Invertebrates
... Some can be parasitic, infect humans Layer of muscle extends the length of body ...
... Some can be parasitic, infect humans Layer of muscle extends the length of body ...
5. Cat Superficial Abdomen
... membrane, the pariental peritoneum which lines the abdominal cavity. Rectus Abdominis- In the mid-ventral area, on either side of the line alba, lie two parallel muscles. They extend from the pubis cranially to insert on the upper ribs and sternum. For much of their course they lie between the apone ...
... membrane, the pariental peritoneum which lines the abdominal cavity. Rectus Abdominis- In the mid-ventral area, on either side of the line alba, lie two parallel muscles. They extend from the pubis cranially to insert on the upper ribs and sternum. For much of their course they lie between the apone ...
Eyecare Terminology
... understanding of the terminology they hear routinely in the office. This skill will enable them to communicate to patients, customers, and other professionals. Learning Objectives Upon completion of this course, the attendees will 1. Understand the basic terminology used 2. Explain basic terminology ...
... understanding of the terminology they hear routinely in the office. This skill will enable them to communicate to patients, customers, and other professionals. Learning Objectives Upon completion of this course, the attendees will 1. Understand the basic terminology used 2. Explain basic terminology ...
Chapter 2 Body Structures
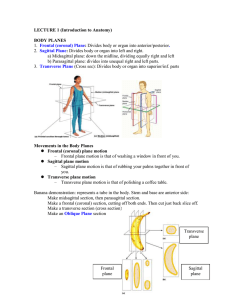
... Body Planes (frames 2-33 – 2-46) Planes are imaginary horizontal and vertical lines that divide the body into sections. A vertical plane is an up and down line at a right angle to the horizon. A horizontal plane is flat, crosswise line like the horizon. a. Vertical planes i. Midsagittal plane also k ...
... Body Planes (frames 2-33 – 2-46) Planes are imaginary horizontal and vertical lines that divide the body into sections. A vertical plane is an up and down line at a right angle to the horizon. A horizontal plane is flat, crosswise line like the horizon. a. Vertical planes i. Midsagittal plane also k ...
Dissection Terminology
... sagital section. It is parallel to the dorsal and ventral surfaces. Median Plane – extends from the dorsal to the ventral surface & passes from the anterior end to the posterior end through the middle of the body – produces the saggital section. Transverse Plane – Any section made ...
... sagital section. It is parallel to the dorsal and ventral surfaces. Median Plane – extends from the dorsal to the ventral surface & passes from the anterior end to the posterior end through the middle of the body – produces the saggital section. Transverse Plane – Any section made ...
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... the opposite side to . • Ipsi lateral : refers to an area or structure which is on the same side as . • Palmer : the anterior surface of the hand • Planter : the inferior surface of the foot ...
... the opposite side to . • Ipsi lateral : refers to an area or structure which is on the same side as . • Palmer : the anterior surface of the hand • Planter : the inferior surface of the foot ...
Science Chapter 5 Study Sheet Name: My child studied for this test
... The muscular system works with the digestive system to move food through the stomach and intestines. It works with the skeletal system to help the body move. How do other systems work together? If the respiratory system does not function properly, then the circulatory system cannot transport enough ...
... The muscular system works with the digestive system to move food through the stomach and intestines. It works with the skeletal system to help the body move. How do other systems work together? If the respiratory system does not function properly, then the circulatory system cannot transport enough ...
Wish List
... Articulated lower limb (also available in library Individual lower limb bones (also available in library) Dissected Human Cadaver ...
... Articulated lower limb (also available in library Individual lower limb bones (also available in library) Dissected Human Cadaver ...
A) Identify the proper anatomical terms for these body regions:
... 6. Is found in both right and left lumbar regions. ____________________ 7. Is found in the epigastric and left hypochondriac region. ____________________ 8. Is found in the right iliac region. ____________________ ...
... 6. Is found in both right and left lumbar regions. ____________________ 7. Is found in the epigastric and left hypochondriac region. ____________________ 8. Is found in the right iliac region. ____________________ ...
powerpoint # 1 anatomical position
... Sagittal plane: Divides the body into right and left segments can be (millions of sagittal planes are possible) Mid-sagittal plane – divides the body into two perfect halves at the mid-line Frontal (coronal) plane: Divides the body into anterior and ...
... Sagittal plane: Divides the body into right and left segments can be (millions of sagittal planes are possible) Mid-sagittal plane – divides the body into two perfect halves at the mid-line Frontal (coronal) plane: Divides the body into anterior and ...
Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle General:
... ¤ Consists of two bones ¤ clavicle (collarbone)-‐ long bone n Latin word “clavicula” = little key ¤ scapula (shoulder blade) ¤ Allows free movement of upper limb ¤ Sternoclavicular joint – where the clavi ...
... ¤ Consists of two bones ¤ clavicle (collarbone)-‐ long bone n Latin word “clavicula” = little key ¤ scapula (shoulder blade) ¤ Allows free movement of upper limb ¤ Sternoclavicular joint – where the clavi ...
Cat Dissection Photos
... Use the list you have for your choices – there are more choices on these photos than you have to know. Go to some of the dissection websites to check your answers. ...
... Use the list you have for your choices – there are more choices on these photos than you have to know. Go to some of the dissection websites to check your answers. ...
Anatomy and Physiology - Haynes Academy for Advanced Studies
... The space between these two membranes is called the pleural cavity, and it is filled with serous fluid. b. Serous Membranes of the HEART: The membrane on the surface of the heart is called visceral ...
... The space between these two membranes is called the pleural cavity, and it is filled with serous fluid. b. Serous Membranes of the HEART: The membrane on the surface of the heart is called visceral ...
DFP FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
... 62. What are the two reading of blood pressure called? (Top and Bottom Number) (pg. 39) 63. What is a healthy blood pressure? (pg. 39) 64. What are the risk factors for hypertension? (pg. 39) 65. What is Cardiovascular Disease? (pg. 36) 66. Why is smoking harmful? (pg. 40) 67. What is Coronary Heart ...
... 62. What are the two reading of blood pressure called? (Top and Bottom Number) (pg. 39) 63. What is a healthy blood pressure? (pg. 39) 64. What are the risk factors for hypertension? (pg. 39) 65. What is Cardiovascular Disease? (pg. 36) 66. Why is smoking harmful? (pg. 40) 67. What is Coronary Heart ...
幻灯片 1
... body into left and right parts. * median (midsagittal) plane right and left parts are equal. b) Coronal (frontal) plane a vertical plane, which divides body into anterior and posterior parts. c) Horizontal (transverse) plane it is at right angle to both sagittal and Coronal planes and divides body i ...
... body into left and right parts. * median (midsagittal) plane right and left parts are equal. b) Coronal (frontal) plane a vertical plane, which divides body into anterior and posterior parts. c) Horizontal (transverse) plane it is at right angle to both sagittal and Coronal planes and divides body i ...
Unit 1 Vocabulary
... Parietal Membrane: Outer Layer – around the organ system. Visceral Membrane: Inner Layer - ATTACHED the organ. Superior: A body part is above another part. Inferior: Opposite of superior. A body part is below another part. Anterior: Towards the front. Posterior: Means the same as dorsal in humans. T ...
... Parietal Membrane: Outer Layer – around the organ system. Visceral Membrane: Inner Layer - ATTACHED the organ. Superior: A body part is above another part. Inferior: Opposite of superior. A body part is below another part. Anterior: Towards the front. Posterior: Means the same as dorsal in humans. T ...
Organ Systems
... Organ – skin, femur, heart, kidney Organ System – skeletal system, digestive system ...
... Organ – skin, femur, heart, kidney Organ System – skeletal system, digestive system ...
Circulatory System - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, removes wastes from the blood and helps to maintain water and electrolyte balance ...
... consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, removes wastes from the blood and helps to maintain water and electrolyte balance ...
Body Organization
... 2. Extension (increases the angle of a joint; returns part to anatomical position). 3. Hyperextension is extension beyond anatomical position. 4. Dorsiflexion (move toes up in the air; When you stand on your heels with your toes up in the air, you are dorsiflexing your ankle joints) 5. Plantarflexio ...
... 2. Extension (increases the angle of a joint; returns part to anatomical position). 3. Hyperextension is extension beyond anatomical position. 4. Dorsiflexion (move toes up in the air; When you stand on your heels with your toes up in the air, you are dorsiflexing your ankle joints) 5. Plantarflexio ...
Human Body Systems
... produce energy by breaking down the food that you eat so it can be used by the body. Digestion begins in the mouth. It continues in the esophagus. In the stomach, digestive juices break down the food further. Next, the food passes to the small intestine where it continues to be broken down. Nutrie ...
... produce energy by breaking down the food that you eat so it can be used by the body. Digestion begins in the mouth. It continues in the esophagus. In the stomach, digestive juices break down the food further. Next, the food passes to the small intestine where it continues to be broken down. Nutrie ...
anatomy1quiz121810
... 4. Patient John Smith was in an accident and his Ilium was crushed. This is: The largest of the pelvic bones. The second, large bone of the forearm. It's the large bone in the upper leg (thigh). No such bone. It's from the book, "The Ilium and the Odyssey" by Homer. 5. The _____ is the primary bone ...
... 4. Patient John Smith was in an accident and his Ilium was crushed. This is: The largest of the pelvic bones. The second, large bone of the forearm. It's the large bone in the upper leg (thigh). No such bone. It's from the book, "The Ilium and the Odyssey" by Homer. 5. The _____ is the primary bone ...
Anatomical Directions Practice
... 11. The thumbs are _________________ to the pinkies 12. The pinkies are _________________ to the thumbs 13. The mouth is __________________ to the nose 14. The nose is ___________________ to the mouth 15. The kidneys are _______________ to the abdominal aorta 16. The abdominal aorta is _____________ ...
... 11. The thumbs are _________________ to the pinkies 12. The pinkies are _________________ to the thumbs 13. The mouth is __________________ to the nose 14. The nose is ___________________ to the mouth 15. The kidneys are _______________ to the abdominal aorta 16. The abdominal aorta is _____________ ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.