LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 1. What is meant by classical approximation in wave mechanics ? 2. Can classical concepts explain the Compton effect ? 3. Define probability density and probability current density. 4. What are stationary states ? 5. What is an observable ? Give an example. 6. State the expansion postulate. 7. Sketc ...
... 1. What is meant by classical approximation in wave mechanics ? 2. Can classical concepts explain the Compton effect ? 3. Define probability density and probability current density. 4. What are stationary states ? 5. What is an observable ? Give an example. 6. State the expansion postulate. 7. Sketc ...
The Structure of the Atom [Режим совместимости]
... an electron with the mass equal to 9.1x10-31 kg and the velocity equal to 108 m/s is associated with a wavelength equal to 10-10 meters n The wavelength approximately equals to the atom’s ...
... an electron with the mass equal to 9.1x10-31 kg and the velocity equal to 108 m/s is associated with a wavelength equal to 10-10 meters n The wavelength approximately equals to the atom’s ...
Document
... could be explained by the statistical process of many collisions of molecules Detailed predictions of properties of the motion verified three years later. So, atoms are real (still controversial at the time) Still an active area of research! 8.01L Fall 2005 ...
... could be explained by the statistical process of many collisions of molecules Detailed predictions of properties of the motion verified three years later. So, atoms are real (still controversial at the time) Still an active area of research! 8.01L Fall 2005 ...
Version C - UCSB Physics
... Explanation: A) This is Exercise 26-1 (c). See page 861 in the textbook. B) C) D) 13) When light reflects from a horizontal surface, like a tabeletop or the surface of lake, it is partially polarized in the A) horizontal direction B) vertical direction Answer: A Explanation: A) We reviewed this in c ...
... Explanation: A) This is Exercise 26-1 (c). See page 861 in the textbook. B) C) D) 13) When light reflects from a horizontal surface, like a tabeletop or the surface of lake, it is partially polarized in the A) horizontal direction B) vertical direction Answer: A Explanation: A) We reviewed this in c ...
PHY 140A: Solid State Physics Solution to Homework #5
... Specific heat of a highly anisotropic solid. Consider a solid which has a highly anisotropic crystalline layer structure. Each atom in this structure can be regarded as performing simple harmonic oscillations in three dimensions. The restoring forces in directions parallel to a layer are very large; ...
... Specific heat of a highly anisotropic solid. Consider a solid which has a highly anisotropic crystalline layer structure. Each atom in this structure can be regarded as performing simple harmonic oscillations in three dimensions. The restoring forces in directions parallel to a layer are very large; ...
Pretest for Uncertainty Principle Part 1
... observable A first and then measure observable B immediately afterwards; (II) directly measure B without measuring A first. The initial state when the first measurement is performed in each of these two situations is the same, i.e., a generic state , which is not an eigenstate of  or B̂ . Will t ...
... observable A first and then measure observable B immediately afterwards; (II) directly measure B without measuring A first. The initial state when the first measurement is performed in each of these two situations is the same, i.e., a generic state , which is not an eigenstate of  or B̂ . Will t ...
Lecture Slides
... warn against a misunderstanding likely to arise when one tries to express the content of Heisenberg's well-known indeterminacy relation by such a statement as ‘the position and momentum of a particle cannot simultaneously be measured with arbitrary accuracy’. According to such a formulation it would ...
... warn against a misunderstanding likely to arise when one tries to express the content of Heisenberg's well-known indeterminacy relation by such a statement as ‘the position and momentum of a particle cannot simultaneously be measured with arbitrary accuracy’. According to such a formulation it would ...
Chapter 12
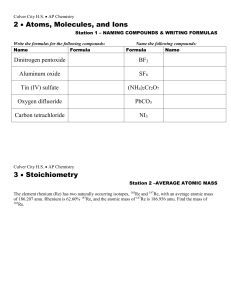
... •Inorganic compounds: cpds which are NOT hydrocarbons (~1.5 million) •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” Carbon Atoms Carb ...
... •Inorganic compounds: cpds which are NOT hydrocarbons (~1.5 million) •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” Carbon Atoms Carb ...
Motors and Generators
... Investigations into the electrical properties of particular metals at different temperatures led to the identification of superconductivity and the exploration of possible applications ...
... Investigations into the electrical properties of particular metals at different temperatures led to the identification of superconductivity and the exploration of possible applications ...
pdf
... resonance to the side that supports a weakly bound molecular state. The magnetic field is spatially constant, so it does not change the speed of the centre-of-mass of an atomic pair. The sweep is also sufficiently rapid to avoid any changes in the overall speed of the atoms due to collisions. As a r ...
... resonance to the side that supports a weakly bound molecular state. The magnetic field is spatially constant, so it does not change the speed of the centre-of-mass of an atomic pair. The sweep is also sufficiently rapid to avoid any changes in the overall speed of the atoms due to collisions. As a r ...
9077590 Chem. Rege. Jan. 01
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
Final Exam Review whole thing
... Protons + with a positive charge Electrons – with a negative charge And Neutrons with a neutral charge ...
... Protons + with a positive charge Electrons – with a negative charge And Neutrons with a neutral charge ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... 3b. Analyze patterns and trends in the organization of elements in the periodic table and compare their relationship to position in the periodic table. (DOK 2) Atomic number, atomic mass, mass number, and number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in isotopes of elements Average atomic mass calc ...
... 3b. Analyze patterns and trends in the organization of elements in the periodic table and compare their relationship to position in the periodic table. (DOK 2) Atomic number, atomic mass, mass number, and number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in isotopes of elements Average atomic mass calc ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.


![The Structure of the Atom [Режим совместимости]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001854271_1-ef1245c1f375ab31b64ec8e56383a02e-300x300.png)