Unit 6:2 – Body Planes, Directions and Cavities
... Medial – toward the midline of the body, dividing it into left and right portions Lateral (Opposite) – toward the side, farther from the midline Proximal – nearer the origin of the structure Distal – farther from the origin of the structure ...
... Medial – toward the midline of the body, dividing it into left and right portions Lateral (Opposite) – toward the side, farther from the midline Proximal – nearer the origin of the structure Distal – farther from the origin of the structure ...
Evolution of Animal Body Plan
... but unsegmented, with soft bodies. They have three general body regions: the mantle, the foot, and the visceral mass. • All mollusks have a strong muscular foot (different in different mollusks), used for creeping, swimming, or catching prey. • Many mollusks have an external shell, which is secreted ...
... but unsegmented, with soft bodies. They have three general body regions: the mantle, the foot, and the visceral mass. • All mollusks have a strong muscular foot (different in different mollusks), used for creeping, swimming, or catching prey. • Many mollusks have an external shell, which is secreted ...
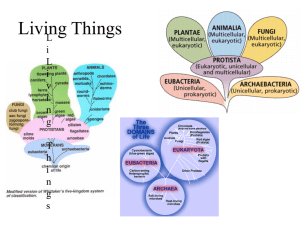
Class: XI Subject: Biology Topic: Structural organization
... (a) Adipose tissue. (b) It consists of variously shaped cells lying wide apart in large amount of non-living intercellular or extracellular matrix. (c) We can maintain good health by having balanced diet and regular physical exercise. ...
... (a) Adipose tissue. (b) It consists of variously shaped cells lying wide apart in large amount of non-living intercellular or extracellular matrix. (c) We can maintain good health by having balanced diet and regular physical exercise. ...
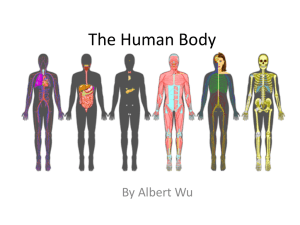
01 The Human Body: An Orientation
... Removes carbon dioxide Gas exchange occurs through walls of air sacs in the lungs ...
... Removes carbon dioxide Gas exchange occurs through walls of air sacs in the lungs ...
Longissimus Thoracis Muscle
... Longissimus Thoracis Muscle Okada Takashi December 3, 2012 Sacrospinalis Sacrospinalis is a lateral part of an epaxial (on the back panel) muscle and a very thick deep muscle which continues toward neck. The sacrospinalis emerges on the spine of the last four thoracic vertebrae and attaches to the f ...
... Longissimus Thoracis Muscle Okada Takashi December 3, 2012 Sacrospinalis Sacrospinalis is a lateral part of an epaxial (on the back panel) muscle and a very thick deep muscle which continues toward neck. The sacrospinalis emerges on the spine of the last four thoracic vertebrae and attaches to the f ...
Document
... Epidermis: outer layer, derived from ectoderm, Kertatin is made of protein and important to epidermis specialized structures in verts made of keratin Dermis: Underlying layer, thicker than epidermis, derived from mesoderm, glands formed by epidermis, but sink into dermis (many times) ...
... Epidermis: outer layer, derived from ectoderm, Kertatin is made of protein and important to epidermis specialized structures in verts made of keratin Dermis: Underlying layer, thicker than epidermis, derived from mesoderm, glands formed by epidermis, but sink into dermis (many times) ...
Intro to human heart - Kleins
... human heart The human heart is approximately the size of your fist ...
... human heart The human heart is approximately the size of your fist ...
Albert - Brookings School District
... Hg. Additional chest muscles may assist in this process. The air moves into the nasal cavity and then into the trachea. It then enters the lungs by passing through the bronchi, the bronchioles, and finally the alveoli, where gas exchange is performed. ...
... Hg. Additional chest muscles may assist in this process. The air moves into the nasal cavity and then into the trachea. It then enters the lungs by passing through the bronchi, the bronchioles, and finally the alveoli, where gas exchange is performed. ...
The nematodes or roundworms (Phylum Nematoda from Gr
... or respiratory systems so they use diffusion to breathe and for circulation of substances around their body. They are thin and are round in cross section, though they are actually bilaterally symmetric. Nematodes are one of the simplest animal groups to have a complete digestive system, with a separ ...
... or respiratory systems so they use diffusion to breathe and for circulation of substances around their body. They are thin and are round in cross section, though they are actually bilaterally symmetric. Nematodes are one of the simplest animal groups to have a complete digestive system, with a separ ...
NAME
... 5. How is the structure of pinna (external ear) related to its function? [1] 6. The nares are located dorsal to the mouth. What function do they have? [1] 7. What is the function of the nictitating membrane of the eyes? Do humans have a nictitating membrane? [2] 8. Describe the texture of the skin o ...
... 5. How is the structure of pinna (external ear) related to its function? [1] 6. The nares are located dorsal to the mouth. What function do they have? [1] 7. What is the function of the nictitating membrane of the eyes? Do humans have a nictitating membrane? [2] 8. Describe the texture of the skin o ...
flatworms, roundworms and segmented worms
... cm long, where it appears lighter colored and has a slightly larger circumference than the rest of the worm. It is found closer to the anterior (front) end of the worm. The end of the worm further from the clitellum is the posterior (rear) end. Most of the interesting structures are found at the ant ...
... cm long, where it appears lighter colored and has a slightly larger circumference than the rest of the worm. It is found closer to the anterior (front) end of the worm. The end of the worm further from the clitellum is the posterior (rear) end. Most of the interesting structures are found at the ant ...
Medical Terminology PP
... Introduction Why do health care providers use medical terminology? Medical terminology is a specialized language used by health care providers. Allows for quick, efficient communication between members of the same profession while minimizing the potential for misunderstandings. ...
... Introduction Why do health care providers use medical terminology? Medical terminology is a specialized language used by health care providers. Allows for quick, efficient communication between members of the same profession while minimizing the potential for misunderstandings. ...
Fig. 32.6b - Bergen.org
... – The multicellular bodies of animals are held together with extracellular proteins (ie.Collagen). – In addition, other structural proteins create several types of intercellular junctions, including tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions, that hold tissues together. Desmosomes use protein ca ...
... – The multicellular bodies of animals are held together with extracellular proteins (ie.Collagen). – In addition, other structural proteins create several types of intercellular junctions, including tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions, that hold tissues together. Desmosomes use protein ca ...
Deuterostome Lab
... How many rows of tube feet does your starfish have? 5. Try to differentiate between the spines and the skin gills. The spines are longer are used for protection. The skin gills are smaller and used for gas exchange. 6. Find the sieve plate/madreporite on the aboral side. This is the water entrance p ...
... How many rows of tube feet does your starfish have? 5. Try to differentiate between the spines and the skin gills. The spines are longer are used for protection. The skin gills are smaller and used for gas exchange. 6. Find the sieve plate/madreporite on the aboral side. This is the water entrance p ...
Circulatory and respiratory systems
... With a partner, choose one of the following body systems to carry out the research activities. You can then present your research findings to your class. ...
... With a partner, choose one of the following body systems to carry out the research activities. You can then present your research findings to your class. ...
Section 04 Lecture Notes
... 6. Body composed of two tissue layers with mesoglea 7. Gastrovascular cavity with only one opening 8. Special stinging cell organelles called nematocysts 9. Non-central nerve net ...
... 6. Body composed of two tissue layers with mesoglea 7. Gastrovascular cavity with only one opening 8. Special stinging cell organelles called nematocysts 9. Non-central nerve net ...
Chapter 7: Phylum Annelida
... immediately under the intestine. Hold the intestine with a forceps and lift it as you cut, or carefully tear, its connections with the septa. The ventral vessel should remain intact. Continue this procedure anteriorly and observe the ventral connection of each of the five aortic arches. As you cut, ...
... immediately under the intestine. Hold the intestine with a forceps and lift it as you cut, or carefully tear, its connections with the septa. The ventral vessel should remain intact. Continue this procedure anteriorly and observe the ventral connection of each of the five aortic arches. As you cut, ...
Adventure Brochure of a Human Body System
... coaster will drop from the very top of the spinal cord to the very end of it. It will travel about 65 mph.) Trendy spots (Left Ventricle of the Heart: Strongest heart contraction really “pumps you up”!) Diagrams of organs, etc. Information (scientifically accurate info on main parts, functions, etc. ...
... coaster will drop from the very top of the spinal cord to the very end of it. It will travel about 65 mph.) Trendy spots (Left Ventricle of the Heart: Strongest heart contraction really “pumps you up”!) Diagrams of organs, etc. Information (scientifically accurate info on main parts, functions, etc. ...
Gross 2 notes B
... Below inferior constrictor Recurrent or (inferior) laryngeal nerve (loops under subclavian artery on left under arch of aorta on right and is mainly motor to voice muscles, some sensory) and inferior laryngeal artery Plate 71 (MEMORIZE) From vagus the Superior laryngeal nerve branches into internal ...
... Below inferior constrictor Recurrent or (inferior) laryngeal nerve (loops under subclavian artery on left under arch of aorta on right and is mainly motor to voice muscles, some sensory) and inferior laryngeal artery Plate 71 (MEMORIZE) From vagus the Superior laryngeal nerve branches into internal ...
activities - Linn-Benton Community College
... Definition Histology 100+ kinds in the human body ...
... Definition Histology 100+ kinds in the human body ...
Phylum Chordata
... with the protostome branch; this is considered unlikely. The important common features are: radial cleavage, anus derived from the blastopore, mouth derived from a secondary opening, and a coelom formed by fusion of enterocoelous pouches. ...
... with the protostome branch; this is considered unlikely. The important common features are: radial cleavage, anus derived from the blastopore, mouth derived from a secondary opening, and a coelom formed by fusion of enterocoelous pouches. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.