* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BODY PARTS حسام العزاوي .د All health care fi elds require
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
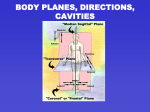
BODY PARTS حسام العزاوي. د All health care fi elds require knowledge of body directions and orientations. Physicians, surgeons, nurses, occupational therapists, and physical therapists, for example, must be thoroughly familiar with the terms used to describe body locations and positions . Radiologic technologists must be able to position a person and direct x-rays to obtain suitable images for diagnosis. Directional Terms In describing the location or direction of a given point in the body, it is always assumed that the subject is in the anatomic position, that is, upright, with face front, arms at the sides with palms forward and feet parallel A frontal plane, also called a coronal plane, is made at right angles to the midline and divides the body into anterior and posterior parts. A sagittal (SAJ-i-tal) plane passes from front to back and divides the body into right and left portions. If the plane passes through the midline, it is a midsagittal or medial plane. A transverse plane passes horizontally, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts. Body Cavities Internal organs are located within dorsal and ventral cavities The dorsal cavity contains the brain in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal cavity (canal). The uppermost ventral space, the thoracic cavity, is separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm, a muscle used in breathing.There is no anatomic separation between the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity, which together make up the abdominopelvic cavity. The large membrane that lines the abdominopelviccavity and covers the organs within it is the peritoneum(per-i-tō-NĒ-um). Abdominal Regions For orientation, the abdomen can be divided by imaginary lines into nine regions—three medial regions and six lateral regions. The sections down the midline are the: ■ epigastric (ep-i-GAS-trik) region, located above the stomach ■ umbilical (um-BIL-i-kal) region, named for the umbilicus, or navel ■ hypogastric (hī-pō-GAS-trik) region, located below the stomach The lateral regions have the same name on the left and right sides They are the: ■ hypochondriac (hī-pō-KON-drē-ak) regions, right and left, named for their positions near the ribs, specifi cally near the cartilages (root: chondr/o) of the ribs ■ lumbar (LUM-bar) regions, right and left, which are located near the small of the back (lumbar region of the spine) ■ iliac (IL-ē-ak) regions, right and left, named for the upper bone of the hip, the ilium. These regions are also called the inguinal (ING-gwi-nal) regions, with reference to the groin. Directional terms. Planes of division. The nine regions of the abdomen. Body Positions POSITION DESCRIPTION anatomic position standing erect,facing forward,arms at sides,palm forward, an-a-TOM-ik legs parallel, toes pointed forward; used for descriptions and studies of the body decubitus position lying down, specifically according to the part of the body dē-KŪ-bi-tus resting on a flat surface, as in left or right lateral decubitus, or dorsal or ventral decubitus dorsal recumbent position on back, with legs bent and separated, feet flat; rē-KUM-bent used for obstetrics and gynecology Fowler position on back, head of bed raised about 18 inches, knees elevated; used to ease breathing and for drainage jackknife position on back with shoulders elevated, legs flexed and thighs at JAK-nīf right angles to the abdomen; used to introduce a tube into the urethra knee–chest position on knees, head and upper chest on table, arms crossed above head; used in gynecology and obstetrics and for flushing the intestine lateral recumbent position on the side with one leg flexed, arm position may vary lithotomy position on back, legs flexed on abdomen, thighs apart; used for li-THOT-ō-mē gynecologic and urologic surgery prone lying face down supine* lying face up SŪ-pīn Trendelenburg position on back with head lowered by tilting bed back at 45tren-DEL-en-berg degree angle; used for pelvic and abdominal surgery, treatment of shock term abdominal cavity The large ventral cavity below the diaphragm and above the ab-DOM-i-nal pelvic cavity abdominopelvic cavity The large ventral cavity between the diaphragm and pelvis ab-dom-i-nō-PEL-vik that includes the abdominal and pelvic cavities anatomic position Standard position for anatomic studies, in which the body is an-a-TOM-ik erect and facing forward, the arms are at the sides with palms forward, and the feet are parallel cranial cavity The dorsal cavity that contains the brain KRĀ-nē-al Diaphragm The muscle that separates the thoracic from the abdominal cavity DĪ-a-fram frontal (coronal) plane Plane of section that separates the body into anterior (front) ko-RŌN-al and posterior (back) portions pelvic cavity The ventral cavity that is below the abdominal cavity PEL-vik peritoneum The large serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic per-i-tō-NĒ-um cavity and covers the organs within it sagittal plane Plane that divides the body into right and left portions SAJ-i-tal spinal cavity (canal) Dorsal cavity that contains the spinal cord SPĪ-nal thoracic cavity The ventral cavity above the diaphragm, the chest cavity thō-RAS-ik transverse (horizontal) plane Plane that divides the body into superior (upper) trans-VERS and inferior (lower) portions digit A finger or toe (adjective: digital) DIJ-it epigastrium The epigastric region ep-i-GAS-trē-um fundus The base or body of a hollow organ, the area of an organ farthest from its FUN-dus opening hypochondrium The hypochondriac region (left or right) hī-pō-KON-drē-um lumen The central opening within a tube or hollow organ LŪ-men Meatus A passage or opening mē-Ā-tus orifice The opening of a cavity OR-i-fis Os Mouth, any body opening septum A wall dividing two cavities SEP-tum Sinus A cavity, as within a bone SĪ-nus sphincter A circular muscle that regulates an opening SFINK-ter TERMS OF POSITION Ab : away (ex :abnormal; abduction :move a limb away from midline) Ad: toward (ex: adrenal gland which is the endocrine gland above the kidney). Adduction: move a limb toward the midline. Trans: across (ex: Transrectal ) ultrasound: transparent or translucent: you can see through ( Transplacental ). Para : near , beside ( paraaortic lymph node, paratesticular mass, paracolic abscess. Per : through (ex: percutaneous cholongiography which is the radiological visualization of the biliary passages by injection of a dye through the skin into the biliary passages of the liver). Medial : toward the midline: The ulnar nerve occupies a medial position in the forearm. Median: in the middle: (the median nerve is in the middle of the forearm; the mediastinum is the space in the middle of the thorax between the pleural sacs and the lungs .T he median is an arithmetic statistical value which is the value in an ordered set of values below and above which there is an equal number of values.) Lateral: to the side :(ex : lateral neck swelling is a swelling at the side of the neck , the radial nerve occupies a lateral position in the forearm). Supra : super: above, beyond : (ex: suprarenal gland which is the adrenal gland , supraorbital swelling i.e. above the orbit ,supraspinatus muscle is above the spinous process of the scapula ;superficial: close to the surface, superimposal : placed above). Peri : (around) : Ex : peritoneum ,pericardium, and the periosteum which are the sheaths around the abdominal viscera, heart and bone respectively). Pro: forward : for ( prothrombin is the protein that generates thrombin ,promyelocyte is the precursor cell of myelocyte in white blood cell formation). Sub: under :(ex: subcutaneous : under the skin; submucosal :under the mucosa). Dextro : right: (ex: dextrocardia : the state of heart on the right side of the thorax). Levo , sinistro : left( levorotation , sinistrocardia , sinistrocerebral : related to left cerebral hemisphere). Dia: across :(ex: diapedesis : passive movement of red blood cells across the blood vessel wall ;dialysis which is the separation of substances in solution by means of their unequal diffusion across a semipermeable membrane ;diaphragm which is the muscular partition that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. Infra: below :(ex: infraorbital foramen : a hole below the orbit, infraspinatus muscle which is located below the spinous process of the scapula.) Dorsal: toward the back. Ventral: toward the abdomen. The spinal and cranial cavities are dorsal .The abdominal (peritoneal cavity) is ventral. Dorsum of hand : back of hand. Opposite is the palm of hand, dorsum of foot : back of foot opposite is the sole of foot. Apex: tip, summit : The uppermost of the lung is its apex .The apical beat of the heart is best heard in the mid-clavicualr line at the fifth intercostal space . Inter: between : (ex : interdigital clefts, intercostal space). Base: bottom, lower part :( fracture at the base of skull). Prone: lying face down. Anterior: in front of ex : the esophagus is anterior to the aorta in the thorax. Posterior: behind. Ex: the pancreas lies posterior to the stomach . Proximal: the part closest to the source or origin. Distal: the part farthest from the source or origin :ex: the cardiac end of the stomach is proximal while the pylorus is distal. ex: the head of femur is proximal ,the tibial end of the femur articulates with the tibial head.