* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download anterior abdominal wall
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
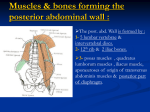
ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL Abdominal region UR UL LR LL Layman term RH EG LH Transpyloric/L1 RL UR LL Subcostal/L3 RI HYPG LI Intertrochentrum/L5 L/midclavi. R/midclavi. Anterior abdominal wall have 6 layers 1) Skin 2) Superficial fascia 3) Deep fascia 4) Muscles 5) Extraperitoneal layer 6) Parietal peritoneum SKIN Loosely attached to underlying structure except umbilicus Line of cleavage (any incision need to follow this line to minimize the scar formation in abdomen Usually for emergency cases, the incision is done in vertical line opposed the usual cleavage line; horizontally Umbilicus =scar that represent the site of attachment of umbilical cord in the fetus Blood supply a) Arteries Midline-branches of sup/inf. epigastric arteries Flanks-branches of IC/lumbar/deep circumflex iliac arteries Inguinal-branches of femoral artery (superficial epigastric /circumflex iliac/external pudendal arteries) b) Vein Above-lateral thoracic to axillary Below-superficial epigastric/great saphenous to femoral vein c) Nerve Ant. Rami of lower 6 thoracic (lower 5 intercostal/subcostal) & 1st lumbar nerve (iliohypogastric/ilioinguinal nerves) Dermatomes 1) T7-epigastrium over xiphoid process 2) T10-umbilicus 3) L1-above inguinal ligt./symphysis pubis MBBS anatomy/iium syerah’s notes SUPERFICIAL FASCIA Divide into 2: 1) Superficial fatty layer=Camper fascia continuous with other fat over the body may too thick up to 10 cm 2) deep membranous layer =Scarpa fascia thin & fade out laterally inferior- get continue with deep fascia one finger above the inguinal ligt. Midline inferiorly-tubular sheath for penis/clitoris Below perineum-enter wall of scrotum/labia majora Colles’fascia-margin of pubic arch Posterior-fuses w perineal body/post margin of perneal membrane Dartos Muscle(thun layer of smooth muscle)-fatty layer of superficial fascia DEEP FASCIA Thin layer of connective tissues Cover muscle Lies deep to membranous layer of superficial fascia FUNCTION OF ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL Oblique muscle flex & rotate the trunk RA=flex trunk, stabilize pelvis Pyrimidalis=keep linea alba taut during the process Muscles of ant/lat abd wall help diaphragm during inspiration by relax diaphragm descend allowing the accomadation of viscera Help in forced expiration during cough & sneeze by pulling down the sternum & ribs Increase intra-abd pressure to help in maturation, defecation. Vomiting, & parturition FASCIA TRANSVERSALIS Lines transverse abdominus Continuous with similar layer lining the diaphragm & iliacus muscle Femoral sheath=fascia transversalis + fascia iliaca EXTRAPERITONEAL FAT Thin layer of connective tissue Variable amount of fat Lies between fascia transversalis and parietal peritoneum PARIETAL PERITONEUM Thin serous membrane Continuous below parietal peritoneum lining pelvis MBBS anatomy/iium syerah’s notes INGUINAL LIGAMENT Strong ligament that connect the right/left ASIS with pubic tubercle Formed by lower border of aponeurosis of external oblique muscle INGUINAL CANAL 4 cm length Passage where the gonads passed In embryo state, the ovary was in abdominal region but then it is descend upon growth The male gonad; testes should be outside the body to allow the optimum temperature of spermatogenesis 37 C Male-the oblique passage pass to & from testes (spermatid cord & iliohypogastric/ilioinguinal nerve) Female-allow round ligt. Of uterus to pass from uterus to labia majora & ilioinguinal nerve 2 opening 1) Deep inguinal ring & oval opening fascia transversalis 2) Superficial inguinal ring-defect of ext. OM Wall of canal 1) Ant- EXT OM 2) Post-fascia transversalis & medial conjugated tendons 3) Roof-INT OM & transverses abdominus muscles 4) Floor-inguinal ligt. & lacuna ligt. MBBS anatomy/iium syerah’s notes POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL Formed by: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 5 lumbar vertebral / intervertebral disc 12 th ribs Upper of bony pelvis -Iliacus Psoas muscle Quadrates lamborum Apo of origin of transverses abdominus muscle Fascia lining the abdominal wall MUSCLES PSOAS MUSCLE Fibers run downwards & laterally Leave abdomen & enter thigh by passing behind inguinal ligt. Enclosed by fibrous sheath from lumbar fascia-thickened to form MEDIAL ARCUATE LIGT. Fx-flex thigh at hip joint like action sitting up from lying. ORIGIN transverse process vertebral bodies intervertebral disc from 12th thoracic to 5th lumbar lesser trochanter of INSERTION femur FACTS NERVE SUPPLY lumbar plexus QUADRATUS LAMBORUM Flat, quadrilateral muscle along the vertebral column Fibers run upward & medially Ant. Surface by lumbar fascia-thickened to form LATERAL ARCUATE LIGT (above) 7 iliolumbar ligt ( below) ILIACUS Fan shaped Combined muscle refer as iliopsoas iliolumbar ligt. iliac crest tip of transverse process of lower lumbar 12th ribs & transverse process of upper 4 lumbar vertebra iliac fossa lesser trochanter of femur with psoas muscle lumbar plexus Femoral plexus RETROPERITONEAL SPACE Lies on posterior abd wall behind the parietal peritoneum. Formed from 12th thoracic to 12th ribs and iliac crest Posterior/floor- form from medial to lateral by psoas and quadrates lamborum and transverse abd muscles ALL the muscle covered with fascia In front of fascia- fatty connective tissue forming a bed for suprarenal gland, kidney, ascending and descending colon & duodenum Also contain ureters, renal and gonadal blood vessels MBBS anatomy/iium syerah’s notes