* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THORACIC CAVITY
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
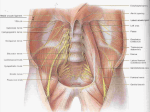
THORACIC CAVITY RESPIRATORY DIAPHRAGM Diaphragm A diaphragm is a muscular sheet with an inferior and a superior fascia: Superior fascia = parietal thoracic fascia. Inferior fascia = transversalis fascia. Separates thorax and abdomen. In moderate expiration: Reaches level of 5th rib on right side and 5th IC space on left. Diaphragm Origins Sternal part: Xiphoid process. Costal part: Lower 6 ribs and cartilages. Lumbar part: Lumbar vertebrae and crura: Right: L1-L3 Left: L1-L2 Central Tendon “Y-shaped” Attaches to lumbar vertebrae via crura. Pierced by three openings (described later). Central Tendon Three parts to central tendon: Right: Largest part. Middle: Left: Smallest part. Fig. 2.71 Crura Muscular pillars Originate from lumbar vertebrae: Right from L3. Left from L2. Right swings left and forms a weak sphincter around the esophagus. Arcuate Ligaments Median: Around aortic opening. Bridges proximal ends of crura. Medial: From deep fascia of psoas major muscle. From transverse process to body of L1. Lateral: From deep fascia of quadratus lumborum muscle. From transverse process of L1 to rib 12. Diaphragm Openings Caval opening: Level T8 Inferior vena cava; right phrenic nerve Esophageal opening: Level T10 Esophagus; vagus nerves Aortic opening: Level T12 Aorta; thoracic duct; azygos vein Diaphragm Innervation Phrenic Nerve C3-5 Diaphragm Arterial Supply Superior aspect: Pericardiacophrenic artery from IT. Musculophrenic artery from IT. Superior phrenic artery from aorta. Inferior aspect: Inferior phrenic artery from aorta.