* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Biology - Honors Class Help
History of anatomy wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Puppy nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
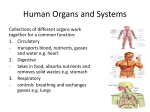
Honors Biology Unit 11 - Body Tissues, regulating internal environment, (excretion) and Digestion/Nutrition Chapter 21: 1. List the structural hierarchy in a human, and explain the difference between the study of "anatomy" and "physiology." Anatomy - study of the structure of an organism and its parts Physiology - study of the function of these structures Cellular level Tissue level Organ level Organ system level Organism level 2. Define "tissue" and describe the following types of tissue: Tissue - a collection of many structurally similar cells that act to perform a specific function (Ex: cardiac muscle tissue) 1. Epithelial -covers surface of body, lines organs and cavities. Sheets of tightly packed cells riveted together. Ex: outer layer of skin, linings of heart, blood vessels digestive tract, respiratory tract, genitourinary tract. 2a. Loose connective - most widespread, binds epithelia to underlying tissues, holds organs in place. Loose weave of protein fibers (ex: collagen), very strong, has elastic fibers. (Ex: under the skin) b. Adipose connective - stores fat in closely packed cells in sparse matrix of fibers. Fats stores energy, insulates body. Contains large globule of fat; cell swells when fat is stored, shrinks when fat is stored, shrinks when fat is used for energy. c. Blood - red and white blood cells are suspended in liquid matrix called plasma. Blood functions in transporting substances through body, and in immunity. d. Fibrous connective tissue - has dense matrix of collagen, forms tendons (attach muscle to bone) anSkeletal muscle - attached to bones by tendons. Voluntary, striated. Fixed number. Weight lifting only enlarges those present. 3a. Cardiac muscle - in heart, striated, branched, involuntary. b. Smooth muscle - in walls of organs, blood vessels. Is involuntary. Contracts slowly, but remains contracted longer than skeletal. No striations. 4. Nervous Tissue - relays information from one body part to another. Neurons (nerve cell) transmit electrical signals 3. Give an overview of the 11 major organ systems in a human: Integument (skin): Protection from the elements Skeletal: Provides body support for locomotion and protects internal organs Respiratory: Allows for gas exchange (waste CO2 and takes in O2 - necessary for all cellular metabolism) Reproductive: Produces offspring Nervous: Senses changes in the environment and enables the body to respond through movement or some other function Muscular: Enables movement Immune: Defends body from pathogens and disease causing agents Excretory: Enables the body to expel waste materials Endocrine: Produces hormones which interact with other systems of the body to allow for other bodily functions Digestive: Breaks down food into its components and absorbs nutrients necessary for bodily activity Circulatory: Transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body and transports waste from the cells to excretory organs 4. Explain how the exchange between the external and internal environments in complex animals is indirect, as compared with lower animals who's exchange is direct. • • • • • • • • • We have an “Open System” = exchange chemicals and energy with surroundings continuously Ex: eat, breathe, defecate, urinate, sweat, radiate heat In = nutrients and O2 Out = waste and CO2 Cells are bathed in water - substances are dissolved in it We are complex animals- have extensively folded/branched internal surfaces for more surface area Ex: alveoli in lungs Ex: villi in small intestine We exchange indirectly via our circulatory system. 5. Explain how the body regulates its internal environment. Utilize the following concepts: 1. Homeostasis = steady state - internal body (interstitial fluid) maintains constant conditions even when external environment changes. Ex: body temperature 2. Negative feedback - the results of some process inhibit that very same process Ex: thermostat-Increase heat, heat shuts down. Ex: FSH-high levels of FSH shuts down FSH. “on and off switch” 3. Positive feedback - the results of a process intensifies that same process Ex: labor - muscles contract uterus, uterus stimulates release of more hormones, more contractions. “On and on more switch” 3. Thermoregulation - the maintenance of internal body temperature close to a set point. • • • Endotherms - derive heat from metabolism Heat loss-is helped regulated by hair, fur, fat, migration, huddling, clothing, sweating, panting. Humans-blood vessels constrict near surface when cold, muscles shiver, metabolic rate increases 4. Osmoregulation - control of the gain or loss of water and dissolved solutes Gain water from eating or drinking Lose water through urinating, defecating, breathing, perspiring Ex: Kidneys help us regulate this 6. Describe the major functions (physiology) of the excretory system, and its anatomy 7. Define the four stages of food processing: • • • • • • 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Absorption - uptake of the small molecules by cells lining the digestive tract Ex: from small intestine to bloodstream 3. Elimination - disposal of undigested materials left over from food we eat 4. Digestion - breakdown of food to small nutrient molecules Ex: glucose, amino acids, fatty acids & glycerol a. Mechanical - physical processes such as chewing, exposes food to chemicals b. Chemical - breakdown of food by enzymes (hydrolysis) 8. Explain the role of the following in human nutritional requirements: Calories - amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a gram of water 1 degree C. Metabolic Rate - the rate of energy consumption by the body = BMR + additional energy consumption above BMR) Basal metabolic rate (BMR) = amount of energy just to maintain basic body functions 8 essential amino acids: phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, and lysine Malnutrition -a deficiency of one or more of the essential nutrients. Cause: Inadequate intake or medical problems. Most = protein deficiency. Victims likely to be retarded in mental and physical development. Ex: Kwashiorkor - (see left) inadequate protein intake. Deficiency in blood proteins causes swelling of the belly and limbs. Undernutrition - body breaks down its own molecules, muscles, brain proteins. Obesity - inappropriately high ratio of weight to height. 1/4 of Americans