* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download anatomical directions anatomical movement
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
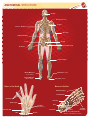
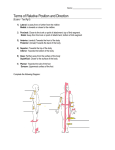
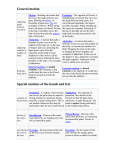
ANATOMICAL DIRECTIONS Fixed anatomical directions Midline of body •Superior - Up •Inferior - Down •Anterior - Front •Posterior - Back •Medial - Towards middle •Lateral - Away from middle Anterior (toward the front) Directions attached to specimen: •Cephal - Towards head •Caudal - Towards tail •Ventral - Towards belly •Dorsal - Towards back Posterior (toward the back) Lateral Specialized directions for limbs (away from midline) Inferior •Proximal - Towards body •Distal - Away from body Medial (toward the bottom) (toward the midline) Specialized directions for Hand •Palmar - towards palm, also volar •Dorsal - opposite of palmar Specialized directions for Foot Dorsal •Plantar - towards bottom of foot, also volar •Dorsal - opposite of plantar (top of foot) Specialized directions for forearm •Ulnar - towards ulna, medial •Radial - towards radius, lateral Plantar (bottom of foot) ANATOMICAL MOVEMENT Adjusting relation to midline of body Hyperextension •Abduction-movementawayfromthemidline,ortoabduct. •Adduction-movementtowardthemidline,ortoadduct. Adjusting angle between two parts Extension •Flexion - bend at a joint, or to reduce the angle. •Extension - straighten at a joint, or to increase the angle, for example, from 90 degrees to 180 degrees. •Hyperextension - Movement of a body part beyond the normal range of motion, such as the position of the head when looking upwards into the sky. Flexion Rotation of forearm •Supination - rotate the forearm so that the palm faces forward. •Pronation - rotate the forearm so that the palm faces backward. Flexion of the entire foot Adduction •Dorsiflexion - flexion of the entire foot superiorly, or upwards as when decelerating in an automobile. •Plantar flexion - Flexion of the entire foot inferiorly, or downwards as when accelerating in an automobile. Movement of the sole of the foot Abduction # ANA806©2016 WoundCareEducationInstitute–www.wcei.net •Eversion - the movement of the sole of the foot away from the median plane. •Inversion - the movement of the sole towards the median plane (same as when an ankle is twisted). ANATOMICAL STRUCTURE Occiput Acromion Process Scapula Thoracic Vertebrae Olecranon Lumbar Vertebrae Sacrum Coccyx Ischial Tuberosity Trochanter Lateral Condyle Metatarsals (Toes) Medial Malleolus (Inner Ankle) Lateral Malleolus (Outer Ankle) Calcaneus (Heel) Bones of the Hand Bones of the Foot Distal Phalanges 1st Metatarsal Phalanges Navicular Metacarpals Carpals (Wrist Bones) Calcaneus Articular Disk Ulna # Talus ANA806©2016 WoundCareEducationInstitute–www.wcei.net Radius Metatarsals Cuboid Proximal Phalanges 1st, 2nd, 3rd Cuneiform (Medial, Intermediate, Lateral)