body system objectives
... 3. Understand how food travels through the digestive system and what organs are involved.. Important information to know would be: Comparing mechanical digestion to chemical digestion. Discussing the importance of the liver and pancreas in digestion. List the substances they produce and explain ...
... 3. Understand how food travels through the digestive system and what organs are involved.. Important information to know would be: Comparing mechanical digestion to chemical digestion. Discussing the importance of the liver and pancreas in digestion. List the substances they produce and explain ...
DISSECTION GUIDE FOR
... Note the fusiform shape of the body. Distinguish the head, trunk and tail regions. On the head notice the shape and position of the mouth. Observe the anterior end of the head and note the nasal apertures which are shaped like a "figure 8". Notice the 2 large eyes on the dorso-lateral surface of the ...
... Note the fusiform shape of the body. Distinguish the head, trunk and tail regions. On the head notice the shape and position of the mouth. Observe the anterior end of the head and note the nasal apertures which are shaped like a "figure 8". Notice the 2 large eyes on the dorso-lateral surface of the ...
Pond Diversity
... • Soft-bodied, multicellular, heterotrophic organism. • Uses tentacles to catch prey. • Radial symmetry. ...
... • Soft-bodied, multicellular, heterotrophic organism. • Uses tentacles to catch prey. • Radial symmetry. ...
Surface Anatomy - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... the skin – Superciliary arches – External occipital protuberance – Mastoid process – Temporalis muscle – at temple region – Frontalis muscle • Feel wrinkling of the forehead when eyebrows are raised ...
... the skin – Superciliary arches – External occipital protuberance – Mastoid process – Temporalis muscle – at temple region – Frontalis muscle • Feel wrinkling of the forehead when eyebrows are raised ...
The Phylum Molluska - MUGAN'S BIOLOGY PAGE
... How does having advanced sensory organs benefit them? • If these animals have more advanced sensory organs then they can find their prey and scope them out easier. Also, if they are the prey, then they could smell or see predators coming and escape from them. ...
... How does having advanced sensory organs benefit them? • If these animals have more advanced sensory organs then they can find their prey and scope them out easier. Also, if they are the prey, then they could smell or see predators coming and escape from them. ...
Human Body Systems Packet
... There are many different kinds of cells in your body. Your muscles are made of muscle cells. Bones are made of bone cells. Different kinds of cells have different shapes and perform different tasks. All cells have three parts to their structure. The cell membrane is the thin outer covering of the ce ...
... There are many different kinds of cells in your body. Your muscles are made of muscle cells. Bones are made of bone cells. Different kinds of cells have different shapes and perform different tasks. All cells have three parts to their structure. The cell membrane is the thin outer covering of the ce ...
Dec10
... Hydrostatic skeleton –fluids push against the inside of the skin to move the worm Segments provide organ organization ...
... Hydrostatic skeleton –fluids push against the inside of the skin to move the worm Segments provide organ organization ...
chapter 40 - Biology Junction
... The efforts of all systems must be coordinated for the animal to survive. For instance, nutrients absorbed from the digestive tract are distributed throughout the body by the circulatory system. The heart that pumps blood through the circulatory system depends on nutrients absorbed by the digest ...
... The efforts of all systems must be coordinated for the animal to survive. For instance, nutrients absorbed from the digestive tract are distributed throughout the body by the circulatory system. The heart that pumps blood through the circulatory system depends on nutrients absorbed by the digest ...
Frog reverse dissection
... Answer: a. frogs must exchange gases with the air, eat and digest food, move substances around their bodies, move their bodies, support their bodies, clean and manufacture their blood, respond to the environment, b. circulatory, respiratory, digestive, musculature, skeletal, urinary, nervous c. mout ...
... Answer: a. frogs must exchange gases with the air, eat and digest food, move substances around their bodies, move their bodies, support their bodies, clean and manufacture their blood, respond to the environment, b. circulatory, respiratory, digestive, musculature, skeletal, urinary, nervous c. mout ...
Word format
... J. Describe the interior of the frog’s lung. K. When comparing the size of the frog to the size of its lungs, we can see that its lungs are quite small. Does this interfere with the frog’s ability to absorb oxygen? Explain. 13. The long continuous tube you see is the digestive tract. Find the follow ...
... J. Describe the interior of the frog’s lung. K. When comparing the size of the frog to the size of its lungs, we can see that its lungs are quite small. Does this interfere with the frog’s ability to absorb oxygen? Explain. 13. The long continuous tube you see is the digestive tract. Find the follow ...
Introduction to Human Body - Mrs. Blackmon`s Science Blackboard
... In this exercise you will start to learn the vocabulary describing human body structures. This vocabulary consists of directional terms, so named because they accurately point out the location (direction) of a body part. The directional terms are presented hear as five pairs. The terms of each pair ...
... In this exercise you will start to learn the vocabulary describing human body structures. This vocabulary consists of directional terms, so named because they accurately point out the location (direction) of a body part. The directional terms are presented hear as five pairs. The terms of each pair ...
Ch 4: Tissues
... Uninucleated Branching cells that fit together & the intercalated disc junctions Involuntary muscle ...
... Uninucleated Branching cells that fit together & the intercalated disc junctions Involuntary muscle ...
THE HUMAN BODY Lesson Plan
... a. Oxygen passes from the blood through the capillaries to tissue cells. b. Carbon dioxide and cell waste passes from tissue cells through capillaries to the blood. c. Oxygen and carbon dioxide pass rapidly across these thin tissue layers through diffusion. d. Diffusion is a passive process in which ...
... a. Oxygen passes from the blood through the capillaries to tissue cells. b. Carbon dioxide and cell waste passes from tissue cells through capillaries to the blood. c. Oxygen and carbon dioxide pass rapidly across these thin tissue layers through diffusion. d. Diffusion is a passive process in which ...
Characteristics Used to Name Skeletal Muscles
... frontalis – frontal bone lateralis – lateral or on the side tibialis anterior – front of tibia fibularis longus – near fibula supra – above infra – below sub - underneath ...
... frontalis – frontal bone lateralis – lateral or on the side tibialis anterior – front of tibia fibularis longus – near fibula supra – above infra – below sub - underneath ...
Respiratory System HS
... • The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases is the respir ...
... • The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases is the respir ...
Sample Chapter
... structural support for the tissues and organs of the body. This function is important for maintaining the form of the body, organs and tissues. The connective tissues serve a nutritive role. All the metabolites from the blood pass from capillary beds and diffuse through the adjacent connective tissu ...
... structural support for the tissues and organs of the body. This function is important for maintaining the form of the body, organs and tissues. The connective tissues serve a nutritive role. All the metabolites from the blood pass from capillary beds and diffuse through the adjacent connective tissu ...
Insects and Their Relatives
... nitrogenous wastes in the tubules from blood • Wastes are concentrated (like a kidney does.) • Excreted out anus - In aquatic arthropods, cellular wastes are diffused into the water ...
... nitrogenous wastes in the tubules from blood • Wastes are concentrated (like a kidney does.) • Excreted out anus - In aquatic arthropods, cellular wastes are diffused into the water ...
Chapter 1--Introduction to Physiology and
... ____________________ are composed of two or more types of primary tissue organized to perform a particular function or functions. ...
... ____________________ are composed of two or more types of primary tissue organized to perform a particular function or functions. ...
Organ systems of the worm HW 11/25
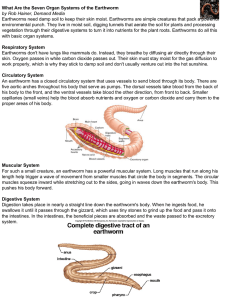
... environmental punch. They live in moist soil, digging tunnels that aerate the soil for plants and processing vegetation through their digestive systems to turn it into nutrients for the plant roots. Earthworms do all this with basic organ systems. Respiratory System Earthworms don't have lungs like ...
... environmental punch. They live in moist soil, digging tunnels that aerate the soil for plants and processing vegetation through their digestive systems to turn it into nutrients for the plant roots. Earthworms do all this with basic organ systems. Respiratory System Earthworms don't have lungs like ...
2011-08-15_PNS2
... • Organs of head, neck, • Organs of head, neck, trunk, & external genitalia trunk, & external genitalia • Adrenal medulla • Sweat glands in skin • Arrector muscles of hair • ALL vascular smooth muscle » Sympathetic system is distributed to essentially all tissues (because of vascular smooth muscle) ...
... • Organs of head, neck, • Organs of head, neck, trunk, & external genitalia trunk, & external genitalia • Adrenal medulla • Sweat glands in skin • Arrector muscles of hair • ALL vascular smooth muscle » Sympathetic system is distributed to essentially all tissues (because of vascular smooth muscle) ...
2010-08-16_PNS2
... • Organs of head, neck, • Organs of head, neck, trunk, & external genitalia trunk, & external genitalia • Adrenal medulla • Sweat glands in skin • Arrector muscles of hair • ALL vascular smooth muscle » Sympathetic system is distributed to essentially all tissues (because of vascular smooth muscle) ...
... • Organs of head, neck, • Organs of head, neck, trunk, & external genitalia trunk, & external genitalia • Adrenal medulla • Sweat glands in skin • Arrector muscles of hair • ALL vascular smooth muscle » Sympathetic system is distributed to essentially all tissues (because of vascular smooth muscle) ...
Answer - Indus World School
... Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task. Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms? Answer: In unicellular organisms, a single cell performs all the basic functions such as respiration, movement, excr ...
... Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task. Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms? Answer: In unicellular organisms, a single cell performs all the basic functions such as respiration, movement, excr ...
The Arthropods:
... body regions specialized for specific functions (tagmatization). Chitinous exoskeleton used for support and protection Paired, jointed appendages Growth accompanied by molting (ecdysis) ...
... body regions specialized for specific functions (tagmatization). Chitinous exoskeleton used for support and protection Paired, jointed appendages Growth accompanied by molting (ecdysis) ...
introduction to digestive system anatomy
... diamond-shaped pelvic outlet is formed by both bone and ligaments. It is limited anteriorly in the midline by the pubic symphysis. The bones of the pelvis consist of the right and left pelvic (hip) bones (ilium+ischium+pubis), the sacrum, and the coccyx. The sacrum articulates superiorly with verteb ...
... diamond-shaped pelvic outlet is formed by both bone and ligaments. It is limited anteriorly in the midline by the pubic symphysis. The bones of the pelvis consist of the right and left pelvic (hip) bones (ilium+ischium+pubis), the sacrum, and the coccyx. The sacrum articulates superiorly with verteb ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.