Enzyme Inhibition
... CN- attach to the –SH groups in the enzyme This destroys the disulfide bridges and thus changing the tertiary structure of the enzyme Change in the shape results in the change in the active site thus the substrate cannot bind and cytochrome c oxidase is nonfuctional. ...
... CN- attach to the –SH groups in the enzyme This destroys the disulfide bridges and thus changing the tertiary structure of the enzyme Change in the shape results in the change in the active site thus the substrate cannot bind and cytochrome c oxidase is nonfuctional. ...
Enzymes Activation and Deactivation
... and permanent, and effectively denature the enzymes which they inhibit. However, there are a lot of non-permanent and reversible non-competitive inhibitors that are vital in controlling metabolic functions in organisms. ...
... and permanent, and effectively denature the enzymes which they inhibit. However, there are a lot of non-permanent and reversible non-competitive inhibitors that are vital in controlling metabolic functions in organisms. ...
Enzymology: Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxide - UNCG GK-12
... Catalase. Catalase is found in all living organisms that are exposed to oxygen. It catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water. The importance of this enzyme is to protect cellular systems from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (you don’t want these in your body). ...
... Catalase. Catalase is found in all living organisms that are exposed to oxygen. It catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water. The importance of this enzyme is to protect cellular systems from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (you don’t want these in your body). ...
Chem 7250 #1
... the absence of an enzyme catalyst. This kinetic stability is essential to the role of ATP and other compounds with ~ bonds. If ATP would rapidly hydrolyze in the absence of a catalyst, it could not serve its important roles in energy metabolism and phosphate transfer. Phosphate is removed from ATP o ...
... the absence of an enzyme catalyst. This kinetic stability is essential to the role of ATP and other compounds with ~ bonds. If ATP would rapidly hydrolyze in the absence of a catalyst, it could not serve its important roles in energy metabolism and phosphate transfer. Phosphate is removed from ATP o ...
(TCA) cycle
... 5.3.2.1 Regulation of the glyoxylate cycle (continued) Dephosphorylation active form of isocitrate dehydrogenase Phosphorylation inactive form of isocitrate dehydrogenase Dephosphorylation to induce flux through the TCA cycle (1) When metabolic intermediates such as isocitrate, PEP, OAA, 2-K ...
... 5.3.2.1 Regulation of the glyoxylate cycle (continued) Dephosphorylation active form of isocitrate dehydrogenase Phosphorylation inactive form of isocitrate dehydrogenase Dephosphorylation to induce flux through the TCA cycle (1) When metabolic intermediates such as isocitrate, PEP, OAA, 2-K ...
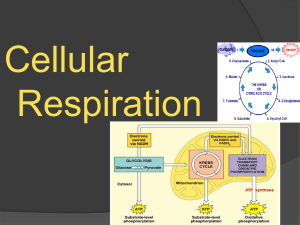
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration - Chemistry
... Hydrogen ions diffuse back into the inner compartment through a carrier protein that adds a phosphate group to ADP, making ATP. ...
... Hydrogen ions diffuse back into the inner compartment through a carrier protein that adds a phosphate group to ADP, making ATP. ...
Breakdown Industrial Digester PowderTM contains bacteria and
... OdormuteTM Septic Tank Maintenance contains 5 strains of Bacillus bacteria including 2 bacterial strains which are facultative anaerobes. Facultative Anaerobic bacteria work both with and without oxygen. OdormuteTM Septic Tank Maintenance contains strains of Bacteria Producing Enzymes that produce d ...
... OdormuteTM Septic Tank Maintenance contains 5 strains of Bacillus bacteria including 2 bacterial strains which are facultative anaerobes. Facultative Anaerobic bacteria work both with and without oxygen. OdormuteTM Septic Tank Maintenance contains strains of Bacteria Producing Enzymes that produce d ...
Lesson element
... You should arrange the learners into small groups and provide them with access to resources about the Krebs cycle; some are provided in the resource list above. In the previous activity the learners will have identified and explained glycolysis and the next stage of the process of aerobic respiratio ...
... You should arrange the learners into small groups and provide them with access to resources about the Krebs cycle; some are provided in the resource list above. In the previous activity the learners will have identified and explained glycolysis and the next stage of the process of aerobic respiratio ...
Citric acid cycle - Issaquah Connect
... In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced by NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced by NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Enzymes - Michael P. Ready
... Common Tasks- Skill Level 1. You may self-administer the injection as follows: • Hold the injector in your hand forming a fist around the injector without covering or holding the needle end. • Place the end of the injector against your outer (lateral) thigh muscle anywhere from about a hand’s width ...
... Common Tasks- Skill Level 1. You may self-administer the injection as follows: • Hold the injector in your hand forming a fist around the injector without covering or holding the needle end. • Place the end of the injector against your outer (lateral) thigh muscle anywhere from about a hand’s width ...
5-2 Necleotide Metabolism (pyrimidine) - Home
... phosphate with aspartate with the release of Pi •ATCase is the major site of regulation in bacteria; it is activated by ATP and inhibited by CTP •carbamoyl phosphate is an “activated” compound, so no energy input is needed at this step ...
... phosphate with aspartate with the release of Pi •ATCase is the major site of regulation in bacteria; it is activated by ATP and inhibited by CTP •carbamoyl phosphate is an “activated” compound, so no energy input is needed at this step ...
TCA
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
to an allosteric site
... • If reversible, the effect of these inhibitors can be overcome by increased substrate concentration. Noncompetitive inhibitors = Enzyme inhibitors that do not enter the enzyme's active site, but bind to another part of the enzyme molecule. • Causes enzyme to change its shape so the active site cann ...
... • If reversible, the effect of these inhibitors can be overcome by increased substrate concentration. Noncompetitive inhibitors = Enzyme inhibitors that do not enter the enzyme's active site, but bind to another part of the enzyme molecule. • Causes enzyme to change its shape so the active site cann ...
103 Lecture Ch23b
... beer and champagne, and also makes bread rise • Alcoholic beverages produced by fermentation can be up to around 15% ethanol - above that concentration the yeast die H+ ...
... beer and champagne, and also makes bread rise • Alcoholic beverages produced by fermentation can be up to around 15% ethanol - above that concentration the yeast die H+ ...
3-energy
... the absence of an enzyme catalyst. This kinetic stability is essential to the role of ATP and other compounds with ~ bonds. If ATP would rapidly hydrolyze in the absence of a catalyst, it could not serve its important roles in energy metabolism and phosphate transfer. Phosphate is removed from ATP o ...
... the absence of an enzyme catalyst. This kinetic stability is essential to the role of ATP and other compounds with ~ bonds. If ATP would rapidly hydrolyze in the absence of a catalyst, it could not serve its important roles in energy metabolism and phosphate transfer. Phosphate is removed from ATP o ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
... oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
Unit 4.4: Anaerobic Respiration
... living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic respira ...
... living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic respira ...
Oxidation of Glucose
... penetrate mitochondria membrane , it can be used to produce energy (4 or , 6ATP) by respiratory chain phosphorylation in the mitochondria. ...
... penetrate mitochondria membrane , it can be used to produce energy (4 or , 6ATP) by respiratory chain phosphorylation in the mitochondria. ...
video slide - Jackson County School District
... Concept 9.3: The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules • In the presence of O2, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion (aerobic respiration) • Before the citric acid cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis ...
... Concept 9.3: The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules • In the presence of O2, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion (aerobic respiration) • Before the citric acid cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis ...
L12_FAS
... – Lots of different enzyme activities in the complex – Can you count them all? • Bringing in acetyl and malonly groups, catalysing the reaction between the decarboxylated malonyl and the growing fatty acid chain, the reduction/dehydration/reduction steps, moving the fatty acid to the right site and ...
... – Lots of different enzyme activities in the complex – Can you count them all? • Bringing in acetyl and malonly groups, catalysing the reaction between the decarboxylated malonyl and the growing fatty acid chain, the reduction/dehydration/reduction steps, moving the fatty acid to the right site and ...
Review session for exam-I
... multiply the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept by -1. multiply the reciprocal of the y-axis intercept by -1. take the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept. take the reciprocal of the y-axis intercept. take the x-axis intercept where V0 = 1/2 ...
... multiply the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept by -1. multiply the reciprocal of the y-axis intercept by -1. take the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept. take the reciprocal of the y-axis intercept. take the x-axis intercept where V0 = 1/2 ...
• Warm-up What are the four macromolecules and their function?
... A. The compound that is before the arrow in a chemical reaction B. Another name for an enzyme C. The material that an enzyme binds to D. The term used to describe the structure formed after an enzyme binds with a complex ...
... A. The compound that is before the arrow in a chemical reaction B. Another name for an enzyme C. The material that an enzyme binds to D. The term used to describe the structure formed after an enzyme binds with a complex ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.