Worksheet 0
... (coronal), and transverse (horizontal). These planes are orthogonal (at right angles) to one another and important for understanding and describing orientation, joint motion, exercises, injuries, and deformities. When viewing an object (such as the body) from a single point of view, one can distingu ...
... (coronal), and transverse (horizontal). These planes are orthogonal (at right angles) to one another and important for understanding and describing orientation, joint motion, exercises, injuries, and deformities. When viewing an object (such as the body) from a single point of view, one can distingu ...
Chapter 1
... 1. A sagittal section divides the body into right and left portions. 2. A transverse section divides the body into superior and inferior portions. It is often called a “cross section” section”. 3. A coronal section divides the body into anterior and posterior sections. ...
... 1. A sagittal section divides the body into right and left portions. 2. A transverse section divides the body into superior and inferior portions. It is often called a “cross section” section”. 3. A coronal section divides the body into anterior and posterior sections. ...
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Human Anatomy and
... Terms of relative position include: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, proximal, distal, superficial (peripheral), and deep. B. Body Sections ...
... Terms of relative position include: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, proximal, distal, superficial (peripheral), and deep. B. Body Sections ...
body organization notes
... Terms of relative position include: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, proximal, distal, superficial (peripheral), and deep. B. Body Sections ...
... Terms of relative position include: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, proximal, distal, superficial (peripheral), and deep. B. Body Sections ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology I
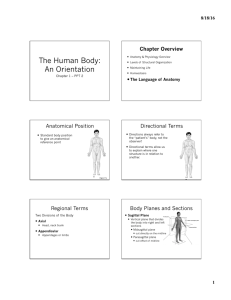
... • Anatomic position- the assumed body position whenever there is any reference to a description of any region or part of the human body • 1. body is standing erect (upright position) • 2. body is facing the observer • 3. arms are placed at the sides of the body • 4. palms of hands are turned forwar ...
... • Anatomic position- the assumed body position whenever there is any reference to a description of any region or part of the human body • 1. body is standing erect (upright position) • 2. body is facing the observer • 3. arms are placed at the sides of the body • 4. palms of hands are turned forwar ...
The Language of Anatomy - E-Learning/An
... example, if you are looking at a ball, “above” always means the area over the top of the ball. Other directional terms can also be used consistently because the ball is a sphere. All sides and surfaces are equal. The human body, of course, has many protrusions and bends. Thus, the question becomes: ...
... example, if you are looking at a ball, “above” always means the area over the top of the ball. Other directional terms can also be used consistently because the ball is a sphere. All sides and surfaces are equal. The human body, of course, has many protrusions and bends. Thus, the question becomes: ...
Body Organization - Appoquinimink High School
... of the body into right and left sides; if passes along midline, then body is in equal parts = median Transverse (horizontal) plane – cut that divides body into superior and inferior portions Coronal (frontal) plane – divides body into anterior and posterior views. ...
... of the body into right and left sides; if passes along midline, then body is in equal parts = median Transverse (horizontal) plane – cut that divides body into superior and inferior portions Coronal (frontal) plane – divides body into anterior and posterior views. ...
1.1 Skeletal System
... acromion process on the scapula and to the axial skeleton on the sternum • Both enhance mobility of the upper limbs ...
... acromion process on the scapula and to the axial skeleton on the sternum • Both enhance mobility of the upper limbs ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... Anatomical Position: reference point used to describe body parts and position accurately (Standard body position) ...
... Anatomical Position: reference point used to describe body parts and position accurately (Standard body position) ...
Clarification of Muscles for Index Cards - mr-youssef-mci
... Clarification of Muscles for Index Cards Upper Body Corrections ...
... Clarification of Muscles for Index Cards Upper Body Corrections ...
Chapter 1 PPT2 - Blair Community Schools
... Body Planes and Sections Sagittal Plane Vertical plane that divides ...
... Body Planes and Sections Sagittal Plane Vertical plane that divides ...
Chapter 11 Muscles of the body
... Name based on muscle location - sternocleidomastoid Name based on muscle shape - deltoid Name based on muscle size – gluteus maximus Name based on muscle fiber direction - rectus abdominis (rectus means straight) Name based on the number of origins – triceps, biceps, quadriceps Name based on the loc ...
... Name based on muscle location - sternocleidomastoid Name based on muscle shape - deltoid Name based on muscle size – gluteus maximus Name based on muscle fiber direction - rectus abdominis (rectus means straight) Name based on the number of origins – triceps, biceps, quadriceps Name based on the loc ...
Physical Education-Components of Physical Fitness
... Flexibility: the ability of a joint and its supporting tissue, (muscles and tendons) to move freely and comfortable through a wide range of motion. Example: a cheerleader performing a split, a gymnast completing a back walkover. Muscular Strength: the ability of a muscle or muscle group to exert max ...
... Flexibility: the ability of a joint and its supporting tissue, (muscles and tendons) to move freely and comfortable through a wide range of motion. Example: a cheerleader performing a split, a gymnast completing a back walkover. Muscular Strength: the ability of a muscle or muscle group to exert max ...
Lecture Pectoral Shoulder
... Attaches to the coricoid process of the scapula. Norm. moves scapula, can elevate the ribs. Subclavius-under clavicle, attached to first rib. Helps fixate clavicle. Shoulder joint is attached to the humerus, mostly By muscle. Strong joint…..only place the appendicular Skeleton attached to the axial ...
... Attaches to the coricoid process of the scapula. Norm. moves scapula, can elevate the ribs. Subclavius-under clavicle, attached to first rib. Helps fixate clavicle. Shoulder joint is attached to the humerus, mostly By muscle. Strong joint…..only place the appendicular Skeleton attached to the axial ...
Summer Task - Anatomy and Physiology
... rotation of shoulder Lateral rotation of shoulder Anterior: Flexion of shoulder Middle: Abduction of shoulder Posterior: Extension of shoulder ...
... rotation of shoulder Lateral rotation of shoulder Anterior: Flexion of shoulder Middle: Abduction of shoulder Posterior: Extension of shoulder ...
Chap1- anatomical terminology
... Anatomy • Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. • Anatomy : Gross anatomy macroscopic. Histology microscopic. • Anatomical position: body is erect, feet together, palms face forward and the thumbs point away from the body . ...
... Anatomy • Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. • Anatomy : Gross anatomy macroscopic. Histology microscopic. • Anatomical position: body is erect, feet together, palms face forward and the thumbs point away from the body . ...
The Skeletal System Two Parts: - axial skeleton 3 Parts – skull
... - Short bones in hands and feet – elasticity, flexibility, shock absorption Directional Definitions For long bones (in anatomical position): - proximal ends – closer to the trunk - distal ends – farther from trunk - lateral side – side away from the midline - medial side – side closest to the midlin ...
... - Short bones in hands and feet – elasticity, flexibility, shock absorption Directional Definitions For long bones (in anatomical position): - proximal ends – closer to the trunk - distal ends – farther from trunk - lateral side – side away from the midline - medial side – side closest to the midlin ...
Learning Objectives Biology 253/Human Anatomy Body cavities are
... what are pleural reflections? -relate their positions to surface anatomy what is the hilus of the lung, and what passes through it? are the right and left lungs symmetrical? identify the lobes of the lungs what is the nerve supply to the respiratory diaphragm? -from what spinal level does it arise? ...
... what are pleural reflections? -relate their positions to surface anatomy what is the hilus of the lung, and what passes through it? are the right and left lungs symmetrical? identify the lobes of the lungs what is the nerve supply to the respiratory diaphragm? -from what spinal level does it arise? ...
Study guide Exam #2 Sp 2012
... Anatomy 35 Study Guide for Exam II Muscles 1. I am giving you a picture of several muscle images which are labeled with the name of the muscles. Be sure you know each muscle in these images and that you are able to label a similar image. 2. What are the functions of muscle? 3. What is the structure ...
... Anatomy 35 Study Guide for Exam II Muscles 1. I am giving you a picture of several muscle images which are labeled with the name of the muscles. Be sure you know each muscle in these images and that you are able to label a similar image. 2. What are the functions of muscle? 3. What is the structure ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.