8 Appendicular Skeleton
... A continuous oval ridge that helps subdivide the entire pelvis into a true pelvis and a false pelvis. true pelvis lies inferior to the pelvic brim encloses the pelvic cavity and forms a deep bowl that contains the pelvic organs false pelvis lies superior to the pelvic brim enclosed by the al ...
... A continuous oval ridge that helps subdivide the entire pelvis into a true pelvis and a false pelvis. true pelvis lies inferior to the pelvic brim encloses the pelvic cavity and forms a deep bowl that contains the pelvic organs false pelvis lies superior to the pelvic brim enclosed by the al ...
Bones and Muscle Test Review Sheet
... Bones and Muscle Test Review Sheet!!! 1. 4 main types of joints and how they work. a. Ball and Socket, hinge, pivot, gliding 2. Mineral that helps prevent osteoporosis? a. Calcium 3. What must muscle tissue do for movement to occur? a. It must contract 4. What happens to blood vessels when heat is a ...
... Bones and Muscle Test Review Sheet!!! 1. 4 main types of joints and how they work. a. Ball and Socket, hinge, pivot, gliding 2. Mineral that helps prevent osteoporosis? a. Calcium 3. What must muscle tissue do for movement to occur? a. It must contract 4. What happens to blood vessels when heat is a ...
Human Anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... A continuous oval ridge that helps subdivide the entire pelvis into a true pelvis and a false pelvis. true pelvis lies inferior to the pelvic brim encloses the pelvic cavity and forms a deep bowl that contains the pelvic organs false pelvis lies superior to the pelvic brim enclosed by the al ...
... A continuous oval ridge that helps subdivide the entire pelvis into a true pelvis and a false pelvis. true pelvis lies inferior to the pelvic brim encloses the pelvic cavity and forms a deep bowl that contains the pelvic organs false pelvis lies superior to the pelvic brim enclosed by the al ...
Introduction, BIO 099 Review, & Chapter 1 ppt
... The cell's interior has a greater concent. of K+ and the outside has a greater concent. of Na+ At rest the plasma membrane is relatively impermeable to Na+ and freely permeable to K+ ...
... The cell's interior has a greater concent. of K+ and the outside has a greater concent. of Na+ At rest the plasma membrane is relatively impermeable to Na+ and freely permeable to K+ ...
Body Systems Study Guide System Main organ Function
... Body Systems Study Guide System Skeletal System ...
... Body Systems Study Guide System Skeletal System ...
c hapter thirteen
... patient’s back is flexed. 6. The three bones in the shoulder region are the scapula, clavicle, and proximal part of the humerus. 7. The tendons of four flexor muscles on the forearm may be palpated along the anterior surface of the wrist: flexor carpi ulnaris, superficial digital flexor, palmaris lo ...
... patient’s back is flexed. 6. The three bones in the shoulder region are the scapula, clavicle, and proximal part of the humerus. 7. The tendons of four flexor muscles on the forearm may be palpated along the anterior surface of the wrist: flexor carpi ulnaris, superficial digital flexor, palmaris lo ...
Cornell Notes: Body Systems - CGW-Life-Science
... Guided Cornell Notes: Organization of the Body How the body is organized: AKA Levels of Organization: get more complex from 1 4 1. Cells 3. Organs 2. Tissues 4. Organ systems Tissue: cells working together with a common purpose. Four main types of tissues: 1. connective tissue: adds support and str ...
... Guided Cornell Notes: Organization of the Body How the body is organized: AKA Levels of Organization: get more complex from 1 4 1. Cells 3. Organs 2. Tissues 4. Organ systems Tissue: cells working together with a common purpose. Four main types of tissues: 1. connective tissue: adds support and str ...
Directional Terms cont
... facing forward, arms are at the sides with palms forward and the thumbs point away from the body, legs are parallel with toes pointing forward. ...
... facing forward, arms are at the sides with palms forward and the thumbs point away from the body, legs are parallel with toes pointing forward. ...
Body Systems
... Caudal: means tail end Superior: upper or above something Inferior: lower or below something ...
... Caudal: means tail end Superior: upper or above something Inferior: lower or below something ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy& Physiology
... anterior and posterior portions. Transverse cut: divides the body into superior and inferior portions. ...
... anterior and posterior portions. Transverse cut: divides the body into superior and inferior portions. ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 14. The two portions of the abdominopelvic cavity are the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. 15. The organs of the abdominal cavity are the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, and the small and large intestines. 16. Organs of the pelvic cavity are the terminal end of the large intestine, the u ...
... 14. The two portions of the abdominopelvic cavity are the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. 15. The organs of the abdominal cavity are the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, and the small and large intestines. 16. Organs of the pelvic cavity are the terminal end of the large intestine, the u ...
Body Planes, Directions, and Cavities
... upper and lower parts Upper part contains the stomach, small intestines, most of the large intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen 3. Pelvic Cavity = lower abdominal cavity containing urinary bladder, the reproductive organs, and last part of the large intestines ...
... upper and lower parts Upper part contains the stomach, small intestines, most of the large intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen 3. Pelvic Cavity = lower abdominal cavity containing urinary bladder, the reproductive organs, and last part of the large intestines ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 12. The two portions of the abdominopelvic cavity are the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. 13. The organs of the abdominal cavity are the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, and the small and large intestines. 14. Organs of the pelvic cavity are the terminal end of the large intestine, the u ...
... 12. The two portions of the abdominopelvic cavity are the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. 13. The organs of the abdominal cavity are the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, and the small and large intestines. 14. Organs of the pelvic cavity are the terminal end of the large intestine, the u ...
HBS2HAA – HUMAN ANATOMY A
... The median sagittal plane is the vertical plane passing longitudinally through the body and divides the body into left and right halves. The plane defines the midline of the head, neck, and trunk where it intersects the surface of the body. Sagittal planes are vertical planes passing through the bod ...
... The median sagittal plane is the vertical plane passing longitudinally through the body and divides the body into left and right halves. The plane defines the midline of the head, neck, and trunk where it intersects the surface of the body. Sagittal planes are vertical planes passing through the bod ...
Ch 1 ppt
... the original stimulus so that the activity is accelerated • The change that occurs is in the same direction as the initial disturbance • Ex. Oxytocin: intensifies labor contractions ...
... the original stimulus so that the activity is accelerated • The change that occurs is in the same direction as the initial disturbance • Ex. Oxytocin: intensifies labor contractions ...
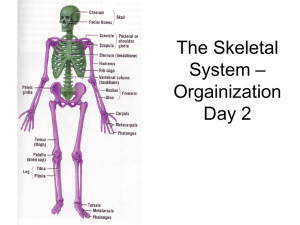
The Skeletal System – Day 2
... • The purpose of the axial skeleton (among other things) is to protect the body's most vital organs ...
... • The purpose of the axial skeleton (among other things) is to protect the body's most vital organs ...
Anatomy and Physiology (Marieb 2002)
... Body Planes and Sections A. Plane – flat surface that results from a section 1. Midsaggital (Median) Plane – divides body into two sections from the front, results in right and left halves 2. Frontal (Coronal) Plane – divides body into two sections from the side, results in anterior and posterior ha ...
... Body Planes and Sections A. Plane – flat surface that results from a section 1. Midsaggital (Median) Plane – divides body into two sections from the front, results in right and left halves 2. Frontal (Coronal) Plane – divides body into two sections from the side, results in anterior and posterior ha ...
the muscular system
... The Muscular system in the body is composed of muscle cells and tissues that brings about movement of an organ or body part. There are three kinds of muscle: skeletal muscle, which is attached to bones and allows the voluntary movement of limbs; smooth muscle, which is found in internal organs and a ...
... The Muscular system in the body is composed of muscle cells and tissues that brings about movement of an organ or body part. There are three kinds of muscle: skeletal muscle, which is attached to bones and allows the voluntary movement of limbs; smooth muscle, which is found in internal organs and a ...
Anatomical Terms of Motion
... The palm (adj palmar) of the hand corresponds to the sole (adj plantar) of the foot. The adjective volar, used mainly in orthopaedics, is synonymous with palmar and plantar. Pronation – A rotation of the forearm that moves the palm from an anterior-facing position to a rotation of posterior-facing p ...
... The palm (adj palmar) of the hand corresponds to the sole (adj plantar) of the foot. The adjective volar, used mainly in orthopaedics, is synonymous with palmar and plantar. Pronation – A rotation of the forearm that moves the palm from an anterior-facing position to a rotation of posterior-facing p ...
ROUNDWORMS
... - cysts within the muscles are consumed (undercooked food) -- worm grows in intestine -- forms cysts in the muscles of the new host -- symptom: terrible pain in muscles ...
... - cysts within the muscles are consumed (undercooked food) -- worm grows in intestine -- forms cysts in the muscles of the new host -- symptom: terrible pain in muscles ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.