Chapter 5 Tissues
... • Pseudostratified columnar epithelium (Figure 5-7) – Columnar cells of differing heights – All cells rest on basement membrane but may not reach the free surface above – Cell nuclei at odd and irregular levels – Found lining air passages and segments of male reproductive system – Motile cilia and m ...
... • Pseudostratified columnar epithelium (Figure 5-7) – Columnar cells of differing heights – All cells rest on basement membrane but may not reach the free surface above – Cell nuclei at odd and irregular levels – Found lining air passages and segments of male reproductive system – Motile cilia and m ...
Summary of Anatomy Lecture 20: Important Slides/Concepts **Note
... -if lesioned numbness in perineum and loss of sexual function (often seen in males who bike) Slide 12 -Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve -innervates the largest patch of sensory material on the body (posterior thigh) -if lesioned lose sensation in that area Slide 13 -Sciatic Nerve Injury (L4-S3) ...
... -if lesioned numbness in perineum and loss of sexual function (often seen in males who bike) Slide 12 -Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve -innervates the largest patch of sensory material on the body (posterior thigh) -if lesioned lose sensation in that area Slide 13 -Sciatic Nerve Injury (L4-S3) ...
The Body Systems – Final Exam Review Packet
... - The skeletal system has five major functions: - Provides your body with support and shape - Many bones give your body the shape you are familiar with. The central part of your skeleton is your vertebral column, or spine. It is made up of 26 disc-shaped vertebrae. - Allows us to move - The skeletal ...
... - The skeletal system has five major functions: - Provides your body with support and shape - Many bones give your body the shape you are familiar with. The central part of your skeleton is your vertebral column, or spine. It is made up of 26 disc-shaped vertebrae. - Allows us to move - The skeletal ...
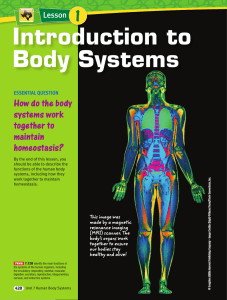
body systems pages 422-429
... 6 Analyze Look closely at the body systems shown on these pages. Then circle the two systems that send messages around the body. ...
... 6 Analyze Look closely at the body systems shown on these pages. Then circle the two systems that send messages around the body. ...
DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
... The digestive and respiratory system share some common spaces. The digestive system is composed of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. There are also a number of glands that lie outside the system that contribute to its function. These include t ...
... The digestive and respiratory system share some common spaces. The digestive system is composed of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. There are also a number of glands that lie outside the system that contribute to its function. These include t ...
Name - Spring Branch ISD
... and water are responsible for the breakdown of complex molecules such as fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. These smaller molecules can then be absorbed for use by cells. Enzymes accelerate digestion, where absence of these enzymes _________ overall digestion. Currently, there are eight digestive en ...
... and water are responsible for the breakdown of complex molecules such as fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. These smaller molecules can then be absorbed for use by cells. Enzymes accelerate digestion, where absence of these enzymes _________ overall digestion. Currently, there are eight digestive en ...
Lab Topic 18 - MDC Faculty Web Pages
... – The Phylum Platyhelminthes (clade Lophotrochozoa) includes planarians, which are free-living flatworms – The body is dorso-ventrally flattened – Body movement is accomplished by muscles in the body wall and cilia on their ventral sides ...
... – The Phylum Platyhelminthes (clade Lophotrochozoa) includes planarians, which are free-living flatworms – The body is dorso-ventrally flattened – Body movement is accomplished by muscles in the body wall and cilia on their ventral sides ...
Unit 12 Invertebrate Diagrams and Videos
... Coelomates with secondary radial anatomy (larvae bilateral; adults radial); unique water vascular system; endoskeleton Coelomates with notochord; dorsal hollow nerve cord; pharyngeal slits; muscular ...
... Coelomates with secondary radial anatomy (larvae bilateral; adults radial); unique water vascular system; endoskeleton Coelomates with notochord; dorsal hollow nerve cord; pharyngeal slits; muscular ...
Organs - Allium-textile
... makes up the wall of the heart called the mydocardium. Also like the skeletal muscles, the cardiac muscle is striated and contracts through the sliding filament method. However it is different from other types of muscles because it forms branching fibers. Unlike the skeletal muscles, the cardiac mus ...
... makes up the wall of the heart called the mydocardium. Also like the skeletal muscles, the cardiac muscle is striated and contracts through the sliding filament method. However it is different from other types of muscles because it forms branching fibers. Unlike the skeletal muscles, the cardiac mus ...
2010-2011 Human Body Systems iv
... a. Outermost cells are dead and rub off b. New cells are constantly made at the base/bottom of the epidermis. c. Cells produce melanin pigment that protects your skin and gives it color ...
... a. Outermost cells are dead and rub off b. New cells are constantly made at the base/bottom of the epidermis. c. Cells produce melanin pigment that protects your skin and gives it color ...
Carefully remove all jointed appendage of the crayfish.
... lift away the remaining parts of the carapace, exposing the underlying gills and other organs. Respiratory system – The exposed feathery gills are found underneath the carapace and are attached to the chelipeds and walking legs. A constant flow of blood the gills releases carbon dioxide and picks up ...
... lift away the remaining parts of the carapace, exposing the underlying gills and other organs. Respiratory system – The exposed feathery gills are found underneath the carapace and are attached to the chelipeds and walking legs. A constant flow of blood the gills releases carbon dioxide and picks up ...
Rat External Anatomy
... colored organ suspended just under the diaphragm. The liver has many functions, one of which is to produce bile which aids in digesting fat. The liver also stores glycogen and transmforms wastes into less harmful substances. Rats do not have a gall bladder which is used for storing bile in other ani ...
... colored organ suspended just under the diaphragm. The liver has many functions, one of which is to produce bile which aids in digesting fat. The liver also stores glycogen and transmforms wastes into less harmful substances. Rats do not have a gall bladder which is used for storing bile in other ani ...
Lecture 5
... force of muscle contraction [mechanical amplification]. A wide range of animals and animal structures lack the rigid skeletal elements that characterize the skeletons of familiar animals such as the vertebrates and the arthropods. Instead these animals rely on a [fluid skeleton]... in which the forc ...
... force of muscle contraction [mechanical amplification]. A wide range of animals and animal structures lack the rigid skeletal elements that characterize the skeletons of familiar animals such as the vertebrates and the arthropods. Instead these animals rely on a [fluid skeleton]... in which the forc ...
Unit 8 Lesson 3
... Circulation or Respiration? • Spiders, birds, fish, and other animals have very different organs for respiration and circulation. • Plants take in air through openings in leaves called stomata. • Most plants transport fluids through plant vessels. ...
... Circulation or Respiration? • Spiders, birds, fish, and other animals have very different organs for respiration and circulation. • Plants take in air through openings in leaves called stomata. • Most plants transport fluids through plant vessels. ...
Chapter 22: Body Organization and Structure
... 1) Smooth Muscle – this is found in the digestive tract and your blood vessels. 2) Cardiac Muscle – this is heart muscle (found only in the muscle tissues of your heart). 3) Skeletal Muscles – these are the muscles attached to your bones for movement and protecting inner organs. Voluntary or Involun ...
... 1) Smooth Muscle – this is found in the digestive tract and your blood vessels. 2) Cardiac Muscle – this is heart muscle (found only in the muscle tissues of your heart). 3) Skeletal Muscles – these are the muscles attached to your bones for movement and protecting inner organs. Voluntary or Involun ...
The Importance of Homeostasis in the Human Body: Keeping Us Alive
... Organ Systems: Their Role in Maintaining Homeostasis There are ten major organ systems in the human body. Each one plays a vital role in maintaining equilibrium within the body. All the systems work in tandem to maintain homeostasis. We will look at each one of these briefly and how they work togeth ...
... Organ Systems: Their Role in Maintaining Homeostasis There are ten major organ systems in the human body. Each one plays a vital role in maintaining equilibrium within the body. All the systems work in tandem to maintain homeostasis. We will look at each one of these briefly and how they work togeth ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Ribs 1–7 are called true ribs. At the anterior body wall, the true ribs connect individually to the sternum by separate cartilaginous extensions called costal cartilages. Ribs 8–12 are called false ribs because their costal cartilages do not attach directly to the sternum. The costal cartilages of r ...
... Ribs 1–7 are called true ribs. At the anterior body wall, the true ribs connect individually to the sternum by separate cartilaginous extensions called costal cartilages. Ribs 8–12 are called false ribs because their costal cartilages do not attach directly to the sternum. The costal cartilages of r ...
Human Anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... Ribs 1–7 are called true ribs. At the anterior body wall, the true ribs connect individually to the sternum by separate cartilaginous extensions called costal cartilages. Ribs 8–12 are called false ribs because their costal cartilages do not attach directly to the sternum. The costal cartilages of r ...
... Ribs 1–7 are called true ribs. At the anterior body wall, the true ribs connect individually to the sternum by separate cartilaginous extensions called costal cartilages. Ribs 8–12 are called false ribs because their costal cartilages do not attach directly to the sternum. The costal cartilages of r ...
Upper respiratory system
... Sympathetic ANS – relaxation/ dilation Parasympathetic ANS – contraction/ constriction ...
... Sympathetic ANS – relaxation/ dilation Parasympathetic ANS – contraction/ constriction ...
CHAPTER 40
... Although exchange with the environment is a problem for animals whose cells are mostly internal, complex forms have distinct benefits. o A specialized outer covering can protect against predators; sensory organs can provide detailed information about the animal’s surroundings; specialized filtration ...
... Although exchange with the environment is a problem for animals whose cells are mostly internal, complex forms have distinct benefits. o A specialized outer covering can protect against predators; sensory organs can provide detailed information about the animal’s surroundings; specialized filtration ...
Body Planes
... coronal plane) is any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal (belly and back) sections. It is one of the three main planes of the body used to describe the location of the body parts in relation to each other. ...
... coronal plane) is any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal (belly and back) sections. It is one of the three main planes of the body used to describe the location of the body parts in relation to each other. ...
Student Background Information 1C
... pins; get out your colored pencils, scissors, and scientific thinking skills because this dissection is one done on paper and requires your ingenuity in making it layer up!!! ...
... pins; get out your colored pencils, scissors, and scientific thinking skills because this dissection is one done on paper and requires your ingenuity in making it layer up!!! ...
Diversity in Living Organism - E
... Bryophytes are the plants which lives on land and in water so they are called amphibians of the plant kingdom. These plants shows following character (a) The plant body is either thallus – like (thalloid) or leaf like (foliose) (b) True leaves and roots are lacking; the plants are anchored to the so ...
... Bryophytes are the plants which lives on land and in water so they are called amphibians of the plant kingdom. These plants shows following character (a) The plant body is either thallus – like (thalloid) or leaf like (foliose) (b) True leaves and roots are lacking; the plants are anchored to the so ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.