Animal Body Systems
... Circulation Purpose: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the other parts of the body There are 2 types of circulatory systems: Open: heart pumps fluid containing oxygen through a series of vessels & is dumped into the body cavity. Closed: heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels. T ...
... Circulation Purpose: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the other parts of the body There are 2 types of circulatory systems: Open: heart pumps fluid containing oxygen through a series of vessels & is dumped into the body cavity. Closed: heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels. T ...
Body systems Review sheet on Integumentary, Excretory
... 18. List the main organs in the excretory system and explain what they do. SKIN- RELEASES HEAT BY PERSPIRATION LUNGS- RELEASES CARBON DIOXIDE LIVER- BREAKS DOWN SOME WASTES LIKE FATS SO THEY CAN BE EXCRETED KIDNEYS-FILTERS THE BLOOD AND REMOVES UREA, EXCESS WATER, AND SOME OTHER WASTE MATERIALS IN ...
... 18. List the main organs in the excretory system and explain what they do. SKIN- RELEASES HEAT BY PERSPIRATION LUNGS- RELEASES CARBON DIOXIDE LIVER- BREAKS DOWN SOME WASTES LIKE FATS SO THEY CAN BE EXCRETED KIDNEYS-FILTERS THE BLOOD AND REMOVES UREA, EXCESS WATER, AND SOME OTHER WASTE MATERIALS IN ...
Animal Body Systems
... Circulation Purpose: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the other parts of the body There are 2 types of circulatory systems: Open: heart pumps fluid containing oxygen through a series of vessels & is dumped into the body cavity. Closed: heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels. T ...
... Circulation Purpose: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the other parts of the body There are 2 types of circulatory systems: Open: heart pumps fluid containing oxygen through a series of vessels & is dumped into the body cavity. Closed: heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels. T ...
Body System Checklist
... Digestive System The goal of your powerpoint is to provide enough information so your students understand the anatomy (structure) and physiology (function) of the your system. If you are not sure if you are covering everything that is needed or if it is not making sense, please speak with the teache ...
... Digestive System The goal of your powerpoint is to provide enough information so your students understand the anatomy (structure) and physiology (function) of the your system. If you are not sure if you are covering everything that is needed or if it is not making sense, please speak with the teache ...
Animal Body Systems
... Circulation Purpose: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the other parts of the body There are 2 types of circulatory systems: Open: heart pumps fluid containing oxygen through a series of vessels & is dumped into the body cavity. Closed: heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels. T ...
... Circulation Purpose: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the other parts of the body There are 2 types of circulatory systems: Open: heart pumps fluid containing oxygen through a series of vessels & is dumped into the body cavity. Closed: heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels. T ...
Section 1 and 2 PowerPoint
... • Ganglia – groups of nerves bundled together. Animals can have a brain and ganglia or just have ganglia depending on how advanced the animal is • Gut – pouch lined with digestive enzymes • Coelom – cavity that allows organs such as the gut, heart etc to work without interference from body movement ...
... • Ganglia – groups of nerves bundled together. Animals can have a brain and ganglia or just have ganglia depending on how advanced the animal is • Gut – pouch lined with digestive enzymes • Coelom – cavity that allows organs such as the gut, heart etc to work without interference from body movement ...
ANIMAL BIOLOGY LABORATORY Lab 9: Phylum Chordata
... Order Caudata (Urodela) (salamanders) • Body with head, trunk, and long tail • Usually 2 pairs of equal-sized limbs • Some respire through skin • Some salamanders retain larval characteristics into adulthood: e.g., external gills, absence of eyelids, presence of lateral line, and a fin-like tail Ord ...
... Order Caudata (Urodela) (salamanders) • Body with head, trunk, and long tail • Usually 2 pairs of equal-sized limbs • Some respire through skin • Some salamanders retain larval characteristics into adulthood: e.g., external gills, absence of eyelids, presence of lateral line, and a fin-like tail Ord ...
SYSTEMS IN ORGANISMS TAKS QUESTIONS SPRING 2003 – 10
... A Circulatory and nervous systems B* Nervous and muscular systems C Muscular and digestive systems D Digestive and circulatory systems ...
... A Circulatory and nervous systems B* Nervous and muscular systems C Muscular and digestive systems D Digestive and circulatory systems ...
Section 18.2 - CPO Science
... thin, outer layer that you see. • The dermis lies underneath and is made of connective tissue and protein fibers. • The subcutaneous fat layer functions as insulation for your body. ...
... thin, outer layer that you see. • The dermis lies underneath and is made of connective tissue and protein fibers. • The subcutaneous fat layer functions as insulation for your body. ...
Organ System Level
... 4. Organ Level Different tissues combine to form organs, such as the urinary bladder 5. Organ System Level Organs such as the urinary bladder and kidneys make up an organ system 6. Organism Level Organ systems make up an organism ...
... 4. Organ Level Different tissues combine to form organs, such as the urinary bladder 5. Organ System Level Organs such as the urinary bladder and kidneys make up an organ system 6. Organism Level Organ systems make up an organism ...
Arthropods and Echinoderms
... • Chelicerae mouthparts: fangs that sting and pedipalps that grab prey • Two body sections: cephalothorax and ...
... • Chelicerae mouthparts: fangs that sting and pedipalps that grab prey • Two body sections: cephalothorax and ...
Normal anatomy with Elements of Topographic Anatomy The term
... 3. Osteal exits of cranial nerves. Temporomandibular joint. Cranial synchondroses and syndesmoses. Anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae. Orbit. Pterygopalatine fossa. Temporal and infatemporal fossae. Nasal cavity. Retromandibular fossa. Passage of cranial nerves through openings in the cra ...
... 3. Osteal exits of cranial nerves. Temporomandibular joint. Cranial synchondroses and syndesmoses. Anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae. Orbit. Pterygopalatine fossa. Temporal and infatemporal fossae. Nasal cavity. Retromandibular fossa. Passage of cranial nerves through openings in the cra ...
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous
... group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. ...
... group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. ...
Review for structures
... _______ Bones -- longest; provide support and movement; levers; example -- legs, ribs, pelvic bones _______ Bones -smaller than long; joints; comfort and mobility example -- feet and hands _______ Bones -- have an irregular shape; support and protect example -- vertebrae ________Bones -- thin and fl ...
... _______ Bones -- longest; provide support and movement; levers; example -- legs, ribs, pelvic bones _______ Bones -smaller than long; joints; comfort and mobility example -- feet and hands _______ Bones -- have an irregular shape; support and protect example -- vertebrae ________Bones -- thin and fl ...
Chapter 19: The Animal Body and How It Moves
... •All vertebrates have the same general architecture: •Food flows through a long tube from mouth to anus •Tube is suspended in coelom, which is divided into •Thoracic cavity – Heart and lungs •Abdominal cavity – Stomach and intestines •Body is supported by a skeleton made up of jointed bones •The sku ...
... •All vertebrates have the same general architecture: •Food flows through a long tube from mouth to anus •Tube is suspended in coelom, which is divided into •Thoracic cavity – Heart and lungs •Abdominal cavity – Stomach and intestines •Body is supported by a skeleton made up of jointed bones •The sku ...
Human Body Adventure Integumentary System (Skin) Muscular
... 2. What do we call the outer layer of the skin? ______________ 3. What do we call the inner layer of the skin? ______________ 4. True or False? Your skin is the largest organ of your body. Challenge: Name three things you can find in the inner layer of skin. R ...
... 2. What do we call the outer layer of the skin? ______________ 3. What do we call the inner layer of the skin? ______________ 4. True or False? Your skin is the largest organ of your body. Challenge: Name three things you can find in the inner layer of skin. R ...
Re-Teach Seventh Grade Science Unit 4 Human Body Place your
... B. the digestive system. C. the respiration system. ...
... B. the digestive system. C. the respiration system. ...
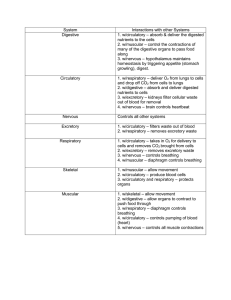
Interactions between the Nervous System and…
... The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into molecules small enough to be used by the body's cells and tissues. The food is broken apart through chewing and stomach churning, but also chemically -- through the stomach's acid-loving enzymes, and on to the small intestine, which rec ...
... The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into molecules small enough to be used by the body's cells and tissues. The food is broken apart through chewing and stomach churning, but also chemically -- through the stomach's acid-loving enzymes, and on to the small intestine, which rec ...
Chapter 18: The Chordates
... The origin of jaws opened up new feeding opportunities. The evolution of lungs, or lung-like structures gave the possibility of life on land. Tetrapods (Greek for four feet) – jawed vertebrates with two pairs of limbs were the first vertebrates on land, and could support their weight on land. Th ...
... The origin of jaws opened up new feeding opportunities. The evolution of lungs, or lung-like structures gave the possibility of life on land. Tetrapods (Greek for four feet) – jawed vertebrates with two pairs of limbs were the first vertebrates on land, and could support their weight on land. Th ...
Animals 26-1PPT - holyoke
... backbone. Everything from insects to squid. 2. Vertebrates- 5% of animals species, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish. ...
... backbone. Everything from insects to squid. 2. Vertebrates- 5% of animals species, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish. ...
Annelida - The Burge
... In Earthworms there are longitudinal vessels running the entire length of the worm, one dorsal and several ventral. Connecting the dorsal and ventral vessels, and so completing the circuit are five pairs of hearts, ...
... In Earthworms there are longitudinal vessels running the entire length of the worm, one dorsal and several ventral. Connecting the dorsal and ventral vessels, and so completing the circuit are five pairs of hearts, ...
27-2 Phylum Annelida - Ms. Sidhu's Biology Website
... In Earthworms there are longitudinal vessels running the entire length of the worm, one dorsal and several ventral. Connecting the dorsal and ventral vessels, and so completing the circuit are five pairs of hearts, ...
... In Earthworms there are longitudinal vessels running the entire length of the worm, one dorsal and several ventral. Connecting the dorsal and ventral vessels, and so completing the circuit are five pairs of hearts, ...
Answers to Review Questions on Porifera, Cnidarians, Nematoda
... 11. All members of the animal kingdom are multicellular, eukaryotic hetertrophs whose cells lack cell walls. They reproduce sexually and are motile at some point during their life cycle. 14. Should use the terms anterior, dorsal, lateral, ventral, dorsal, bilateral symmetry, and motile when labeling ...
... 11. All members of the animal kingdom are multicellular, eukaryotic hetertrophs whose cells lack cell walls. They reproduce sexually and are motile at some point during their life cycle. 14. Should use the terms anterior, dorsal, lateral, ventral, dorsal, bilateral symmetry, and motile when labeling ...
Body Organization
... – Hierarchy is the arrangement of a particular set of items that are represented as being "above," "below," or "at the same level as" one another. ...
... – Hierarchy is the arrangement of a particular set of items that are represented as being "above," "below," or "at the same level as" one another. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.