HAP UNIT 6 STUDY GUIDE KEY THE SKELETON GENERAL VOCAB
... 1. Bones in the axial skeleton make up the trunk of the body (skull, vertebrae and rib cage). The appendicular skeleton makes up the limbs including the pectoral girdle/arms and pelvic girdle/legs. 2. Bone markings have 3 functions: to provide movement in a joint, as an attachment site for tendons a ...
... 1. Bones in the axial skeleton make up the trunk of the body (skull, vertebrae and rib cage). The appendicular skeleton makes up the limbs including the pectoral girdle/arms and pelvic girdle/legs. 2. Bone markings have 3 functions: to provide movement in a joint, as an attachment site for tendons a ...
homework for the week of August 22, 2016
... What cavities is the spine in? What is the function of the kidney? What is the function of the heart? What is the function of the liver? How many lungs does the body contain? What cavities ...
... What cavities is the spine in? What is the function of the kidney? What is the function of the heart? What is the function of the liver? How many lungs does the body contain? What cavities ...
introduction to basic human anatomy
... We always speak of the parts of the body as if the body were in the anatomical position. This is true regardless of what position the body is actually in. In the anatomical position, the body stands erect, with heels together. Upper members are along the sides, with the palms of the hands facing for ...
... We always speak of the parts of the body as if the body were in the anatomical position. This is true regardless of what position the body is actually in. In the anatomical position, the body stands erect, with heels together. Upper members are along the sides, with the palms of the hands facing for ...
BODY PARTS حسام العزاوي .د All health care fi elds require
... upright, with face front, arms at the sides with palms forward and feet parallel A frontal plane, also called a coronal plane, is made at right angles to the midline and divides the body into anterior and posterior parts. A sagittal (SAJ-i-tal) plane passes from front to back and divides the body in ...
... upright, with face front, arms at the sides with palms forward and feet parallel A frontal plane, also called a coronal plane, is made at right angles to the midline and divides the body into anterior and posterior parts. A sagittal (SAJ-i-tal) plane passes from front to back and divides the body in ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Respiratory, Digestive and Urinary
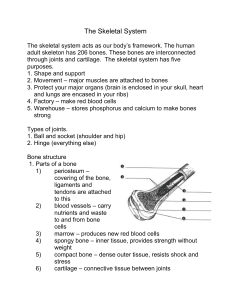
... 3. Marrow – produces red blood cells List the two parts of the skeletal system and all of their components. 1. Axial – skull, spinal column, and ribs 2. Appendicular – shoulders, hips, arms and legs Define: 1. Tendon – tissue that attach muscle to bone 2. Ligament - tissue that attach bone to bone 3 ...
... 3. Marrow – produces red blood cells List the two parts of the skeletal system and all of their components. 1. Axial – skull, spinal column, and ribs 2. Appendicular – shoulders, hips, arms and legs Define: 1. Tendon – tissue that attach muscle to bone 2. Ligament - tissue that attach bone to bone 3 ...
Sem 1 Final Review
... AP 4.1 Describe the structure of a typical long bone and indicate how each part functions in the physiology and growth of the bone. AP 4.2 Distinguish the axial from the appendicular skeleton, and name the major bones of each. Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that ma ...
... AP 4.1 Describe the structure of a typical long bone and indicate how each part functions in the physiology and growth of the bone. AP 4.2 Distinguish the axial from the appendicular skeleton, and name the major bones of each. Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that ma ...
U_5_Human_body_nove
... 1. The ____________ system supports and protects, regulates body temperature, makes chemicals and hormones, and acts as a sense organ. 2. The _____________ system supports and protects, makes movement easier (with joints), stores minerals, and makes blood cells. 3. The __________ system brings about ...
... 1. The ____________ system supports and protects, regulates body temperature, makes chemicals and hormones, and acts as a sense organ. 2. The _____________ system supports and protects, makes movement easier (with joints), stores minerals, and makes blood cells. 3. The __________ system brings about ...
Intro Notes (new)
... For the following 11 body systems, know the main function(s) and structures (parts) that make up each. ! ...
... For the following 11 body systems, know the main function(s) and structures (parts) that make up each. ! ...
Color Atlas of Human Anatomy - ReadingSample - Beck-Shop
... addition, very often from the inferior angle of the scapula as the scapular part (17). The latissimus dorsi thus usually arises in four parts which have different functions. It develops embryologically with the teres major, with which it is inserted on the crest of the lesser tubercle (18). The subt ...
... addition, very often from the inferior angle of the scapula as the scapular part (17). The latissimus dorsi thus usually arises in four parts which have different functions. It develops embryologically with the teres major, with which it is inserted on the crest of the lesser tubercle (18). The subt ...
Anatomical Terminology, Skeletal system
... Lateral rotation: rotation away from median plane Medial rotation: rotation toward median plane Circumduction: combined movements of flexion, extension, abduction & adduction Opposition: bringing tips of fingers and thumb together as in picking something upOpposite of above movement ...
... Lateral rotation: rotation away from median plane Medial rotation: rotation toward median plane Circumduction: combined movements of flexion, extension, abduction & adduction Opposition: bringing tips of fingers and thumb together as in picking something upOpposite of above movement ...
Respiratory System -
... Esophagus: The tube through which food passes from the mouth down into the stomach. Heart: The muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. ...
... Esophagus: The tube through which food passes from the mouth down into the stomach. Heart: The muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. ...
Bone Human Blood Smear
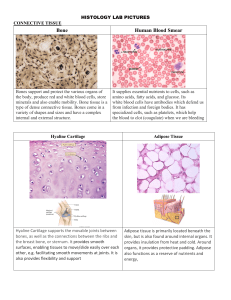
... amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose. Its white blood cells have antibodies which defend us from infection and foreign bodies. It has specialized cells, such as platelets, which help the blood to clot (coagulate) when we are bleeding ...
... amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose. Its white blood cells have antibodies which defend us from infection and foreign bodies. It has specialized cells, such as platelets, which help the blood to clot (coagulate) when we are bleeding ...
doc Organ systems table Table to fill in which will
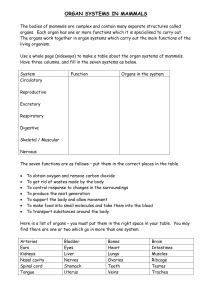
... The bodies of mammals are complex and contain many separate structures called organs. Each organ has one or more functions which it is specialised to carry out. The organs work together in organ systems which carry out the main functions of the living organism. Use a whole page (sideways) to make a ...
... The bodies of mammals are complex and contain many separate structures called organs. Each organ has one or more functions which it is specialised to carry out. The organs work together in organ systems which carry out the main functions of the living organism. Use a whole page (sideways) to make a ...
The Lower Limbs - Thigh
... One of the posterior muscles of the hip region. Muscle origin: Posterior aspects of the sacrum and coccyx bones. Muscle insertion: Blends with Tensor fascia latae from Iliotibial Band (down the side of your leg) Cyclists and runners often have tight I.T. bands. Muscle action: Hip extension and exter ...
... One of the posterior muscles of the hip region. Muscle origin: Posterior aspects of the sacrum and coccyx bones. Muscle insertion: Blends with Tensor fascia latae from Iliotibial Band (down the side of your leg) Cyclists and runners often have tight I.T. bands. Muscle action: Hip extension and exter ...
Example Test Two
... 3) The ___________________________ muscle of mastication protracts the mandible. 4) The head of the femur fits into the ___________________________ of the ox coxa. 5) A ____________________ is a type of cartilaginous joint found between a diaphysis and an epiphysis at the epiphyseal plate. 6) ______ ...
... 3) The ___________________________ muscle of mastication protracts the mandible. 4) The head of the femur fits into the ___________________________ of the ox coxa. 5) A ____________________ is a type of cartilaginous joint found between a diaphysis and an epiphysis at the epiphyseal plate. 6) ______ ...
Muscles - Western Springs College
... From the distal aspect of the femur to the tarsals (via the ...
... From the distal aspect of the femur to the tarsals (via the ...
Unit 1 Part II Notes
... • The system of anatomy he developed was so influential that it was used for the next 1400 years. Galen continued to be influential into the 16th century, when a young & rebellious physician began the practice of using real human bodies to study the inner workings of the human body. ...
... • The system of anatomy he developed was so influential that it was used for the next 1400 years. Galen continued to be influential into the 16th century, when a young & rebellious physician began the practice of using real human bodies to study the inner workings of the human body. ...
BASIC ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY
... –If the body is lying face down, it is in the prone position. –If the body is lying face up, it is in the supine position. ...
... –If the body is lying face down, it is in the prone position. –If the body is lying face up, it is in the supine position. ...
Honors Biology - Honors Class Help
... 1. List the structural hierarchy in a human, and explain the difference between the study of "anatomy" and "physiology." Anatomy - study of the structure of an organism and its parts Physiology - study of the function of these structures Cellular level Tissue level Organ level Organ system level Org ...
... 1. List the structural hierarchy in a human, and explain the difference between the study of "anatomy" and "physiology." Anatomy - study of the structure of an organism and its parts Physiology - study of the function of these structures Cellular level Tissue level Organ level Organ system level Org ...
Introduction to Human Body - Mrs. Blackmon`s Science Blackboard
... is much larger. It has two main cavity subdivisions, the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity. The thoracic cavity is superior to the diaphragm, a domeshaped skeletal muscle. Right and left pleural cavities form part of this thoracic or chest cavity. Each pleural cavity contains a lung. The ...
... is much larger. It has two main cavity subdivisions, the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity. The thoracic cavity is superior to the diaphragm, a domeshaped skeletal muscle. Right and left pleural cavities form part of this thoracic or chest cavity. Each pleural cavity contains a lung. The ...
Welcome to Anatomy and Physiology
... • Urinary-Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. • Reproductive-Male and female reproductive structures. ...
... • Urinary-Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. • Reproductive-Male and female reproductive structures. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.