Anatomical Planes Transverse plane
... left portions – Midsagittal or median are names for the plane dividing the body into equal right and left halves ...
... left portions – Midsagittal or median are names for the plane dividing the body into equal right and left halves ...
Test #1
... e. The large intestine has a significantly different function than that of the small intestine, and therefore lacks the specializations for absorption seen in the small intestine. However, the large intestine (colon) possesses several distinct specializations of its own: haustra and teniae coli. f. ...
... e. The large intestine has a significantly different function than that of the small intestine, and therefore lacks the specializations for absorption seen in the small intestine. However, the large intestine (colon) possesses several distinct specializations of its own: haustra and teniae coli. f. ...
Preview Sample 1
... b. Contains abdominal organs: stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen ii. Pelvic cavity a. Inferior to imaginary line at pelvis b. Contains pelvic organs such as the urinary bladder, reproductive system, rectum, and anus 2. Dorsal cavity a. Cranial cavity houses the brain b. Sp ...
... b. Contains abdominal organs: stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen ii. Pelvic cavity a. Inferior to imaginary line at pelvis b. Contains pelvic organs such as the urinary bladder, reproductive system, rectum, and anus 2. Dorsal cavity a. Cranial cavity houses the brain b. Sp ...
The Human Body: An Orientation
... in anatomy reference deviations from the anatomical position (e.g. abduction of arm) Additionally, the terms right and left always refer to the person, cadaver, or skeleton being viewed and are not the viewers right and left. ...
... in anatomy reference deviations from the anatomical position (e.g. abduction of arm) Additionally, the terms right and left always refer to the person, cadaver, or skeleton being viewed and are not the viewers right and left. ...
The Human Body: An Orientation
... in anatomy reference deviations from the anatomical position (e.g. abduction of arm) Additionally, the terms right and left always refer to the person, cadaver, or skeleton being viewed and are not the viewers right and left. ...
... in anatomy reference deviations from the anatomical position (e.g. abduction of arm) Additionally, the terms right and left always refer to the person, cadaver, or skeleton being viewed and are not the viewers right and left. ...
THE VOYAGE OF H.M.S. CHALLENGER. R0BENTAL, F., Ueber die
... a. The Platysina is pale, and covers the muscles between the rami of the lower jaw, and extends backwards to the junction of the presternum with the meso-sternum. The fibres are longitudinal where they spring from the side of the presternum, but turn outwards at their anterior ends; some of these te ...
... a. The Platysina is pale, and covers the muscles between the rami of the lower jaw, and extends backwards to the junction of the presternum with the meso-sternum. The fibres are longitudinal where they spring from the side of the presternum, but turn outwards at their anterior ends; some of these te ...
exc 4360 anatomy and physiology
... 5. The four types of teeth are: ___________________, ___________________, _____________________, ______________________. 6. The INTRINSIC/EXTRINSIC muscles of the tongue are responsible for fine grade articulatory movements, while the INTRINSIC/EXTRINSIC muscles of the tongue are for basic tongue po ...
... 5. The four types of teeth are: ___________________, ___________________, _____________________, ______________________. 6. The INTRINSIC/EXTRINSIC muscles of the tongue are responsible for fine grade articulatory movements, while the INTRINSIC/EXTRINSIC muscles of the tongue are for basic tongue po ...
Chapter 1: The Human Body
... toward the side or away from the midline of the body Medial nearest the midline of the body Posterior toward the back Proximal nearest the point of attachment or origin Superior uppermost or above Ventral the belly side ...
... toward the side or away from the midline of the body Medial nearest the midline of the body Posterior toward the back Proximal nearest the point of attachment or origin Superior uppermost or above Ventral the belly side ...
L2-THE MUSCLES INVOLVED IN RESPIRATION 2014
... which a fourth muscles lies (rectus abdominis) Muscles are attached to: sternum, costal cartilages and ribs + hip bones The aponeurosis of the 3 muscles on both sides fuse in the midline to form linea alba Action (during forced expiration): Compression of abdominal viscera to help in ascent of ...
... which a fourth muscles lies (rectus abdominis) Muscles are attached to: sternum, costal cartilages and ribs + hip bones The aponeurosis of the 3 muscles on both sides fuse in the midline to form linea alba Action (during forced expiration): Compression of abdominal viscera to help in ascent of ...
Appendicular Skeleton
... The scapulae (2) are triangular, flat bones lying on the dorsal surface of the rib cage, between the second and seventh ribs Scapulae have three borders - superior, lateral, medial Major markings include the spine, the acromion, the glenoid cavity and the coracoid process ...
... The scapulae (2) are triangular, flat bones lying on the dorsal surface of the rib cage, between the second and seventh ribs Scapulae have three borders - superior, lateral, medial Major markings include the spine, the acromion, the glenoid cavity and the coracoid process ...
8th Grade Strength Training Terms And Lifts Weight Room
... 1. Weight Room Equipment: bars, plates, dumbbells, Squat racks, benches, Platforms 2. Spotting: Working with a partner while training; provide assistance, encouragement, coaching and feedback 3. Joint: Point in a body at which separate bones meet; joints may be moveable or immoveable 4. Full Range o ...
... 1. Weight Room Equipment: bars, plates, dumbbells, Squat racks, benches, Platforms 2. Spotting: Working with a partner while training; provide assistance, encouragement, coaching and feedback 3. Joint: Point in a body at which separate bones meet; joints may be moveable or immoveable 4. Full Range o ...
Anatomical Planes - MizzBedenareaROP
... often divided or sectioned to facilitate viewing of its structures • Allow one to obtain a three-dimensional perspective by studying the body from different views ...
... often divided or sectioned to facilitate viewing of its structures • Allow one to obtain a three-dimensional perspective by studying the body from different views ...
Human Systems - Net Start Class
... Digestive system-contains organs like esophagusstomach-small intestine-large intestine Skeletal System-206 different organs (bones) like the femur-patella-cranium-ribs-phalanges Muscular System- over 600 different organs (muscles) like the triceps-biceps-pectorals Nervous System-brain-peripheral ner ...
... Digestive system-contains organs like esophagusstomach-small intestine-large intestine Skeletal System-206 different organs (bones) like the femur-patella-cranium-ribs-phalanges Muscular System- over 600 different organs (muscles) like the triceps-biceps-pectorals Nervous System-brain-peripheral ner ...
Body Systems Quiz
... 4. What protects the body from injury and infection? SKIN 5. The process by which an organism's internal environment is kept stable in spite of changes in the external environment is called HOMEOSTASIS. ...
... 4. What protects the body from injury and infection? SKIN 5. The process by which an organism's internal environment is kept stable in spite of changes in the external environment is called HOMEOSTASIS. ...
Advanced Matching – The Organ Systems
... E) Integumentary System F) Lymphatic System G) Muscular System H) Nervous System I) Reproductive System J) Respiratory System K) Skeletal System L) Urinary System ...
... E) Integumentary System F) Lymphatic System G) Muscular System H) Nervous System I) Reproductive System J) Respiratory System K) Skeletal System L) Urinary System ...
Take the sample of body fluid and use the pH meter to
... the Y start at the anterior surface of shoulders and join at the inferior point of the breastbone to form a single cut that extends to the pubic area. Draw the incision in green pencil (you may want to do that after you have drawn all the organs). After the ribcage is sawn through, the abdominopelvi ...
... the Y start at the anterior surface of shoulders and join at the inferior point of the breastbone to form a single cut that extends to the pubic area. Draw the incision in green pencil (you may want to do that after you have drawn all the organs). After the ribcage is sawn through, the abdominopelvi ...
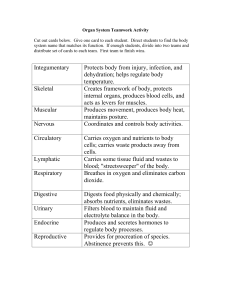
Organ System Teamwork Activity
... Organ System Teamwork Activity Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
... Organ System Teamwork Activity Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
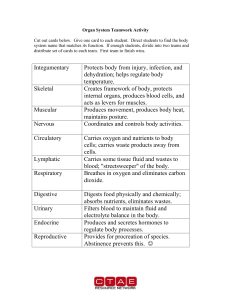
Organ System Teamwork Activity
... Organ System Teamwork Activity Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
... Organ System Teamwork Activity Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
nerve supply of LEx ppt
... Dermatomes of the Lower Limb Ref: Moore & Dalley, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th edn ...
... Dermatomes of the Lower Limb Ref: Moore & Dalley, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th edn ...
Wish List
... Articulated upper limb (also available in library Individual upper limb bones (also available in library) Dissected Human Cadaver ...
... Articulated upper limb (also available in library Individual upper limb bones (also available in library) Dissected Human Cadaver ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.