ENZYMES A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical
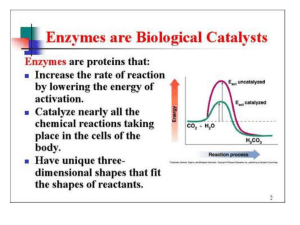
... The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to release energy is actually a series of dozens of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to speed up these reactions, energy would not be released fast enough to support all but the smallest organisms. Enzymes are not changed during the chemica ...
... The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to release energy is actually a series of dozens of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to speed up these reactions, energy would not be released fast enough to support all but the smallest organisms. Enzymes are not changed during the chemica ...
Summer 2003 Test 3
... 20) DNA technology has many medical applications. Which of the following is not done routinely at present? a) production of hormones for treating diabetes and dwarfism b) introduction of genetically engineered genes into human gametes c) prenatal identification of genetic disease genes d) genetic te ...
... 20) DNA technology has many medical applications. Which of the following is not done routinely at present? a) production of hormones for treating diabetes and dwarfism b) introduction of genetically engineered genes into human gametes c) prenatal identification of genetic disease genes d) genetic te ...
2008 exam with answers
... but not without the 5’ to 3’ exo. Therefore it must be the 5’ to 3’ exo of enzyme X that is critical in DNA replication, and cannot be replaced by action of another enzyme. The function of 5’ to 3’ exo is to degrade the primer. The other activities of enzyme X could be used for elongation and proof ...
... but not without the 5’ to 3’ exo. Therefore it must be the 5’ to 3’ exo of enzyme X that is critical in DNA replication, and cannot be replaced by action of another enzyme. The function of 5’ to 3’ exo is to degrade the primer. The other activities of enzyme X could be used for elongation and proof ...
Determination of nucleotide sequences in DNA
... to be determined. The approach that we have used is to prepare clones at random from restriction enzyme digests and determine the sequence with the flanking primer. Computer programs (21) are then used to store, overlap, and arrange the data. Another important advantage of the cloning technique is t ...
... to be determined. The approach that we have used is to prepare clones at random from restriction enzyme digests and determine the sequence with the flanking primer. Computer programs (21) are then used to store, overlap, and arrange the data. Another important advantage of the cloning technique is t ...
Anthraquinone Photonuclease Structure Determines Its Mode of
... AQI19 shows spontaneous cleavage with low quantum efficiency20 and essentially equal effectiveness at every nucleotide.12 In contrast, irradiation of AQS or AQC under these conditions gives only insignificant amounts of spontaneous cleavage, and treatment of these samples with hot piperidine reveals ...
... AQI19 shows spontaneous cleavage with low quantum efficiency20 and essentially equal effectiveness at every nucleotide.12 In contrast, irradiation of AQS or AQC under these conditions gives only insignificant amounts of spontaneous cleavage, and treatment of these samples with hot piperidine reveals ...
Section 1 Workbook Unit 2 ANSWERS File
... Label each base given in the diagram below and describe the 4 primary characteristics of DNA. -‐Deoxyribose s ugar, phosphate group and one of nitrogen bases making up a nucleotide. -‐Double helix shape -‐Two strands held together ...
... Label each base given in the diagram below and describe the 4 primary characteristics of DNA. -‐Deoxyribose s ugar, phosphate group and one of nitrogen bases making up a nucleotide. -‐Double helix shape -‐Two strands held together ...
Exam 3
... B form to the Z form WITHOUT breakage of the phosphodiester backbone. What is the CHANGE in its linking number (L), twist (T), and writhing number (W)? Your answers need not be integers. ...
... B form to the Z form WITHOUT breakage of the phosphodiester backbone. What is the CHANGE in its linking number (L), twist (T), and writhing number (W)? Your answers need not be integers. ...
Enzymes - Madison County Schools
... Equilibrium eventually reached b/c all the substrate is being broken down and adding more enzymes will not affect the reaction rate (Because those enzymes will have no substrate to break down). ...
... Equilibrium eventually reached b/c all the substrate is being broken down and adding more enzymes will not affect the reaction rate (Because those enzymes will have no substrate to break down). ...
dNTP Mix, 10mM - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... preparation, was tested by incubation of single stranded and double stranded radiolabeled oligonucleotides with 1 µL of 20 mM dNTP for 4 hours at 37°C and separation of reaction mixtures on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Phosphoimaging has not detected DNA degradation. Ribonucleases. Each dNTP, us ...
... preparation, was tested by incubation of single stranded and double stranded radiolabeled oligonucleotides with 1 µL of 20 mM dNTP for 4 hours at 37°C and separation of reaction mixtures on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Phosphoimaging has not detected DNA degradation. Ribonucleases. Each dNTP, us ...
20_Lecture_Presentation_PC
... by the dideoxy chain termination method, the first automated method to be employed • Modified nucleotides called dideoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (ddNTP) attach to synthesized DNA strands of different lengths • Each type of ddNTP is tagged with a distinct fluorescent label that identifies the nuc ...
... by the dideoxy chain termination method, the first automated method to be employed • Modified nucleotides called dideoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (ddNTP) attach to synthesized DNA strands of different lengths • Each type of ddNTP is tagged with a distinct fluorescent label that identifies the nuc ...
chapter_5_Mod_2009
... – Those molecules feedback and bind to an enzyme early in the sequence’. – They inhibit that enzyme, and stop the sequence. – This decreases the amount of end-product made. This functions to keep levels of the end-product within a certain range. ...
... – Those molecules feedback and bind to an enzyme early in the sequence’. – They inhibit that enzyme, and stop the sequence. – This decreases the amount of end-product made. This functions to keep levels of the end-product within a certain range. ...
6.1 Digestion and absorption assessment statements
... Pancreatic endopeptidase – proteolytic enzymes that hydrolyze internal peptide bonds digesting proteins/polypeptides into shorter amino acid chains. Trypsin that works at pH 8 is an example. Explain the need for enzymes to digest most macromolecules in food into monomers in the small intestine. ...
... Pancreatic endopeptidase – proteolytic enzymes that hydrolyze internal peptide bonds digesting proteins/polypeptides into shorter amino acid chains. Trypsin that works at pH 8 is an example. Explain the need for enzymes to digest most macromolecules in food into monomers in the small intestine. ...
Non-competitive
... May be a metal ion such as Zn2+ of Mg2+ May also be an organic molecule such as vitamin B or heme – called a coenzyme Substrate – the molecule an enzyme acts on Activation – any process that initiates or increases the action of an enzyme Inhibition – any process that inactivates an enzyme or reduces ...
... May be a metal ion such as Zn2+ of Mg2+ May also be an organic molecule such as vitamin B or heme – called a coenzyme Substrate – the molecule an enzyme acts on Activation – any process that initiates or increases the action of an enzyme Inhibition – any process that inactivates an enzyme or reduces ...
Enzyme basic concepts, Enzyme Regulation IIII
... Binding to proteins: Some enzymes can be regulated by binding to other proteins. For example Ca 2+ calmodulin is a protein that binds to kinases activating these enzymes (regulation of glycogen metabolism during muscle contraction). Allosteric regulation: Allosteric enzymes are enzymes w ...
... Binding to proteins: Some enzymes can be regulated by binding to other proteins. For example Ca 2+ calmodulin is a protein that binds to kinases activating these enzymes (regulation of glycogen metabolism during muscle contraction). Allosteric regulation: Allosteric enzymes are enzymes w ...























