Title Superficial brachial artery continuing as the common
... Superficial artery of the arm having a course anterior to that of the median nerve is found at incidence of about 13%, and it continues as the radial artery twice as frequently as it continues as the ulnar artery, although it less frequently continues as both arteries (Bergman et al., 1988). We rep ...
... Superficial artery of the arm having a course anterior to that of the median nerve is found at incidence of about 13%, and it continues as the radial artery twice as frequently as it continues as the ulnar artery, although it less frequently continues as both arteries (Bergman et al., 1988). We rep ...
Humerus Site Identification - American College of Emergency
... For situations in which the patient’s hand cannot be placed over the umbilicus, such as during a surgical procedure, the clinician should ensure the humerus is fully rotated internally. This movement rotates most of the anterior structures of the region toward the axilla and shifts the greater tuber ...
... For situations in which the patient’s hand cannot be placed over the umbilicus, such as during a surgical procedure, the clinician should ensure the humerus is fully rotated internally. This movement rotates most of the anterior structures of the region toward the axilla and shifts the greater tuber ...
Unusual high-origin of the pronator teres muscle from a Struthers
... spike, representing a “supracondylar process” of the humerus. In that aspect, the tendinous arch of the variant PT extending between the supracondylar process and the medial epicondyle represented a Struthers’ ligament. Additionally, in this case, there was no ulnar head of the PT observed. The vari ...
... spike, representing a “supracondylar process” of the humerus. In that aspect, the tendinous arch of the variant PT extending between the supracondylar process and the medial epicondyle represented a Struthers’ ligament. Additionally, in this case, there was no ulnar head of the PT observed. The vari ...
joint
... • ankle if frequently sprained • Strain • generally less serious injury • overstretched or partially torn muscle ...
... • ankle if frequently sprained • Strain • generally less serious injury • overstretched or partially torn muscle ...
Knee Anatomy - Indiana University
... Cruciate Ligaments • Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)-It prevents the tibia from sliding backwards under the femur. • Injuries usually caused by Hyperextension ...
... Cruciate Ligaments • Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)-It prevents the tibia from sliding backwards under the femur. • Injuries usually caused by Hyperextension ...
PDF - SAS Publishers
... The deep plane of flexors in the forearm is represented by three groups of the muscles, all of them spindle shaped, prolonged by long tendons and inserting into the distal phalanges of the five digits of the hand. They are classically described as two separate muscles: Flexor digitorum profundus, wh ...
... The deep plane of flexors in the forearm is represented by three groups of the muscles, all of them spindle shaped, prolonged by long tendons and inserting into the distal phalanges of the five digits of the hand. They are classically described as two separate muscles: Flexor digitorum profundus, wh ...
PP 6 - FA Joints_Pal_ROM - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Subtalar joint: This joint is the posterior joint formed between the talus and the calcaneus. It’s a synovial joint, and it’s stabilized by medial, lateral, and interosseous talocalcaneal ligaments. • Transverse tarsal joint: The transverse tarsal joint is actually a combination of the following t ...
... • Subtalar joint: This joint is the posterior joint formed between the talus and the calcaneus. It’s a synovial joint, and it’s stabilized by medial, lateral, and interosseous talocalcaneal ligaments. • Transverse tarsal joint: The transverse tarsal joint is actually a combination of the following t ...
Joint Anatomy and Physiology The Chicken Wing Dissection Name: .
... Movement in the human body results from a series of structures that work collaboratively to provide range of motion. Skeletal muscles, connective tissue and bones all play a significant role in movement. Joints occur where bones articulate. Joints are classified as synovial, fibrous or cartilaginous ...
... Movement in the human body results from a series of structures that work collaboratively to provide range of motion. Skeletal muscles, connective tissue and bones all play a significant role in movement. Joints occur where bones articulate. Joints are classified as synovial, fibrous or cartilaginous ...
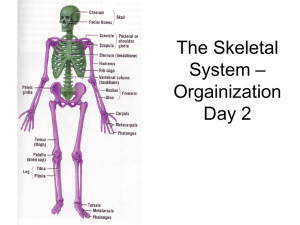
The Skeletal System – Day 2
... • The purpose of the axial skeleton (among other things) is to protect the body's most vital organs ...
... • The purpose of the axial skeleton (among other things) is to protect the body's most vital organs ...
Elbow
In primates, including humans, the elbow joint is the synovial hinge joint between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The superior radioulnar joint shares joint capsule with the elbow joint but plays no functional role at the elbow. The elbow region includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon (the bony prominence at the very tip of the elbow), the elbow pit, and the lateral and medial epicondyles. The name for the elbow in Latin is cubitus, and so the word cubital is used in some elbow related terms, as in cubital nodes for example.