pdf
... interaction strength between two fermions, as this determines the binding energy and size of the pairs, and thus the macroscopic properties of the quantum system. In an ultracold gas, the pair interaction can be varied conveniently with a magnetic field if a so-called Feshbach resonance is present. ...
... interaction strength between two fermions, as this determines the binding energy and size of the pairs, and thus the macroscopic properties of the quantum system. In an ultracold gas, the pair interaction can be varied conveniently with a magnetic field if a so-called Feshbach resonance is present. ...
- Palisades School District
... cyclohexane (D=0.778 g/mL) do not form a solution when mixed, but separate into distinct layers. Sketch how the liquids would position themselves in a beaker? ...
... cyclohexane (D=0.778 g/mL) do not form a solution when mixed, but separate into distinct layers. Sketch how the liquids would position themselves in a beaker? ...
Homework 3 solutions File
... For each of a conductor, insulator and/or semiconductor the valance band is full. However, for a conductor, there additional electrons left after filling the valance band, and these can only go into the conduction band, and hence are not bound to individual atoms and are free to be conducted. Neithe ...
... For each of a conductor, insulator and/or semiconductor the valance band is full. However, for a conductor, there additional electrons left after filling the valance band, and these can only go into the conduction band, and hence are not bound to individual atoms and are free to be conducted. Neithe ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... atomic number. Elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. Historically, elements were ordered by atomic mass, but now scientists know that this order would lead to misplaced elements (e.g., tellurium and iodine) because differences in the number of neutrons for ...
... atomic number. Elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. Historically, elements were ordered by atomic mass, but now scientists know that this order would lead to misplaced elements (e.g., tellurium and iodine) because differences in the number of neutrons for ...
Calculating particle properties of a wave
... • For ultraviolet light, X-rays, Gamma rays: In a Geiger counter a photon knocks electrons from gas molecules, creating a miniature spark. • For visible light: In a photomultiplier a photon kicks an electron out of a solid (the photocathode). The electron is multiplied into a million electrons by mu ...
... • For ultraviolet light, X-rays, Gamma rays: In a Geiger counter a photon knocks electrons from gas molecules, creating a miniature spark. • For visible light: In a photomultiplier a photon kicks an electron out of a solid (the photocathode). The electron is multiplied into a million electrons by mu ...
2016-2017 Summer Assignment AP Chem 2017 Summer
... Which reagent is the limiting reactant when 1.85 mol of sodium hydroxide and 1.00 mol carbondioxide are allowed to react? How many moles of sodium carbonate can be produced? How many moles of the excess reactant remain after the completion of the reaction? 52. WHEN benzene (C6H6) reacts with bromin ...
... Which reagent is the limiting reactant when 1.85 mol of sodium hydroxide and 1.00 mol carbondioxide are allowed to react? How many moles of sodium carbonate can be produced? How many moles of the excess reactant remain after the completion of the reaction? 52. WHEN benzene (C6H6) reacts with bromin ...
Chemistry EOC Review 2015 Name Per ___ This review is part of
... Radiation comes from atoms with unstable nuclei- which usually mean too many neutrons. Fusion is nuclear change where two lighter elements “fuse” together to make a heavier element. This is what happens in our Sun and other stars when two hydrogen atoms fuse together to make a helium atom. Energy is ...
... Radiation comes from atoms with unstable nuclei- which usually mean too many neutrons. Fusion is nuclear change where two lighter elements “fuse” together to make a heavier element. This is what happens in our Sun and other stars when two hydrogen atoms fuse together to make a helium atom. Energy is ...
Exam I
... 11. Two like charges of the same magnitude are 3.0 mm apart. If the force of repulsion they exert upon each other is 3.0 N, what is the magnitude of each charge? (The constant of proportionality for the Coulombic force is 9.0 x 10 9 Nœm2/C2.) A) 3.0 x 103 C B) 5.5 x 10-2 C C) 5.5 x 10-8 C D) 5.5 x 1 ...
... 11. Two like charges of the same magnitude are 3.0 mm apart. If the force of repulsion they exert upon each other is 3.0 N, what is the magnitude of each charge? (The constant of proportionality for the Coulombic force is 9.0 x 10 9 Nœm2/C2.) A) 3.0 x 103 C B) 5.5 x 10-2 C C) 5.5 x 10-8 C D) 5.5 x 1 ...
Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VIII Atomic Physics: Unit VIII Review
... fundamental particle: a particle that cannot be divided into smaller particles; an elementary particle fusion: reaction in which two low-mass nuclei combine to form a single nucleus with A < 60, resulting in a nucleus that is more tightly bound; the energy given off equals the difference between the ...
... fundamental particle: a particle that cannot be divided into smaller particles; an elementary particle fusion: reaction in which two low-mass nuclei combine to form a single nucleus with A < 60, resulting in a nucleus that is more tightly bound; the energy given off equals the difference between the ...
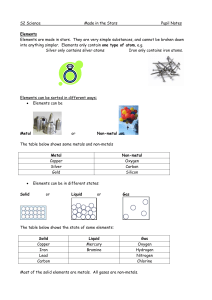
Made in the Stars Notes
... Elements can join together to form compounds. They have to be chemically joined, not just mixed together. A compound is a substance that has more than one kind of atom joined together. For example, if iron joins with oxygen from the air, it forms the compound iron oxide (rust). ...
... Elements can join together to form compounds. They have to be chemically joined, not just mixed together. A compound is a substance that has more than one kind of atom joined together. For example, if iron joins with oxygen from the air, it forms the compound iron oxide (rust). ...
The Physics of Particle Detectors
... The Bethe-Bloch equation describes the mean energy loss When a charged particle passes the layer of material with thickness x , the energy distribution of the δ-electrons and the fluctuations of their number (nδ) cause fluctuations of the energy losses ΔE The energy loss ΔE in a layer of material is ...
... The Bethe-Bloch equation describes the mean energy loss When a charged particle passes the layer of material with thickness x , the energy distribution of the δ-electrons and the fluctuations of their number (nδ) cause fluctuations of the energy losses ΔE The energy loss ΔE in a layer of material is ...
Reactions of Metals and Their Compounds
... I will give you the answer, you have to write the question! For example: Answer = Ms. Lee Question? Who is the most awesome teacher in the world, with beautiful long hair and a wonderful personality. And she is very nice and funny too. ...
... I will give you the answer, you have to write the question! For example: Answer = Ms. Lee Question? Who is the most awesome teacher in the world, with beautiful long hair and a wonderful personality. And she is very nice and funny too. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.