Document
... • The ability of light to dislodge electrons from a metallic surface • The electrons can be detected and the resulting signals amplified • Lots of applications in visual imaging ...
... • The ability of light to dislodge electrons from a metallic surface • The electrons can be detected and the resulting signals amplified • Lots of applications in visual imaging ...
document
... Ball A of mass 5.0 kg moving at 20 m/s collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10 m/s in the same direction. After the collision, ball A moves at 10 m/s and ball B at 15 m/s, both still in the same direction. What is the mass of ball B? (A) 6.0 kg (B) 2.0 kg (C) 10. kg (D) 12 kg ...
... Ball A of mass 5.0 kg moving at 20 m/s collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10 m/s in the same direction. After the collision, ball A moves at 10 m/s and ball B at 15 m/s, both still in the same direction. What is the mass of ball B? (A) 6.0 kg (B) 2.0 kg (C) 10. kg (D) 12 kg ...
Fermi-Dirac Statistics
... Quantum Statistics: The product D(E)×f(E) gives the number of occupied states at temperature T. The observed value of the heat capacity is reduced from the classical value by order T/TF (factor of 0.01). ...
... Quantum Statistics: The product D(E)×f(E) gives the number of occupied states at temperature T. The observed value of the heat capacity is reduced from the classical value by order T/TF (factor of 0.01). ...
Chapter 3. Basic Instrumentation for Nuclear Technology
... • A UV photon at 200nm carries an energy of about 6 eV, this is enough to “jump” over the work function of most ...
... • A UV photon at 200nm carries an energy of about 6 eV, this is enough to “jump” over the work function of most ...
Theoretical Problem 2
... discussion above. That is, the frequency of the laser beams ω L and ω ′L may have any value and the absorption-emission process can still occur. These will happen with different (quantum) probabilities and, as one should expect, the maximum probability is found at the exact resonance condition. On t ...
... discussion above. That is, the frequency of the laser beams ω L and ω ′L may have any value and the absorption-emission process can still occur. These will happen with different (quantum) probabilities and, as one should expect, the maximum probability is found at the exact resonance condition. On t ...
10. Molecules and Solids
... The higher the starting energy level, the greater the photon energy. ...
... The higher the starting energy level, the greater the photon energy. ...
BANDS AND BONDS
... Hydrogen bonded solids consist primarily of the hydrides of fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen. The cohesive forces are derived from the unique nature of the hydrogen bridge bond between two neighboring atoms, which enhances the normal intermolecular attraction. Chemical Trends in Covalent Solids Primar ...
... Hydrogen bonded solids consist primarily of the hydrides of fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen. The cohesive forces are derived from the unique nature of the hydrogen bridge bond between two neighboring atoms, which enhances the normal intermolecular attraction. Chemical Trends in Covalent Solids Primar ...
Document
... energy levels. “Until after some weeks of the most strenuous work of my life, light came into the darkness, and a new undreamed-of perspective opened up before meIthe whole procedure was an act of despair because a theoretical interpretation had to be found at any price, no matter how high that migh ...
... energy levels. “Until after some weeks of the most strenuous work of my life, light came into the darkness, and a new undreamed-of perspective opened up before meIthe whole procedure was an act of despair because a theoretical interpretation had to be found at any price, no matter how high that migh ...
practice exercise - Needham.K12.ma.us
... (b) By referring to a periodic table or a table of elements, we see that sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16. Thus, each atom or ion of sulfur must contain 16 protons. We are told that the ion also has 16 neutrons, meaning the mass number of the ion is 16 + 16 = 32. Because the ion has 16 protons ...
... (b) By referring to a periodic table or a table of elements, we see that sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16. Thus, each atom or ion of sulfur must contain 16 protons. We are told that the ion also has 16 neutrons, meaning the mass number of the ion is 16 + 16 = 32. Because the ion has 16 protons ...
Electric potential
... If the charge of each particle tripled and the distance also tripled, how would the electrostatic force between the particles change? ...
... If the charge of each particle tripled and the distance also tripled, how would the electrostatic force between the particles change? ...
Atoms and Energies
... Different elements have different allowed energies (since different numbers of protons and electrons provide different structure of attraction Light emitted when electrons move from a high energy level to a lower energy level in an atom will have only certain, QUANTIZED, allowed energies and wavelen ...
... Different elements have different allowed energies (since different numbers of protons and electrons provide different structure of attraction Light emitted when electrons move from a high energy level to a lower energy level in an atom will have only certain, QUANTIZED, allowed energies and wavelen ...
Introduction, Introduction to lasers, Properties of light
... if the photon is absorbed – neither of the detectors clicks if the photon takes the other path – at the last bs it has an equal chance to be transmitted or reflected – the two detectors click with equal frequencies - the interference has been destroyed by the presence of the absorber the presence of ...
... if the photon is absorbed – neither of the detectors clicks if the photon takes the other path – at the last bs it has an equal chance to be transmitted or reflected – the two detectors click with equal frequencies - the interference has been destroyed by the presence of the absorber the presence of ...
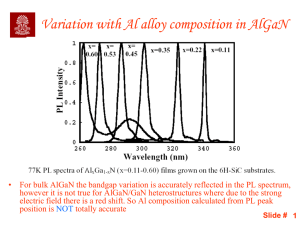
Neutral Atoms Behave Much Like Classical Spherical Capacitors
... nonzero values have no analog in the classical Eq. (2b) for an isolated spherical conductor. The nonzero intercept does have an analog, though, in the equations for a classical spherical capacitor if ra+1 is not very much larger than ra , as in Eq. (2c), and if the sum there in square brackets is ne ...
... nonzero values have no analog in the classical Eq. (2b) for an isolated spherical conductor. The nonzero intercept does have an analog, though, in the equations for a classical spherical capacitor if ra+1 is not very much larger than ra , as in Eq. (2c), and if the sum there in square brackets is ne ...
EDM Searches Based on Alkali or Alkaline
... excited a 2⌸ and b 2⌺ states arising from the alkali-metal np configurations. This is the starting configuration for the multireference configuration-interaction 共MRCI兲 关20,21兴 calculation performed in each molecular symmetry group. We use an active space of 兵6,3,3,0其 with no closed orbitals. We use ...
... excited a 2⌸ and b 2⌺ states arising from the alkali-metal np configurations. This is the starting configuration for the multireference configuration-interaction 共MRCI兲 关20,21兴 calculation performed in each molecular symmetry group. We use an active space of 兵6,3,3,0其 with no closed orbitals. We use ...
Scattering_RAL_2011
... j is the phase of oscillator j = atomic position j is its (random) natural frequency = thermal velocity Coupling constant K pump power The Kuramoto model has been used to model a wide range of synchronisation phenomena in physics and mathematical biology. Similar equations describe synchronizati ...
... j is the phase of oscillator j = atomic position j is its (random) natural frequency = thermal velocity Coupling constant K pump power The Kuramoto model has been used to model a wide range of synchronisation phenomena in physics and mathematical biology. Similar equations describe synchronizati ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.