animal evolution
... Fossils from the Ediacara Hills of Australia (565 to 543 million years ago) and other sites around the world consist primarily of cnidarians, but soft-bodied mollusks were also present, and numerous fossilized burrows and tracks indicate the presence of worms. ...
... Fossils from the Ediacara Hills of Australia (565 to 543 million years ago) and other sites around the world consist primarily of cnidarians, but soft-bodied mollusks were also present, and numerous fossilized burrows and tracks indicate the presence of worms. ...
Lecture Notes - Austin Community College
... Nasal conchae keep air in the cavity long enough to be cleansed, moistened, and warmed The nasal cavity serves as a chamber for sound resonance 2. Location/Gross Structure Important structures in the nasal cavity are the nasal conchae (KON-kē) and meatuses. a. Nasal Conchae and Meatuses (superio ...
... Nasal conchae keep air in the cavity long enough to be cleansed, moistened, and warmed The nasal cavity serves as a chamber for sound resonance 2. Location/Gross Structure Important structures in the nasal cavity are the nasal conchae (KON-kē) and meatuses. a. Nasal Conchae and Meatuses (superio ...
WAPT - Human Anatomy
... List the histological features of cardiac muscle and relate these to function Describe the conducting system of the heart by listing the structures through which an electrical impulse passes List the three layers which form the wall of a blood vessel and give the function of each layer Compare the s ...
... List the histological features of cardiac muscle and relate these to function Describe the conducting system of the heart by listing the structures through which an electrical impulse passes List the three layers which form the wall of a blood vessel and give the function of each layer Compare the s ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 37
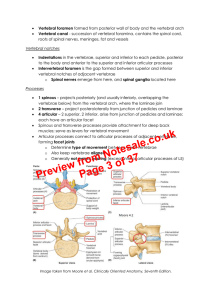
... o Foramina transversarii develop between the two ossification centres; costotransverse bar links the centres, forming the lateral boundary o Anterior tubercle formed from costal element and posterior tubercle from the transverse element Atypical ossification at C1, C2, and C7 and the sacrum C1 centr ...
... o Foramina transversarii develop between the two ossification centres; costotransverse bar links the centres, forming the lateral boundary o Anterior tubercle formed from costal element and posterior tubercle from the transverse element Atypical ossification at C1, C2, and C7 and the sacrum C1 centr ...
WAPT - Human Anatomy
... List the histological features of cardiac muscle and relate these to function Describe the conducting system of the heart by listing the structures through which an electrical impulse passes List the three layers which form the wall of a blood vessel and give the function of each layer Compare the s ...
... List the histological features of cardiac muscle and relate these to function Describe the conducting system of the heart by listing the structures through which an electrical impulse passes List the three layers which form the wall of a blood vessel and give the function of each layer Compare the s ...
25-2 PowerPoint
... During embryological development, the cells of most animal embryos differentiate into three layers called germ layers. Cells of the endoderm, or innermost germ layer, develop into the linings of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system. Cells of the mesoderm, or middle layer, give rise ...
... During embryological development, the cells of most animal embryos differentiate into three layers called germ layers. Cells of the endoderm, or innermost germ layer, develop into the linings of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system. Cells of the mesoderm, or middle layer, give rise ...
Head, Facial, & Neck Trauma
... Other Structures Cervical Spine Musculoskeletal Function • External Skeletal support of the head and neck • Attachment point for spinal column ligaments • Attachment point for tendons to move head and shoulders ...
... Other Structures Cervical Spine Musculoskeletal Function • External Skeletal support of the head and neck • Attachment point for spinal column ligaments • Attachment point for tendons to move head and shoulders ...
Tissues: Groups of cells similar in structure and function
... Nervous tissue: Internal communication • Brain, spinal cord, and nerves ...
... Nervous tissue: Internal communication • Brain, spinal cord, and nerves ...
chapter 25 section 2 notes
... As the first cells of most animals develop, they differentiate into specialized cells that are organized into tissues. A tissue is a group of cells that perform a similar function. Animals typically have several types of tissues, including epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous tissues. Epithel ...
... As the first cells of most animals develop, they differentiate into specialized cells that are organized into tissues. A tissue is a group of cells that perform a similar function. Animals typically have several types of tissues, including epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous tissues. Epithel ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Microanatomy of hyaline cartilage Development of pancreas Right atrium of heart Mediastinal surface of left lung ...
... Microanatomy of hyaline cartilage Development of pancreas Right atrium of heart Mediastinal surface of left lung ...
biol 218 f 2013 practice final exam q 131213
... Fill in the following check list for muscle structure and function. Mark all that apply. Attribute ...
... Fill in the following check list for muscle structure and function. Mark all that apply. Attribute ...
The Nose
... immediately below the bulla . The anterior end of the hiatus leads into a funnel – shaped channel called the infundibulum. the maxillary sinus opens into the middle meatus via the hiatus semilunaris. The frontal sinus opens into & is continuous with the infundibulum . The anterior ethmoidal sinuses ...
... immediately below the bulla . The anterior end of the hiatus leads into a funnel – shaped channel called the infundibulum. the maxillary sinus opens into the middle meatus via the hiatus semilunaris. The frontal sinus opens into & is continuous with the infundibulum . The anterior ethmoidal sinuses ...
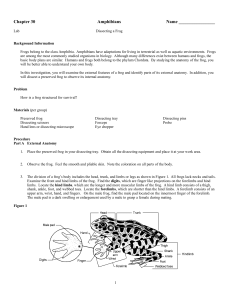
Frog Dissection
... jaw as shown in Figure 4. Clip the skin at a right angle to the incision as shown. Now sever the layers of muscle that have been exposed. Make this incision a little to the right of center to avoid cutting a major vein. The large blood vessel lying under the muscle layer is the abdominal vein that o ...
... jaw as shown in Figure 4. Clip the skin at a right angle to the incision as shown. Now sever the layers of muscle that have been exposed. Make this incision a little to the right of center to avoid cutting a major vein. The large blood vessel lying under the muscle layer is the abdominal vein that o ...
145 CHAPTER SUMMARY
... organs as endothelium. 5. Simple cuboidal epithelium, commonly active in secretion and absorption, is found in glands and in kidney tubules. 6. Simple columnar epithelium, specialized for secretion and absorption, consists of a single layer of tall columnar cells that exhibit microvilli and often mu ...
... organs as endothelium. 5. Simple cuboidal epithelium, commonly active in secretion and absorption, is found in glands and in kidney tubules. 6. Simple columnar epithelium, specialized for secretion and absorption, consists of a single layer of tall columnar cells that exhibit microvilli and often mu ...
massage therapist study guide - Advanced Massage Education
... heart. The muscles are labeled involuntary because they contract without conscious control. The heart contracts involuntarily but the heart is comprised of a separate classification of cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle is formed of thin layers of unstriated cells. ...
... heart. The muscles are labeled involuntary because they contract without conscious control. The heart contracts involuntarily but the heart is comprised of a separate classification of cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle is formed of thin layers of unstriated cells. ...
Kingdom Animalia - College of the Atlantic
... • Characterized by highly developed cephalization, exoskeleton (made from armor-tough chitin), division of body into head, thorax and abdomen • Open circulatory system, including haemocoel as well as coelom • Modified appendages per segment: first evolutionary development of flight ...
... • Characterized by highly developed cephalization, exoskeleton (made from armor-tough chitin), division of body into head, thorax and abdomen • Open circulatory system, including haemocoel as well as coelom • Modified appendages per segment: first evolutionary development of flight ...
Phylogenetic tree of the multicellular animals
... • Variety of growth forms from encrusting sheets living beneath stones to branching stalks upright in the water column. • All colors, forms and sizes. • They tend to be large and only exhibit the leucon grade of organization. ...
... • Variety of growth forms from encrusting sheets living beneath stones to branching stalks upright in the water column. • All colors, forms and sizes. • They tend to be large and only exhibit the leucon grade of organization. ...
Subrata Kumar Banerjea B.H.M.S Solved Papers on Anatomy
... (i) Posterior ramus of 1st cervical nerve or sub-occipital nerve, (ii) Anterior rami of 1st cervical nerve. Artery (iii) 3rd part of of vertebra? artery. Distinguishing Points (i) It has no body and no spine. (ii) It consists of— (A) 2 arches : anterior and posterior. (B) 2 lateral masses. Descripti ...
... (i) Posterior ramus of 1st cervical nerve or sub-occipital nerve, (ii) Anterior rami of 1st cervical nerve. Artery (iii) 3rd part of of vertebra? artery. Distinguishing Points (i) It has no body and no spine. (ii) It consists of— (A) 2 arches : anterior and posterior. (B) 2 lateral masses. Descripti ...
CONCERNING VISCERAL ORGANISMS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL
... pad placed under the tray, or simply by the addition from time to time of Ringer solution at the right temperature. Ordinarily the heart still pulsated slowly and regularly, but the blood pressure was low and the appearance of the organs anemic. After a few minutes the blood pressure began to rise, ...
... pad placed under the tray, or simply by the addition from time to time of Ringer solution at the right temperature. Ordinarily the heart still pulsated slowly and regularly, but the blood pressure was low and the appearance of the organs anemic. After a few minutes the blood pressure began to rise, ...
Phylum Ctenophora - Austin Community College
... sometimes cause serious bioinvasions eg. introduced by cargo ships from North America into the Black ...
... sometimes cause serious bioinvasions eg. introduced by cargo ships from North America into the Black ...
Neuro Anatomy Lec.11 د.عبد الجبار الحبي طي The spinal cord
... (bodies of neurons) as H-shaped in appearance (2 anterior & 2 posterior horns with grey commissure) & an outer layer of white matter (nerve fibers) occupied by tracts. The cord is divided into R. & L. halves by: - ...
... (bodies of neurons) as H-shaped in appearance (2 anterior & 2 posterior horns with grey commissure) & an outer layer of white matter (nerve fibers) occupied by tracts. The cord is divided into R. & L. halves by: - ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.