers in the human heart that receives blood returning from the body or lungs. blood -the red liquid that circulates in the arteries and veins of humans and other vertebrate animals, carrying oxygen to and carbon ...
... oxygen-enriched blood to body tissues. Atrium (plural: atria) -One of the two upper chambers in the human heart that receives blood returning from the body or lungs. blood -the red liquid that circulates in the arteries and veins of humans and other vertebrate animals, carrying oxygen to and carbon ...
Human Body Systems and Single Cell vs. Multicellular
... v. Amoeba = consumer=eats other living organisms (surrounds food as it traps & eats it) 5. Multicellular Organism: an organism with more than 1 cell that work together to carry out life processes, multicellular organisms are more complex (have many parts) a. Transport System: a system that moves nut ...
... v. Amoeba = consumer=eats other living organisms (surrounds food as it traps & eats it) 5. Multicellular Organism: an organism with more than 1 cell that work together to carry out life processes, multicellular organisms are more complex (have many parts) a. Transport System: a system that moves nut ...
IPAnatomy Review for Respiration 1
... 2. Each lung is surrounded by two layers of serous membrane known as pleurae. ______________ pleura covers the surface of the lung; __________ pleura lines the thoracic wall. The space in between them is called the ____________ cavity and it is filled with ___________ fluid. This fluid assists breat ...
... 2. Each lung is surrounded by two layers of serous membrane known as pleurae. ______________ pleura covers the surface of the lung; __________ pleura lines the thoracic wall. The space in between them is called the ____________ cavity and it is filled with ___________ fluid. This fluid assists breat ...
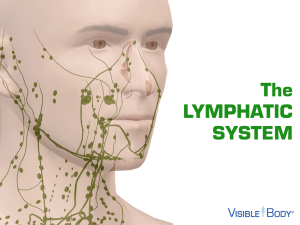
The LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
... through the vessels and add lymphocytes to it. White blood cells that produce antibodies target foreign cells and attack them. Factoid: Overly large lymph nodes are red flags for doctors, usually indicating an infection or disease. ...
... through the vessels and add lymphocytes to it. White blood cells that produce antibodies target foreign cells and attack them. Factoid: Overly large lymph nodes are red flags for doctors, usually indicating an infection or disease. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.