* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Skeletal System – Day 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
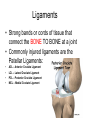
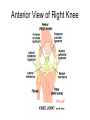
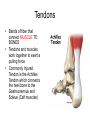
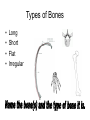
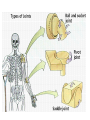
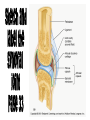
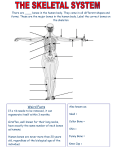
The Skeletal System – Orgainization Day 2 Axial Skeleton • Consists of the 80 bones in the head and trunk of the human body • The purpose of the axial skeleton (among other things) is to protect the body's most vital organs Bones of the Axial Skeleton • • • • Cranial Bones (22) Facial Bones (14) Ossicles – Inner Ear (6) Hyoid Bone - U-shape bone located in the neck. It anchors the tongue and is associated with swallowing (1) • Vertebral Column – Includes Sacrum and Sternum(26) • Thoracic Cage – Includes Ribs (25) Appendicular Skeleton • Consists of 126 bones in the human body which make motion possible and protects the organs of digestion, excretion, and reproduction • The word appendicular means referring to an appendage or anything attached to a major part of the body, such as the upper and lower extremities Bones of the Appendicular Skeleton • Shoulder girdle (Clavicle, Scapula) • Arm (Humerus, Ulna, Radius) • Hand (Metacarpals, Phalanges) • Pelvic girdle • Leg (Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Patella) • Foot (Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges) • THE AXIAL AND APPENDICULAR SKELETON TOGETHER MAKE UP THE COMPLETE SKELETON Cartilage/Meniscus • A strong, flexible material that supports and provides a smooth surface that makes movement at a joint smooth • 3 Functions: • Stability • Lubrication & Nutrition • Shock absorption Ligaments • Strong bands or cords of tissue that connect the BONE TO BONE at a joint • Commonly injured ligaments are the Patellar Ligaments: • • • • ACL – Anterior Cruciate Ligament LCL – Lateral Cruciate Ligament PCL – Posterior Cruciate Ligament MCL – Medial Cruciate Ligament Anterior View of Right Knee Tendons • Bands of fiber that connect MUSCLE TO BONES • Tendons and muscles work together to exert a pulling force • Commonly Injured Tendon is the Achilles Tendon which connects the heel bone to the Gastrocnemius and Soleus (Calf muscles) Types of Bones • • • • Long Short Flat Irregular Types of Joints • 3 main types: • Immovable i.e. Cranium • Slightly Movable i.e. Vertebral Joint, Tibiofibular Joint • Freely Movable (Synovial) i.e. All other joints in the body • The Synovial Joint contains synovial fluid which allows the joint to move freely and decreases friction • Synovial Joints are classified into 3 different sections: Hinge, Condyloid, Ball and Socket Types of Joints Cont’d • Hinge – Allows movement in One plane of motion ONLY i.e. Elbow, Knee • Condyloid – Allows movement in Two planes of motion i.e. Wrist, Ankle • Ball and Socket – Allows movement in Three directions and a great range of motion i.e. Shoulder, Hip • Saddle – found in the thumb Synovial Joints - Worksheets • Worksheets: • “Types of Synovial Joints” • “The Synovial Joint” Make sure you are ready to present!