
Chapter 14
... (composed of simple cuboidal epithelium) located deep in the dermis or in the underlying hypodermis. Its slender, coiled duct traverses the dermis and epidermis to open on the surface of the skin at a sweat pore. Apocrine sweat glands are found only in certain locations: the axilla (arm pit), the ar ...
... (composed of simple cuboidal epithelium) located deep in the dermis or in the underlying hypodermis. Its slender, coiled duct traverses the dermis and epidermis to open on the surface of the skin at a sweat pore. Apocrine sweat glands are found only in certain locations: the axilla (arm pit), the ar ...
Notes
... 2) Interoceptors – stimulation arising inside of the body (examples: chemical levels, stretching of tissues, and internal temperature) 3) Proprioceptors – respond to internal stimuli but located only in skeletal muscle, tendons, joints, ligaments, and connective tissue covering bones and muscles a) ...
... 2) Interoceptors – stimulation arising inside of the body (examples: chemical levels, stretching of tissues, and internal temperature) 3) Proprioceptors – respond to internal stimuli but located only in skeletal muscle, tendons, joints, ligaments, and connective tissue covering bones and muscles a) ...
P6 M3
... Space above and behind the nose Made of cartilage and bone Divided into 2 by a cartilaginous septum Hairs within the nostrils filter out dust etc before air passes into two nasal ...
... Space above and behind the nose Made of cartilage and bone Divided into 2 by a cartilaginous septum Hairs within the nostrils filter out dust etc before air passes into two nasal ...
Document
... Anatomy • Fibrous sacrococcygeal joint connects the sacrum to the one to four bone segments of the coccyx • Joint is reinforced by sacrococcygeal ligaments which encloses the s5 nerve root • S4,5 make the coccygeal plexus ...
... Anatomy • Fibrous sacrococcygeal joint connects the sacrum to the one to four bone segments of the coccyx • Joint is reinforced by sacrococcygeal ligaments which encloses the s5 nerve root • S4,5 make the coccygeal plexus ...
1 - cloudfront.net
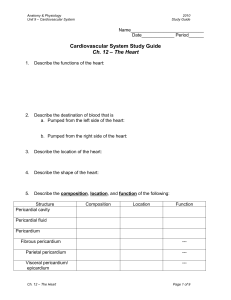
... 6. What is the name of the blood vessels that take deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs? Pulmonary arteries (which branch from the pulmonary trunk) 7. What is the name of the blood vessels that take oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium? Pulmonary veins 8. The larges ...
... 6. What is the name of the blood vessels that take deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs? Pulmonary arteries (which branch from the pulmonary trunk) 7. What is the name of the blood vessels that take oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium? Pulmonary veins 8. The larges ...
Earthworm_dissection..
... cavity (coelom) . Now cut upward and forward ( anterior), until you reach the very end of the worm. ...
... cavity (coelom) . Now cut upward and forward ( anterior), until you reach the very end of the worm. ...
ABSS Fifth Grade Science Unit 4
... Students know that in complex multi-cellular organisms, only the surface cells that are in contact with the external environment are able to exchange substances with it. Cells within the organism are too far away from the environment for direct exchange. This is the reason multi-cellular organisms ...
... Students know that in complex multi-cellular organisms, only the surface cells that are in contact with the external environment are able to exchange substances with it. Cells within the organism are too far away from the environment for direct exchange. This is the reason multi-cellular organisms ...
An Introduction to Exercise and Sport Physiology
... Incorporate both hard and easy workouts into your training routine. Example: – On a day following a high intensity workout, prescribe an easy training day so that the body can rest. ...
... Incorporate both hard and easy workouts into your training routine. Example: – On a day following a high intensity workout, prescribe an easy training day so that the body can rest. ...
Surgical Anatomy of the Temporal Bone and Measurements of the
... intrinsic anatomy of the petrous bone become essential for transtemporal approaches to the petroclival region. Some relatively constant bony landmarks can be chosen, the anatomical relationships among these structures can be studied, and the results can be used in the major skull base operations to ...
... intrinsic anatomy of the petrous bone become essential for transtemporal approaches to the petroclival region. Some relatively constant bony landmarks can be chosen, the anatomical relationships among these structures can be studied, and the results can be used in the major skull base operations to ...
Human Body Test - Mrs. Ward`s Science Class
... Crohn's disease causes in ammation of the digestive tract, particularly the small intestine. In ammation of the small intestine would directly interfere with which of the following digestive functions? A. ...
... Crohn's disease causes in ammation of the digestive tract, particularly the small intestine. In ammation of the small intestine would directly interfere with which of the following digestive functions? A. ...
Lecture Notes [Type text] Anatomy 2B 1 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... [Type text] Three connective tissue membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord ...
... [Type text] Three connective tissue membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord ...
COCKROACH (Madagascar Hissing)
... All parts are protected by a hard outer covering, the exoskeleton. The head is a small triangle found under the front of the thorax. Interesting Facts: Hissing is produced by contracting the abdomen and forcing air out of the spiracles. Adult males are armed with short, blunt horns which are used in ...
... All parts are protected by a hard outer covering, the exoskeleton. The head is a small triangle found under the front of the thorax. Interesting Facts: Hissing is produced by contracting the abdomen and forcing air out of the spiracles. Adult males are armed with short, blunt horns which are used in ...
Homologous Structures
... • Comparative anatomy looks at the similarities and differences in the anatomy of organisms, and how these structures are used. – The anatomy is the way the body is designed: bone structure and organ structures. – Comparing the way organisms are put together ...
... • Comparative anatomy looks at the similarities and differences in the anatomy of organisms, and how these structures are used. – The anatomy is the way the body is designed: bone structure and organ structures. – Comparing the way organisms are put together ...
Introduction to the Human Body
... ultimately its cells' functions. Survival is the body's most important business. Survival depends on the body's maintaining or restoring homeostasis, a state of relative constancy, of its internal environment. More than a century ago, French physiologist, Claude Bernard (1813-1878), made a remarkabl ...
... ultimately its cells' functions. Survival is the body's most important business. Survival depends on the body's maintaining or restoring homeostasis, a state of relative constancy, of its internal environment. More than a century ago, French physiologist, Claude Bernard (1813-1878), made a remarkabl ...
Neuroskeletal system
... disturbed and perspiration weak or absent Need to manually control the environment temperature ...
... disturbed and perspiration weak or absent Need to manually control the environment temperature ...
Annelid Webquest - Effingham County Schools
... Use the green arrow button on the right hand side to move to the next page or the green arrow button on the left to move back to a previous page. 5. How do we tell the difference between the dorsal and ventral sides of the earthworm? ...
... Use the green arrow button on the right hand side to move to the next page or the green arrow button on the left to move back to a previous page. 5. How do we tell the difference between the dorsal and ventral sides of the earthworm? ...
BBA IInd SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2008-09
... BDS I (First) Prof. Special Examination 2011-12 Course Code: BDS101 ...
... BDS I (First) Prof. Special Examination 2011-12 Course Code: BDS101 ...
Chordates
... • In fish and amphibians these pouches connect to form slits outside the body (used as gills for breathing/gas exchange) ...
... • In fish and amphibians these pouches connect to form slits outside the body (used as gills for breathing/gas exchange) ...
2D15 – BD0041 Code Questions Answers 1. Write a brief essay on
... The lateral angle is the thickest part of the scapula, ends in a shallow, oval depression called the “glenoid fossa”. Glenoid fossa articulates with the head of the humerus. Constricted region around the glenoid fossa is called the neck of the scapula. The coracoid process arises from a thick base t ...
... The lateral angle is the thickest part of the scapula, ends in a shallow, oval depression called the “glenoid fossa”. Glenoid fossa articulates with the head of the humerus. Constricted region around the glenoid fossa is called the neck of the scapula. The coracoid process arises from a thick base t ...
The Respiratory System
... soft palate, contains adenoids. Only an air passage. During swallowing, the soft palate and its uvula move superiorly and close it off. Lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. High on its posterior wall is the pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) which traps entering pathogens. The e ...
... soft palate, contains adenoids. Only an air passage. During swallowing, the soft palate and its uvula move superiorly and close it off. Lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. High on its posterior wall is the pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) which traps entering pathogens. The e ...
Phylum Arthropoda - University of Evansville
... A lobe-limbed, segmented animal. Also note the spines on the legs. The head end has a pair of tapering limbs with spines, and three small projections near the mouth. Traces of the digestive tract can also be seen. ...
... A lobe-limbed, segmented animal. Also note the spines on the legs. The head end has a pair of tapering limbs with spines, and three small projections near the mouth. Traces of the digestive tract can also be seen. ...
CB098-008.46_The_Stem_A
... Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The information contained in this product was created by a grantee organization and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. All references to non-governmental companies or organizations, their services, produ ...
... Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The information contained in this product was created by a grantee organization and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. All references to non-governmental companies or organizations, their services, produ ...
Available - Ggu.ac.in
... Coelom or Body Cavity Coelom refers to a large fluid-filled space lying between the outer body wall and inner digestive tube. It arises as a secondary cavity between two layers of embryonic mesoderm and contains most of the visceral organs. A true coelom may be defined as “a secondary body cavity fo ...
... Coelom or Body Cavity Coelom refers to a large fluid-filled space lying between the outer body wall and inner digestive tube. It arises as a secondary cavity between two layers of embryonic mesoderm and contains most of the visceral organs. A true coelom may be defined as “a secondary body cavity fo ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.








![Lecture Notes [Type text] Anatomy 2B 1 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003637999_1-a5a7e3dcd601a6d575e9df7c645290cf-300x300.png)













