Muscles of the Deep Back, Abdominal Wall, and Pelvic Outlet
... have numerous origins, insertions, and subgroups, the muscles overlap each other. The deep back muscles can extend the spine when contracting as a group but also help to maintain posture and normal spine curvatures. The anterior and lateral walls of the abdomen contain broad, flattened muscles arran ...
... have numerous origins, insertions, and subgroups, the muscles overlap each other. The deep back muscles can extend the spine when contracting as a group but also help to maintain posture and normal spine curvatures. The anterior and lateral walls of the abdomen contain broad, flattened muscles arran ...
midterm review packet _2 skeletal and muscular systems student
... o Anatomy of a Long Bone – You should be able to label the following on a diagram of a long bone: (Diaphysis, Epiphysis, Compact Bone, Spongy Bone and Periosteum) You should also know where the red bone marrow is found and where yellow bone marrow is found along with the functions of both. ...
... o Anatomy of a Long Bone – You should be able to label the following on a diagram of a long bone: (Diaphysis, Epiphysis, Compact Bone, Spongy Bone and Periosteum) You should also know where the red bone marrow is found and where yellow bone marrow is found along with the functions of both. ...
Muscular Systerm - Granbury ISD / Home
... Myofascial damage – tenderness and swelling of the muscles and their surrounding tissues. ...
... Myofascial damage – tenderness and swelling of the muscles and their surrounding tissues. ...
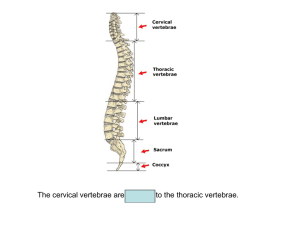
I. axial vs appendicular axial skeleton forms long axis of body: skull
... 2. suture = interlocking, fused joint between flat bones coronal - frontal and parietal sagittal - left and right parietal squamous - parietal and temporal lambdoidal - parietal and occipital sutural bones = small bones within sutures, no always present ...
... 2. suture = interlocking, fused joint between flat bones coronal - frontal and parietal sagittal - left and right parietal squamous - parietal and temporal lambdoidal - parietal and occipital sutural bones = small bones within sutures, no always present ...
Movement 101
... left to right near the waist of the stick figure, just above where the legs begin. The crease represents an axis of rotation, in this case the rotation of the upper and lower body at the hip. If the top half of the paper is folded down, the upper body has rotated around a transverse axis. If you fol ...
... left to right near the waist of the stick figure, just above where the legs begin. The crease represents an axis of rotation, in this case the rotation of the upper and lower body at the hip. If the top half of the paper is folded down, the upper body has rotated around a transverse axis. If you fol ...
Hamstring Muscles
... The hamstrings got their name from the way European butchers would hook through these muscles, behind the knee, to hang up legs of slaughtered pigs in their shops to sell, hence the “ham” and the “stringing”. This also correlated to the battle fields of swordsmen, and in Roman times, and as a form o ...
... The hamstrings got their name from the way European butchers would hook through these muscles, behind the knee, to hang up legs of slaughtered pigs in their shops to sell, hence the “ham” and the “stringing”. This also correlated to the battle fields of swordsmen, and in Roman times, and as a form o ...
Body Planes, Directions, and Cavities
... • Proximal = body parts closer to the point of reference (where the limb joins the body) • Distal = body parts farther from the point of reference (where the limb joins the body) – **Proximal and distal are only used when referring to the limbs** ...
... • Proximal = body parts closer to the point of reference (where the limb joins the body) • Distal = body parts farther from the point of reference (where the limb joins the body) – **Proximal and distal are only used when referring to the limbs** ...
PE terminology - Horton High School
... center of the body. (lateral arm raise) Adduction – is the opposite of abduction, moving an arm or leg from the side toward the center of the body. (the arm outstretched to the side is dropped to your side) ...
... center of the body. (lateral arm raise) Adduction – is the opposite of abduction, moving an arm or leg from the side toward the center of the body. (the arm outstretched to the side is dropped to your side) ...
BOX 2.3 ANATOMICAL RELATIONSHIPS IN THE VERTEBRATE
... runs from the dorsum (back) to the ventrum (belly). Finally, the third perpendicular axis, the mediolateral axis, is horizontal and runs from the midline (medial) to the lateral margin of the animal (lateral). Unfortunately, the rostrocaudal axis undergoes complex bending during embryogenesis, and t ...
... runs from the dorsum (back) to the ventrum (belly). Finally, the third perpendicular axis, the mediolateral axis, is horizontal and runs from the midline (medial) to the lateral margin of the animal (lateral). Unfortunately, the rostrocaudal axis undergoes complex bending during embryogenesis, and t ...
rat dissection guide
... trunk area, and the platysma in the neck area). You will probably have to cut these muscles close to the skin before the skin can be removed. MUSCULAR SYSTEM The diagram below illustrates the muscles of the ventral surface of the rat. Be able to identify those listed. Use the photographs on the foll ...
... trunk area, and the platysma in the neck area). You will probably have to cut these muscles close to the skin before the skin can be removed. MUSCULAR SYSTEM The diagram below illustrates the muscles of the ventral surface of the rat. Be able to identify those listed. Use the photographs on the foll ...
Guided notes for ppt 7 muscles of the hip and lower limb
... Anterior and Posterior Muscles acting on the Knee and Leg: The anterior compartment of the thigh contains ____________________________ This muscle group has many functions:___________________________________ These 4 muscles ________________________________________________, extends to the patella, _ ...
... Anterior and Posterior Muscles acting on the Knee and Leg: The anterior compartment of the thigh contains ____________________________ This muscle group has many functions:___________________________________ These 4 muscles ________________________________________________, extends to the patella, _ ...
cardiorespiratory endurance
... ASPECTS of FITNESS PHYSICAL FITNESS CARDIORESPIRATORY ENDURANCE STRENGTH MUSCLAR ENDURANCE FLEXIBILITY POWER SPEED ...
... ASPECTS of FITNESS PHYSICAL FITNESS CARDIORESPIRATORY ENDURANCE STRENGTH MUSCLAR ENDURANCE FLEXIBILITY POWER SPEED ...
Body Systems
... Turn to partner and explain what terms mean the top, bottom, front and back of body Switch Tell partner what terms mean middle, side, inside and outside ...
... Turn to partner and explain what terms mean the top, bottom, front and back of body Switch Tell partner what terms mean middle, side, inside and outside ...
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E Chapter 24
... Synarthosis: joints are immovable (skull sutures). Amphiarthosis: slightly movable (vertebrae and pelvic bones). ...
... Synarthosis: joints are immovable (skull sutures). Amphiarthosis: slightly movable (vertebrae and pelvic bones). ...
Mercury Swimming 2010-2011
... Quadriceps: that muscle group found on the anterior aspect of the upper leg and responsible for knee extension. ...
... Quadriceps: that muscle group found on the anterior aspect of the upper leg and responsible for knee extension. ...
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
... nausea and vomiting = Pt. c/o LLQ pain & N/V • To understand medical terminology we have to: – Analyze words by dividing them into parts • Prefix • Root word • Suffix – Relate the terms to the structure and function of the body ...
... nausea and vomiting = Pt. c/o LLQ pain & N/V • To understand medical terminology we have to: – Analyze words by dividing them into parts • Prefix • Root word • Suffix – Relate the terms to the structure and function of the body ...
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is
... body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary line called a plane. Since the body is three-dimensional, we can refer to three types of planes or sections that lie at the right angles to one another. Figure no.2. a. Sagittal plane; is a vertical plane that divides the body or an organ ...
... body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary line called a plane. Since the body is three-dimensional, we can refer to three types of planes or sections that lie at the right angles to one another. Figure no.2. a. Sagittal plane; is a vertical plane that divides the body or an organ ...
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology 5
... 1. The hands are _______________ to the shoulders. 2.The nose is _____________ to the ears. 3.The knee is _________ to the hip. 4.The hip is __________ to the knees. 5.The shoulder is __________to the elbow. 6.The feet are __________ to the knee. 7.The fingers are __________ to the wrist. 8.The wris ...
... 1. The hands are _______________ to the shoulders. 2.The nose is _____________ to the ears. 3.The knee is _________ to the hip. 4.The hip is __________ to the knees. 5.The shoulder is __________to the elbow. 6.The feet are __________ to the knee. 7.The fingers are __________ to the wrist. 8.The wris ...
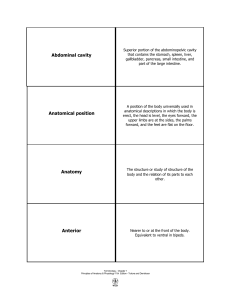
Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
... VI. ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Terms with precise meanings are used to help investigators communicate effectively. 2. The anatomical position is standing erect, the face is forward, and the arms are at the sides, with the palms forward ...
... VI. ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Terms with precise meanings are used to help investigators communicate effectively. 2. The anatomical position is standing erect, the face is forward, and the arms are at the sides, with the palms forward ...
Nervous MusclesSkeleton
... How do Skeletal Muscles Work? • Muscles do their work when the contract—that’s why each muscle in your body has two sets, one to contract your arm or leg in one direction, and another muscle to contract and move it back. • But, in order for the muscle to contract, special steps have to happen insid ...
... How do Skeletal Muscles Work? • Muscles do their work when the contract—that’s why each muscle in your body has two sets, one to contract your arm or leg in one direction, and another muscle to contract and move it back. • But, in order for the muscle to contract, special steps have to happen insid ...
L - BEHS Science
... The origin of the obturator internus (F) on the right cannot be seen, but the origin of the muscle on the contralateral side can be colored. See plate 44 for additional views of these muscles. ...
... The origin of the obturator internus (F) on the right cannot be seen, but the origin of the muscle on the contralateral side can be colored. See plate 44 for additional views of these muscles. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.