Body Organization
... • Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells. • The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. • Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. ...
... • Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells. • The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. • Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. ...
A Closer Look at the Human Body Systems
... directly controlled by the brain and heart, while others are not. Let’s look closer at each body system and its responsibilities. ...
... directly controlled by the brain and heart, while others are not. Let’s look closer at each body system and its responsibilities. ...
Zoology Chapter 8-9: Introduction to Animals Review for Test List the
... 25. ___bidirectional___________________: type of digestive system in which there is only one opening, so food enters and exits same opening 26. ____unidirectional________________________________: type of digestive system in which there are two openings, so food enters one opening and exits another 2 ...
... 25. ___bidirectional___________________: type of digestive system in which there is only one opening, so food enters and exits same opening 26. ____unidirectional________________________________: type of digestive system in which there are two openings, so food enters one opening and exits another 2 ...
Zoology Chapter 8-‐9: Introduction to Animals Review for Test
... openings, so food enters one opening and exits another 27. ___integumentary_________________________________: body system consisting of skin, scales, or feathers 28. ____digestive________________________________: body system th ...
... openings, so food enters one opening and exits another 27. ___integumentary_________________________________: body system consisting of skin, scales, or feathers 28. ____digestive________________________________: body system th ...
Medical roots 11
... 46. cardi- Heart- a hollow muscular organ that pumps the blood through the circulatory system by rhythmic contraction and dilation. ...
... 46. cardi- Heart- a hollow muscular organ that pumps the blood through the circulatory system by rhythmic contraction and dilation. ...
Bellringer: All directional terms are relative to proper anatomical
... • Anterior and Posterior have a different meaning! • Anterior- towards head • Posterior- towards tail ...
... • Anterior and Posterior have a different meaning! • Anterior- towards head • Posterior- towards tail ...
Cellular Hierarchy
... Several types of tissues group together and form an organ. The brain, heart, stomach and lungs are some examples of organs. Organs usually perform a complex task. Figure 3.4 shows a four chambered human heart. This organ is made of specialized tissues that act as a pump to move blood (and other flui ...
... Several types of tissues group together and form an organ. The brain, heart, stomach and lungs are some examples of organs. Organs usually perform a complex task. Figure 3.4 shows a four chambered human heart. This organ is made of specialized tissues that act as a pump to move blood (and other flui ...
4. The embryo of flatworms has a third germ tissue
... Some flukes have fishes or water birds as their primary hosts so if they burrow into human skin, they cannot live there b/c they are ...
... Some flukes have fishes or water birds as their primary hosts so if they burrow into human skin, they cannot live there b/c they are ...
Orientation to Human Body PPT
... structures or forms of living things. • Physiology is defined as the study of the functions and vital processes of living organisms. ...
... structures or forms of living things. • Physiology is defined as the study of the functions and vital processes of living organisms. ...
i. cardiovascular system
... 6.Avoid inhaling harmful chemicals 7.Seek medical help for respiratory infections ...
... 6.Avoid inhaling harmful chemicals 7.Seek medical help for respiratory infections ...
Kingdom Animalia - Invertebrates
... • Has brain and nerve cord down length of body • Eat soil with dead organisms – decompose • Form tunnels in soil for aeration and drainage that is great for plants. • Hermphroditic – but need 2 worms, both produce eggs and lay them in a cocoon. • Movement by Peristalsis using circular and long muscl ...
... • Has brain and nerve cord down length of body • Eat soil with dead organisms – decompose • Form tunnels in soil for aeration and drainage that is great for plants. • Hermphroditic – but need 2 worms, both produce eggs and lay them in a cocoon. • Movement by Peristalsis using circular and long muscl ...
Animals in a `nutshell` #1 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... Cephalochordata: amphioxus Vertebrata: lampreys, sharks, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals ...
... Cephalochordata: amphioxus Vertebrata: lampreys, sharks, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals ...
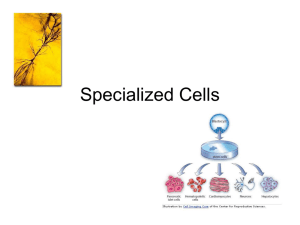
Specialized Cells
... -joins other tissue together and also stores fat and makes blood cells. - made of specialized cells and fibers that stick to living cells. *exs. Bone, cartilage, and blood. ...
... -joins other tissue together and also stores fat and makes blood cells. - made of specialized cells and fibers that stick to living cells. *exs. Bone, cartilage, and blood. ...
Kingdom Animalia
... POLYP is sessile – does not move MEDUSA is motile – squeezes bell (umbrella) to move uses simple ring of contractile tissue (not muscle tissue yet) ...
... POLYP is sessile – does not move MEDUSA is motile – squeezes bell (umbrella) to move uses simple ring of contractile tissue (not muscle tissue yet) ...
A Trip Through The Human Body
... 6. Where does gas exchange occur within the Respiratory System? P. 1003 7. What muscle assists the respiratory system to allow air to enter and expel from your body? P. 1002 The Circulatory & Cardiovascular System 1. What is the circulatory system composed of? P. 992 2. What are the 3 main vessels o ...
... 6. Where does gas exchange occur within the Respiratory System? P. 1003 7. What muscle assists the respiratory system to allow air to enter and expel from your body? P. 1002 The Circulatory & Cardiovascular System 1. What is the circulatory system composed of? P. 992 2. What are the 3 main vessels o ...
Anatomy & Physiology Mid Term Review
... superior and caudal inferior and cranial inferior and cephalad anterior and ventral anterior and dorsal ...
... superior and caudal inferior and cranial inferior and cephalad anterior and ventral anterior and dorsal ...
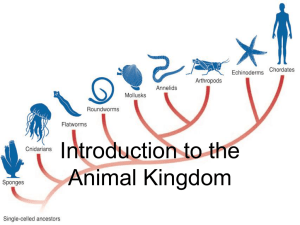
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end, or head, with sense organs, and a body cavity. ...
... specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end, or head, with sense organs, and a body cavity. ...
Anatomical Position and Directional Terms
... Embryo: when cell division begins Blastula: fluid-filled cell Gastrulation: cell division continues until one side of the blastula moves inward ...
... Embryo: when cell division begins Blastula: fluid-filled cell Gastrulation: cell division continues until one side of the blastula moves inward ...
Study Guide for Lab Practicals in Biol 241
... Four practical quizzes will be administered in the lab and will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to le ...
... Four practical quizzes will be administered in the lab and will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to le ...
Document
... the ___________________ with the __________________________. The larynx is composed of nine pieces of _______________________________. The major portion is known as the _________________________________ which is nicknamed the Adam’s apple. The opening through the larynx is called the _______________ ...
... the ___________________ with the __________________________. The larynx is composed of nine pieces of _______________________________. The major portion is known as the _________________________________ which is nicknamed the Adam’s apple. The opening through the larynx is called the _______________ ...
Ch 25 Introduction to Animals
... Produces sense organs, nerves, and the outer layer of the skin. ...
... Produces sense organs, nerves, and the outer layer of the skin. ...
25.2_Animal_Body_Plans_and_Evolution
... Produces sense organs, nerves, and the outer layer of the skin. ...
... Produces sense organs, nerves, and the outer layer of the skin. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.