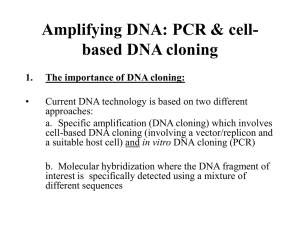
Working With Enzymes - Southern Biological
... To get a reaction in a suitable time frame, you should ensure that the concentrations of the enzyme and the substrate are correct. Although enzymes are catalysts and therefore able to react many times, overall reaction rates can be increased by using more enzyme because it allows more substrate mole ...
... To get a reaction in a suitable time frame, you should ensure that the concentrations of the enzyme and the substrate are correct. Although enzymes are catalysts and therefore able to react many times, overall reaction rates can be increased by using more enzyme because it allows more substrate mole ...
DNA is - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... rRNA and t-RNA images from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved mRNA image from http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/tmp/labeling/1140654_dyn.gif ...
... rRNA and t-RNA images from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved mRNA image from http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/tmp/labeling/1140654_dyn.gif ...
Cybertory Manual (WP) - Attotron Biosensor Corporation
... A nuclease is an enzyme that breaks the phosphodiester bonds in nucleic acid strands. Ribonuclease (or RNase) breaks down RNA, and deoxyribonuclease (or DNase) breaks DNA. An exonuclease starts at one end of the strand; some enzymes are specifically 5’ exonucleases, and some are 3’ exonucleases. An ...
... A nuclease is an enzyme that breaks the phosphodiester bonds in nucleic acid strands. Ribonuclease (or RNase) breaks down RNA, and deoxyribonuclease (or DNase) breaks DNA. An exonuclease starts at one end of the strand; some enzymes are specifically 5’ exonucleases, and some are 3’ exonucleases. An ...
UNIT 2: The Chemistry of Life
... and old parts in the cell. Each cell contains many lysosomes. Each lysosome has specific molecules inside that help break down different substances. These molecules are called enzymes. ...
... and old parts in the cell. Each cell contains many lysosomes. Each lysosome has specific molecules inside that help break down different substances. These molecules are called enzymes. ...
iProof™ High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase - Bio-Rad
... good results, but optimal amounts could range from 0.5–2 units per 50 µl reaction depending on amplicon length and difficulty. Do not exceed 2 U/50 µl (0.04 U/µl), especially for amplicons that are > 5kb. ...
... good results, but optimal amounts could range from 0.5–2 units per 50 µl reaction depending on amplicon length and difficulty. Do not exceed 2 U/50 µl (0.04 U/µl), especially for amplicons that are > 5kb. ...
Chymotrypsin is a Serine Protease
... • Correct positioning of two reacting groups (in model reactions or at enzyme active sites): (1) Reduces their degrees of freedom (2) Results in a large loss of entropy (3) The relative enhanced concentration of substrates (“effective molarity”) predicts the rate acceleration expected due to this ef ...
... • Correct positioning of two reacting groups (in model reactions or at enzyme active sites): (1) Reduces their degrees of freedom (2) Results in a large loss of entropy (3) The relative enhanced concentration of substrates (“effective molarity”) predicts the rate acceleration expected due to this ef ...
Enzyme structure and function
... undergoing any permanent chemical change. 2. An enzyme speeds up the rate of a specific reaction, without being used up. 3. What does each enzyme do? Complete the sentences about specific enzymes. a. Lipase breaks down lipids (fats) to form fatty acids and glycerol. b. Amylase breaks down starch to ...
... undergoing any permanent chemical change. 2. An enzyme speeds up the rate of a specific reaction, without being used up. 3. What does each enzyme do? Complete the sentences about specific enzymes. a. Lipase breaks down lipids (fats) to form fatty acids and glycerol. b. Amylase breaks down starch to ...
Unit 04 Enzymes and respiration Review
... it on the food right before eating it? Explain. 3. In the lactase lab, what were the substrate, the enzyme, and the product? 4. Enzymes are a type of _______________________. The characteristics of enzymes are that they can __________________________________, are a ______________________ fit to thei ...
... it on the food right before eating it? Explain. 3. In the lactase lab, what were the substrate, the enzyme, and the product? 4. Enzymes are a type of _______________________. The characteristics of enzymes are that they can __________________________________, are a ______________________ fit to thei ...
ENZYMES
... Enzymes are soluble ,colloidal organic catalyst ,specific in action , protein in nature. They catalyze the hundreds of stepwise reactions that degrade nutrient molecules ,conserve and transform chemical energy from simple precursors. Wilhelm Kühne first used the term enzymes. For e.g. maltose is the ...
... Enzymes are soluble ,colloidal organic catalyst ,specific in action , protein in nature. They catalyze the hundreds of stepwise reactions that degrade nutrient molecules ,conserve and transform chemical energy from simple precursors. Wilhelm Kühne first used the term enzymes. For e.g. maltose is the ...
peran serta masyarakat dalam plh
... such as the ions of magnesium, zinc, ion or manganese), the cofactor is called an activator – Examples: K+, Mn+2, Mg+2, Ca+2 dan Zn+2 ...
... such as the ions of magnesium, zinc, ion or manganese), the cofactor is called an activator – Examples: K+, Mn+2, Mg+2, Ca+2 dan Zn+2 ...
G3: Genes, Genomes and Genetics Whole organism genome
... precisely ligated junctions. Our method makes targeted mutagenesis possible in experimental systems like Sciara where genetic resources have been limited. In addition, the ability to integrate relatively long DNA fragments into a specified genomic target site with high efficiency combined with the e ...
... precisely ligated junctions. Our method makes targeted mutagenesis possible in experimental systems like Sciara where genetic resources have been limited. In addition, the ability to integrate relatively long DNA fragments into a specified genomic target site with high efficiency combined with the e ...
MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER TWO EXAMIN
... 4. Insertion of a piece of DNA into a plasmid is possible only if both the circular plasmid and the source of DNA have ________ for the same restriction enzymes. a. Recognition sites b. Sticky ends c. DNA ligase d. Endonuclease 1 mark 5. Type II class enzymes are the most commonly used for gene clon ...
... 4. Insertion of a piece of DNA into a plasmid is possible only if both the circular plasmid and the source of DNA have ________ for the same restriction enzymes. a. Recognition sites b. Sticky ends c. DNA ligase d. Endonuclease 1 mark 5. Type II class enzymes are the most commonly used for gene clon ...