Investigating the Human Body - On-site student
... Our muscles and skeleton: the power within Our movements depend on our muscles and skeleton. We have a bony skeleton with muscles attached. Our muscles and skeleton allow us to move, they support us and protect our inside organs. Look at the Body parts - muscles and skeletal displays. ...
... Our muscles and skeleton: the power within Our movements depend on our muscles and skeleton. We have a bony skeleton with muscles attached. Our muscles and skeleton allow us to move, they support us and protect our inside organs. Look at the Body parts - muscles and skeletal displays. ...
Daily Activity 4-12-2012
... • Don’t forget – sponges are animals and belong to the Animal Kingdom 1. Multicellular 2. No organs or body systems 3 . Cellular digestion (heterotrophic) 4. Asymmetry ...
... • Don’t forget – sponges are animals and belong to the Animal Kingdom 1. Multicellular 2. No organs or body systems 3 . Cellular digestion (heterotrophic) 4. Asymmetry ...
Phylum Cnidaria: Hydroids, jellyfish, anemones, corals.
... Medusae 2. have a shorter longitudinal axis a. mouth often with oral arms. 3. body wall also diploblastic a. highly thickened meosglea - forms bell. ...
... Medusae 2. have a shorter longitudinal axis a. mouth often with oral arms. 3. body wall also diploblastic a. highly thickened meosglea - forms bell. ...
PE terminology - Horton High School
... Abduction – moving an arm or leg sideways away from the center of the body. (lateral arm raise) Adduction – is the opposite of abduction, moving an arm or leg from the side toward the center of the body. (the arm outstretched to the side is dropped to your side) ...
... Abduction – moving an arm or leg sideways away from the center of the body. (lateral arm raise) Adduction – is the opposite of abduction, moving an arm or leg from the side toward the center of the body. (the arm outstretched to the side is dropped to your side) ...
Evaluation of the Lumbar Spine
... • At some time in their lives, 80% of the general population will experience some type of low back pain (LBP) - it is second only to the common cold as a reason for physician visits, and the most expensive source of compensated work related injury in modern industrialized countries • Despite the fre ...
... • At some time in their lives, 80% of the general population will experience some type of low back pain (LBP) - it is second only to the common cold as a reason for physician visits, and the most expensive source of compensated work related injury in modern industrialized countries • Despite the fre ...
full text - World Register of Marine Species
... This form of the ventral surface of the body. the nervous system, common to the articulated classes of animals, is expressed by the term diplo-neura, and it is found to accompany an organization generally more complex than that of the cyclo-neurose classes, and inferior to that of most of the succee ...
... This form of the ventral surface of the body. the nervous system, common to the articulated classes of animals, is expressed by the term diplo-neura, and it is found to accompany an organization generally more complex than that of the cyclo-neurose classes, and inferior to that of most of the succee ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Lab
... umbilical cord (INCISION 2), again leaving about a 1" 2-inch border. Stop your cut about one inch short of the anus. 11.Make the two lateral incisions just in front of the hind legs (INCISION 3). If you have a male pig, cutting off-center ensures that you do not cut the penis, which is incompletely ...
... umbilical cord (INCISION 2), again leaving about a 1" 2-inch border. Stop your cut about one inch short of the anus. 11.Make the two lateral incisions just in front of the hind legs (INCISION 3). If you have a male pig, cutting off-center ensures that you do not cut the penis, which is incompletely ...
Body Planes, Directions, and Cavities
... muscle that aids in breathing and separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities – Abdominopelvic cavity ...
... muscle that aids in breathing and separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities – Abdominopelvic cavity ...
Fetal Pig Dissection HB
... 4. All of the stomachs of the pigs were empty. Why wouldn’t any of them be full? (hint: where does the fetal pig get its food from?) __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
... 4. All of the stomachs of the pigs were empty. Why wouldn’t any of them be full? (hint: where does the fetal pig get its food from?) __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
Ch. 25
... the system consists of a network of fine tubules that run through the body enlarged flame cells (cilia-lined bulbs) are located on the side branches of the tubules the cilia move water and excretory substances into the tubules and then into exit pores the primary function of the flame cells ...
... the system consists of a network of fine tubules that run through the body enlarged flame cells (cilia-lined bulbs) are located on the side branches of the tubules the cilia move water and excretory substances into the tubules and then into exit pores the primary function of the flame cells ...
Biology & Anatomy of the Honey Bee
... the top of the head between the bee’s two larger compound eyes. The ocelli detect light but can’t focus or arrange an image like the larger compound eyes •Honey Bees use their antennae to learn about their environment: Tiny sensory hairs on each antenna allow them to smell, taste, feel air movements ...
... the top of the head between the bee’s two larger compound eyes. The ocelli detect light but can’t focus or arrange an image like the larger compound eyes •Honey Bees use their antennae to learn about their environment: Tiny sensory hairs on each antenna allow them to smell, taste, feel air movements ...
matodes and Arthropods
... Parasitize both plants and animals Pinworms and hookworms cause intestinal problems in humans and other animals Trichonella causes trichonosis (attaches to intestinal wall and robs host of nutrients) One species causes what we call elephantiasis Digestion – mouth and anus Circulation - none ...
... Parasitize both plants and animals Pinworms and hookworms cause intestinal problems in humans and other animals Trichonella causes trichonosis (attaches to intestinal wall and robs host of nutrients) One species causes what we call elephantiasis Digestion – mouth and anus Circulation - none ...
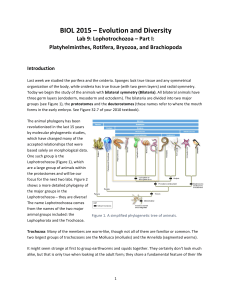
BIOL 2015 – Evolution and Diversity
... openings are the diverticula of the gastrovascular cavity. Pharynx region: This cross section shows the pharynx, which is retracted into the pharyngeal cavity (the empty white space surrounding the pharynx). The pharynx itself is a thick, muscular tube; when Planaria eats, it everts the pharynx ...
... openings are the diverticula of the gastrovascular cavity. Pharynx region: This cross section shows the pharynx, which is retracted into the pharyngeal cavity (the empty white space surrounding the pharynx). The pharynx itself is a thick, muscular tube; when Planaria eats, it everts the pharynx ...
4 Planes
... – Used to describe locations of extremities in relation to the main trunk Proximal – Close to Distal – Distant from ...
... – Used to describe locations of extremities in relation to the main trunk Proximal – Close to Distal – Distant from ...
Chapter 40 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Lecture
... The rates of exchange of nutrients, wastes, and gases are proportional to the membrane surface area, while the amount of material that must be exchanged is proportional to cell volume. o For example, a single-celled protist living in water has a sufficient surface area of plasma membrane to service ...
... The rates of exchange of nutrients, wastes, and gases are proportional to the membrane surface area, while the amount of material that must be exchanged is proportional to cell volume. o For example, a single-celled protist living in water has a sufficient surface area of plasma membrane to service ...
Document
... c. paralyzing small crustaceans with stinging cells d. absorbing nutrients from the guts of their hosts e. performing photosynthesis 16. Sponges lack _____. a. a complete digestive tract b. germ layers c. true tissues d. all of the above 17. Which characteristic is not true of sponges? a. They have ...
... c. paralyzing small crustaceans with stinging cells d. absorbing nutrients from the guts of their hosts e. performing photosynthesis 16. Sponges lack _____. a. a complete digestive tract b. germ layers c. true tissues d. all of the above 17. Which characteristic is not true of sponges? a. They have ...
Invertebrates v2
... • Their gut is equipped with jaws, tongue like structure with teeth • Nerves ring around the gut • The heart is located at the back end of the body • Must stay moist in order to survive • Muscular foot to move, dig, and hang on • Examples of mollusks: snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons, limpets, oc ...
... • Their gut is equipped with jaws, tongue like structure with teeth • Nerves ring around the gut • The heart is located at the back end of the body • Must stay moist in order to survive • Muscular foot to move, dig, and hang on • Examples of mollusks: snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons, limpets, oc ...
Serous Membranes
... All contain an epithelial sheet combined with an underlying layer of connective tissue. These membranes are actually simple organs. ...
... All contain an epithelial sheet combined with an underlying layer of connective tissue. These membranes are actually simple organs. ...
Muscular System - cloudfront.net
... produces movement provides stabilization generates heat pumps lymph ...
... produces movement provides stabilization generates heat pumps lymph ...
Digestive Systems: The Anatomy of Representative Vertebrates
... The digestive system participates in the procurement and metabolism of energy-containing materials. Food is taken in through the mouth and digested in the digestive tract, and nutrients are transported to all parts of the body by the circulatory system. Molecules obtained as food are stored at a var ...
... The digestive system participates in the procurement and metabolism of energy-containing materials. Food is taken in through the mouth and digested in the digestive tract, and nutrients are transported to all parts of the body by the circulatory system. Molecules obtained as food are stored at a var ...
ANS = general visceral motor portion of PNS sympathetic division
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
Chapter 15 ()
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
Health: Body Systems - Minnesota Literacy Council
... automatically by the nervous system and hormones—you often don't even realize they're at work. The body is made up of three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Each of these has the ability to contract and expand, which allows the body to move and function. Skeletal muscles help th ...
... automatically by the nervous system and hormones—you often don't even realize they're at work. The body is made up of three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Each of these has the ability to contract and expand, which allows the body to move and function. Skeletal muscles help th ...
anterior abdominal wall
... Oblique muscle flex & rotate the trunk RA=flex trunk, stabilize pelvis Pyrimidalis=keep linea alba taut during the process Muscles of ant/lat abd wall help diaphragm during inspiration by relax diaphragm descend allowing the accomadation of viscera Help in forced expiration during cough & ...
... Oblique muscle flex & rotate the trunk RA=flex trunk, stabilize pelvis Pyrimidalis=keep linea alba taut during the process Muscles of ant/lat abd wall help diaphragm during inspiration by relax diaphragm descend allowing the accomadation of viscera Help in forced expiration during cough & ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.