Section 3: Crystal Binding
... where pij is defined by rij ≡ pij R . The value of the Madelung constant plays an important role in the theory of ionic crystals. In general it is not possible to compute the Madelung constant analytically. A powerful method for calculation of lattice sums was developed by Ewald, which is called Ewa ...
... where pij is defined by rij ≡ pij R . The value of the Madelung constant plays an important role in the theory of ionic crystals. In general it is not possible to compute the Madelung constant analytically. A powerful method for calculation of lattice sums was developed by Ewald, which is called Ewa ...
Introduction to PHY 855 “Introduction to field theory as it
... Particle Systems; more recent, with an emphasis on the Feynman path integral. Dickhoff and Van Ne, Many Body Theory Exposed; more recent, with some emphasis on comparison to more recent experiments. There are many other books on this subject. ...
... Particle Systems; more recent, with an emphasis on the Feynman path integral. Dickhoff and Van Ne, Many Body Theory Exposed; more recent, with some emphasis on comparison to more recent experiments. There are many other books on this subject. ...
Final Review 2
... 57) How many decimeters are there in 15 centimeters? a) 150 dm b) 1.5 dm c) 0.15 dm d) none of these 58) How many kilograms are there in 4.21 pounds? There are 2.2 pounds in 1 kilogram. a) 9.26 kg b) 1.91 kg c) 0.523 kg d) none of these 59) An example of a chemical property is: a) density b) mass c) ...
... 57) How many decimeters are there in 15 centimeters? a) 150 dm b) 1.5 dm c) 0.15 dm d) none of these 58) How many kilograms are there in 4.21 pounds? There are 2.2 pounds in 1 kilogram. a) 9.26 kg b) 1.91 kg c) 0.523 kg d) none of these 59) An example of a chemical property is: a) density b) mass c) ...
Itty-Bitty Atoms
... science? Would you like to be a scientist? If so, what would you like to study? What do you think scientists of the future will study? 4. Answer the following questions: a. Who is Dmitry Mendeleyev and what did he do? b. What is chemistry? c. How big are atoms? 5. When a teacher calls out a symbol f ...
... science? Would you like to be a scientist? If so, what would you like to study? What do you think scientists of the future will study? 4. Answer the following questions: a. Who is Dmitry Mendeleyev and what did he do? b. What is chemistry? c. How big are atoms? 5. When a teacher calls out a symbol f ...
James Moir as Inorganic Chemist
... analyzing the correct composition of these compounds: modern analysis shows that gold and thiourea in acid medium form the single complex Au[CS(NH2)2]2+ which should give the salts Au2(tu)4SO4 and Au(tu)2Cl.15,16 His analysis methods were as follows:7 – Au determined by direct ignition, which was kn ...
... analyzing the correct composition of these compounds: modern analysis shows that gold and thiourea in acid medium form the single complex Au[CS(NH2)2]2+ which should give the salts Au2(tu)4SO4 and Au(tu)2Cl.15,16 His analysis methods were as follows:7 – Au determined by direct ignition, which was kn ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Newton(1642-27) - Robert Boyle (1627-91): the first “chemist” - Performed quantitative experiments. - Dalton (1766-44), Darwin(1809-82) ...
... Newton(1642-27) - Robert Boyle (1627-91): the first “chemist” - Performed quantitative experiments. - Dalton (1766-44), Darwin(1809-82) ...
Full Review
... B. SI Units (Mass – kg; Length – m; Time – sec, volume L) C. Prefix Multipliers milli (m) 0.001 centi (c) 0.01 kilo (k) 1000 Mega (M) 1,000,000 ...
... B. SI Units (Mass – kg; Length – m; Time – sec, volume L) C. Prefix Multipliers milli (m) 0.001 centi (c) 0.01 kilo (k) 1000 Mega (M) 1,000,000 ...
AP Chemistry Summer Work
... SO WHAT IS THE SUMMER WORK? All work should be done neatly and clearly on paper and organized in the order it was assigned. All work for every problem including units throughout is necessary for AP. This is an expectation on the AP exam in the spring and we want to get into the good habit early ____ ...
... SO WHAT IS THE SUMMER WORK? All work should be done neatly and clearly on paper and organized in the order it was assigned. All work for every problem including units throughout is necessary for AP. This is an expectation on the AP exam in the spring and we want to get into the good habit early ____ ...
midterm answers
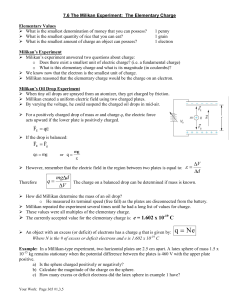
... Why must this time interval t be greater than zero? only a full electron can be detected, neither 10 % of it nor 99%, …, so there must be a finite time greater zero, there is a finite probability density at t 0 as we are talking about a steady state, used the time independent Schrödinger equatio ...
... Why must this time interval t be greater than zero? only a full electron can be detected, neither 10 % of it nor 99%, …, so there must be a finite time greater zero, there is a finite probability density at t 0 as we are talking about a steady state, used the time independent Schrödinger equatio ...
Further Quantum Mechanics: Problem Set 2. Trinity term weeks 1 – 2
... This problem set is taken mainly from the book by Binney and Skinner. Qu 1. Problem 7.1 from Prof Blundell’s lecture course is repeated with some modifications below. If you have already attempted it, explain how the approach you used fits within the more general understanding you should now have of ...
... This problem set is taken mainly from the book by Binney and Skinner. Qu 1. Problem 7.1 from Prof Blundell’s lecture course is repeated with some modifications below. If you have already attempted it, explain how the approach you used fits within the more general understanding you should now have of ...
Slide 1
... • The potential energy difference is due to a physical separation (a distance) between the two points • This potential difference provides a force which can move charges from place to place. • This is sometimes called an electromotive force (emf) ...
... • The potential energy difference is due to a physical separation (a distance) between the two points • This potential difference provides a force which can move charges from place to place. • This is sometimes called an electromotive force (emf) ...
SPC Teachers Problems - University of Oxford
... The first nitrogen would be too heavy, if it contained residual oxygen. But on this hypothesis, something like 1 per cent would be required. I could detect none whatever by means of alkaline pyrogallate. It may be remarked that the density of the nitrogen agrees closely with that recently obtained b ...
... The first nitrogen would be too heavy, if it contained residual oxygen. But on this hypothesis, something like 1 per cent would be required. I could detect none whatever by means of alkaline pyrogallate. It may be remarked that the density of the nitrogen agrees closely with that recently obtained b ...
Nuclear and Particle Physics
... Nuclear Part: Course handouts will be available on course web portal at end of course (useful as in colour!) ...
... Nuclear Part: Course handouts will be available on course web portal at end of course (useful as in colour!) ...
Lecture 2 Hamiltonian operators for molecules CHEM6085: Density
... the electronic Hamiltonian operator of any molecule, with any number of nuclei and electrons. 2) Write down an expression for the expectation value of each of the terms of the above Hamiltonian (i.e. Kinetic energy, electron-electron repulsion energy, etc.) 3) Assume that charged particles such as e ...
... the electronic Hamiltonian operator of any molecule, with any number of nuclei and electrons. 2) Write down an expression for the expectation value of each of the terms of the above Hamiltonian (i.e. Kinetic energy, electron-electron repulsion energy, etc.) 3) Assume that charged particles such as e ...
1 - BrainMass
... The net electric field due to the particles is zero at x = d/4. With V = 0 at infinity, locate (in terms of d) any point on the x axis (other than at infinity) at which the electric potential due to the two particles is zero. ...
... The net electric field due to the particles is zero at x = d/4. With V = 0 at infinity, locate (in terms of d) any point on the x axis (other than at infinity) at which the electric potential due to the two particles is zero. ...
... possible values of the angular momentum. Calculate the energy eigenvalues. What is the energy difference between the ground state of zero angular momentum and the first rotational state? Show that this approaches infinity as N . Contrast this with the comparable energy for a “nicked” cylinder, wh ...
... possible values of the angular momentum. Calculate the energy eigenvalues. What is the energy difference between the ground state of zero angular momentum and the first rotational state? Show that this approaches infinity as N . Contrast this with the comparable energy for a “nicked” cylinder, wh ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.